Paediatrician | 5 min read
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Symptoms, Risk Factors
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
ADHD is a neurological illness affecting children's regular activities. A child with ADHD finds it difficult to concentrate, wait in queues, sit comfortably for a long time, or behave like other normal kids in crowded places. It is commonly caused due to genetic malfunctions and is seen more commonly in premature babies.
Key Takeaways
- ADHD is a widespread disease affecting millions of children worldwide
- It is an ailment of the nervous system which affects concentration, posture, and other behaviors
- No tests are available for diagnosing ADHD. Only specialists can judge it with the symptoms of physical evaluation
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a condition that typically persists into adulthood and affects millions of children. It is characterized by persistent difficulties, such as difficulty sustaining focus, hyperactivity, and impulsive behavior.
Children with ADHD are more prone to have challenges such as low self-esteem, challenging relationships, and poor academic performance. Occasionally, as people age, their symptoms improve. However, some individuals continue to exhibit ADHD symptoms well into adulthood. However, they are capable of acquiring the necessary abilities for success.
Although Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder treatment can considerably reduce symptoms, it is not a cure for the disorder. Medication and behavior-focused therapy are frequently components of treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can have a substantial impact on the prognosis of a patient.
What is Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)?
ADHD is a neurological ailment that inhibits a person's ability to focus attention, sit still, and exercise behavioral control. This condition affects children and teenagers, and it may remain into adulthood. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in childhood is children's most prevalent mental condition. Men are more prone to disease as compared to women. Typically, the problem is identified during the early years of elementary school, when a child first demonstrates difficulties paying attention in class.
Prevention and therapy are currently unattainable. A child or adult with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms with the help of a solid treatment and education program, as well as early diagnosis.

What are the Symptoms of ADHD?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder symptoms in children and adolescents are well-defined and often manifest before six. They present themselves in multiple contexts, including the home and the classroom. Children may exhibit symptoms of all three forms of behavior, including inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, or they may exhibit only one. Colic in babies may also be a symptom of ADHD.
Additional Read: 5 Crucial Newborn Baby Care StepsA Difficulty Concentrating and Concentrating Owing to Inattention
The following are the most prominent signs of inattention:
- Unable to concentrate for extended periods and easily distracted.
- Committing careless errors in one's academic work, for example.
- Putting on an impression of forgetfulness or clumsiness.
- Being incapable of enduring tedious or time-consuming tasks.
- Conveying the appearance that they cannot follow instructions or pay attention.
- An endeavor or activity that is in constant flux.
- Having difficulty keeping up with job organization.
Hyperactivity-Impulsivity
People who commonly exhibit the signs and symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity:
- While you are seated, move about and fidget.
- In places where they are expected to remain seated, such as the classroom or the office, they rise from their seats.
- In inappropriate situations, they may run, rush, or climb; alternatively, adolescents and adults regularly experience sensations of restlessness.
- Incapable of playing games or engaging in hobbies in a tranquil setting.
- Be in a constant state of motion or activity, or act as though being propelled by a motor.
- Excessive verbal discharge.
- In a conversation, answering questions before they are entirely posed, completing other participants' sentences, or speaking without waiting your turn is impolite.
- Have difficulty waiting in line or in a queue.
- Intervene or make yourself known during conversations, games, or other people-related activities.
These symptoms can lead to severe problems in a child's life, such as poor academic performance, decreased social connection with other children and adults, and difficulties following regulations. You may book an online consultation with a pediatrician if you encounter these symptoms.
