Diabetes | 4 min read
A Guide to Diabetic Neuropathy: What are its Symptoms and Causes?
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- There are four main diabetic neuropathy types you should know about
- Numbness in feet is one of the common diabetic neuropathy symptoms
- Diabetic neuropathy treatment involves medication and physical therapy
Diabetic neuropathy is a condition in which high blood sugar levels damage your nerves [1]. If you ignore the early signs of diabetes, you are likely to experience this disease. This condition usually impacts the nerves of your feet and legs. A severe form of it can affect your urinary tract, digestive system, heart and blood vessels.
In case you have this condition, you may experience mild or painful symptoms. This condition may occur in all three types of diabetes, gestational, type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Read on to understand more about this condition and how it can affect your health.
Additional Read: Type 2 Diabetes SymptomsDiabetic Neuropathy Types
There are four main types of this health condition. They are
- Proximal neuropathy
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Focal neuropathy

According to reports, approximately 6-50% of diabetic adults suffer from peripheral neuropathy [2]. This condition affects your legs and feet. A few common symptoms seen include:
- Feeling numb
- Tingling sensation
- Pain
- Burning, especially during evenings
If you are at an early stage of the disease, all you need to do is keep your blood sugar levels under control. Remember to follow these preventive measures:
- Do not forget to check your legs and feet daily
- Observe your toenails regularly
- Apply lotion on your feet to remove dryness
- Always wear comfortable fitting shoes to avoid a leg injury
Autonomic neuropathy affects primarily the digestive system and causes symptoms such as:
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Stomach bloating
To avoid this, ensure that you have smaller but more frequent meals. Make sure you also have the prescribed medicines for reducing the symptoms. This condition can also affect your urinary system, reproductive organs and blood vessels.
In proximal neuropathy, you may experience pain on one side of the buttocks, thighs or hips. As a result, your legs may become weak. Medication and physical therapy can help treat this condition.
Focal neuropathy usually affects specific nerves of your leg, torso or head. It may also result in muscle pain and weakness. Double vision and eye pain are a few common symptoms of proximal neuropathy.
Diabetic Neuropathy Symptoms
Symptoms appear gradually in this condition. These are some of the most common symptoms you can observe:
- Pain or numbness in your feet or hands
- Sensitivity to touch
- Bloating
- Weakness or decay in muscles
- Inability to coordinate properly while walking
- Excessive or minimal sweating
- Nausea
- Vaginal dryness
- Urinary bladder issues
- Increased heartbeat
- Problems in vision
Diabetic Neuropathy Causes
The main cause of this condition is consistently high blood sugar. This may happen when you don't track your levels frequently. Increased cholesterol can damage your blood vessels and eventually affect your nerves. Having too much alcohol and smoking often can also lead to diabetic neuropathy. A mechanical injury also may damage your nerves and lead to this problem. A deficiency of vitamin B12 can cause diabetic retinopathy as well. This is a condition that causes loss of nerve cells in your retina that causes problems in vision.