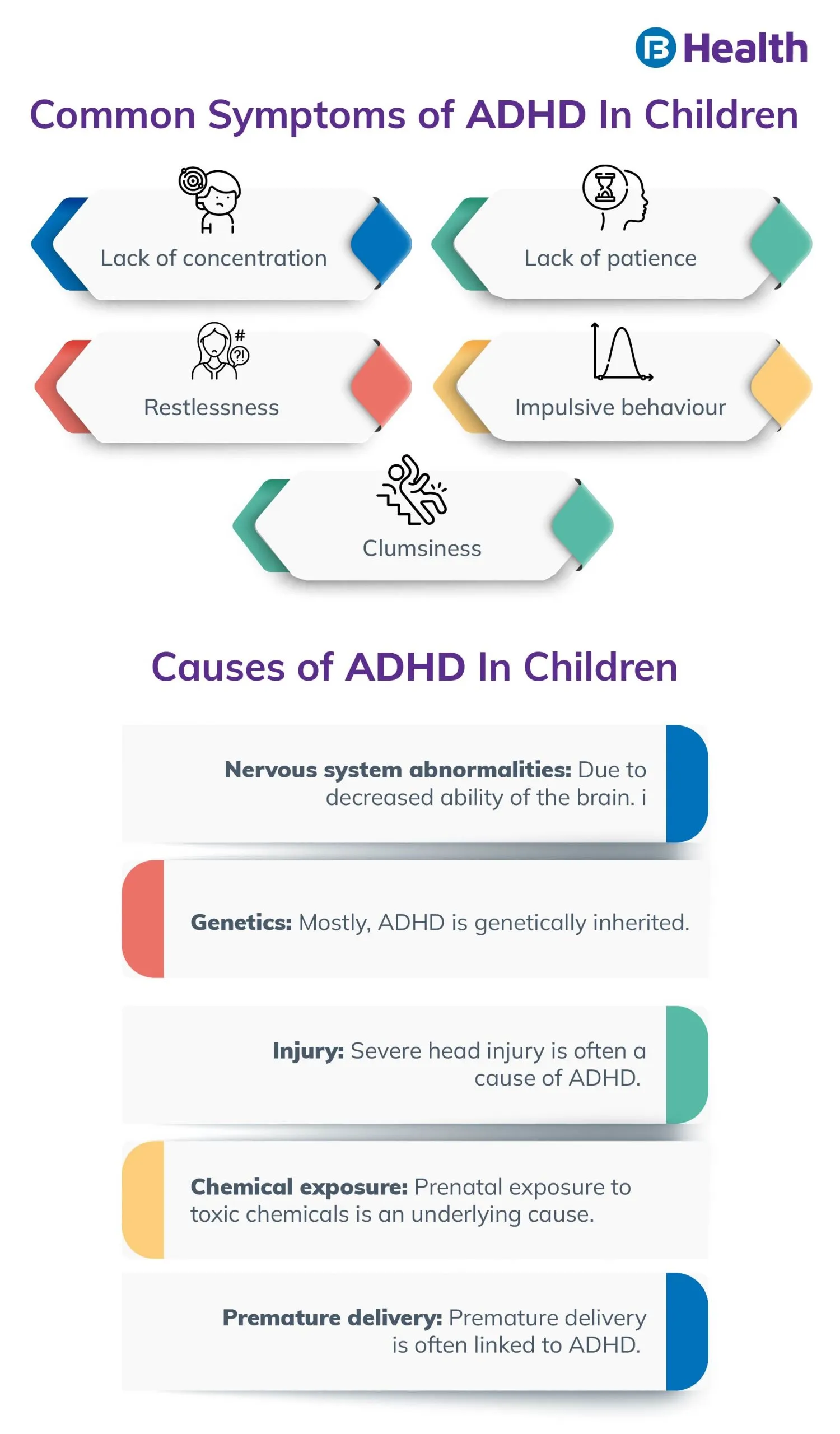
Causes of ADHD
- The anatomy and function of the brain: There is some evidence that Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is associated with decreased brain activity in regions that regulate activity level and attention.
- The genetic code and inherited features: ADD and ADHD are frequently hereditary disorders. A child with ADHD has a one-in-four probability of having a parent with the disorder. Another close relative, such as a sibling, may also have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Occasionally, a parent will also obtain an ADHD diagnosis at the same time as their child.
- Some individuals will acquire ADHD after experiencing a severe head injury.
- There is a link between premature delivery and the likelihood of having ADHD.
- There is an association between prenatal exposure to chemicals that increase the risk of ADHD, such as alcohol or nicotine from smoking, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, and the development of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.
- In exceedingly rare instances, environmental toxins may produce ADHD symptoms. Lead exposure throughout youth, for instance, can have detrimental impacts on development and behavior.
What are the Risk Factors for ADHD?
Even though multiple studies indicate genetics as a crucial component in the development of ADHD, researchers are still uncertain as to the precise etiology of the disorder. ADHD is likely caused by a combination of factors, similar to most other mental disorders. It is also related to severe newborn cough. Environmental factors that may have a role in the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder are being investigated in addition to genetics. Brain trauma, food, and social settings are examples of environmental variables.
Attention, Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is more common in males than in girls, and in women with ADHD, inattention symptoms are more likely to prevail than hyperactive symptoms. People with ADHD experience co-occurring mental health concerns, such as learning challenges, anxiety disorders, behavior disorders, depression, and substance addiction.
How is ADHD diagnosed in children?
No simple test exists to establish whether you or your child has Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in childhood. Still, a specialist can accurately diagnose the condition after a thorough evaluation. Among the possible components of the evaluation is a physical examination, which can help rule out some of the other probable causes of the symptoms. A compilation of conversations between you and your child.
The majority of kids with ADHD get better after treatment. And if your child's symptoms persist as they mature into an adult, book an online consultation now with us, You can pay your medical payment for ADHD using a Bajaj Health Card, and the bill amount will be converted to a manageable EMI.
References
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.