Additional Read: Normal Diabetic Blood Sugar Levels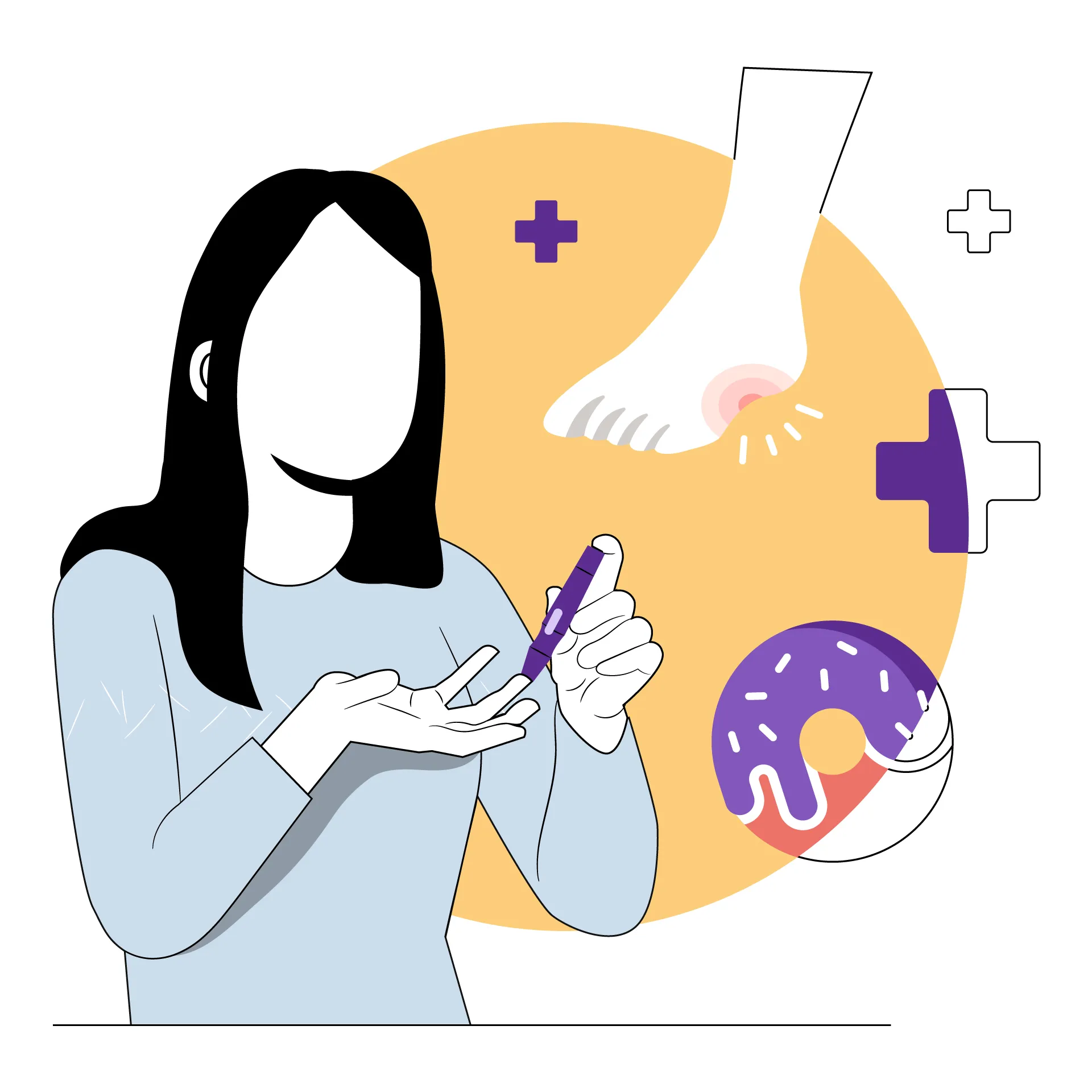
Diabetic Neuropathy Prevention
You can avoid this condition if you follow the precautionary measures below.
- Check your blood glucose levels regularly
- Take proper medication as prescribed by your doctor
- Lead an active lifestyle and follow a healthy diet
- Devote at least 30 minutes of your time daily for exercising or walking
- Avoid consuming processed foods and eat plenty of fruits and vegetables
If you already have this condition, you can reduce the damage to your nerves with these measures. They help in avoiding any further complications.
Diabetic Neuropathy Treatment
The main treatment is to manage your blood sugar and cholesterol. Usually, the key focus of treatment is reducing your pain and managing your symptoms. A few common diabetic neuropathy medications include tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsant drugs and opioids.
Along with these, physical therapy may help you reduce pain and muscle weakness. It can also reduce the tingling and burning sensations in your feet. Electrical nerve stimulation is a type of therapy that can reduce the stiffness in your legs. Gait training is another way you can improve your foot complications. It can help you walk without any problems. You can also try aerobic exercises and swimming to increase your muscle strength.
To avoid this condition or manage it better, get your sugar test done regularly. To address unusual symptoms, connect with top diabetologists or you can also buy diabetes health insurance from Bajaj Finserv Health. Simply book an online doctor consultation and discuss your concerns. You may also book a diabetes health test package to assess your sugar levels. Such preventative measures can help you live a healthier life.
References
- http://repository.ias.ac.in/92714/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6755905/#:~:text=The%20prevalence%20of%20peripheral%20neuropathy,asymptomatic%20to%20painful%20neuropathic%20symptoms
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.