Orthopaedic | 5 min read
Bone Tuberculosis: Types, Causes, Complications, Diagnosis
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes the highly contagious illness tuberculosis. When tuberculosis affects your skeletal system, it is known as bone tuberculosis. Bone TB is treatable if it is contracted and identified early.
Key Takeaways
- Bone tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is highly contagious
- There are various treatment options for those who are suffering from bone tuberculosis
- Bone TB can lead to many symptoms or complications that may affect one’s quality of life
Bone tuberculosis affects your skeletal system, including your bones and joints. Spinal tuberculosis is the most prevalent form of bone tuberculosis which occurs when your spinal cord becomes infected with Mycobacterium. Pott's illness is another name for spinal TB.
Bone tuberculosis is prevalent in developing nations and is among the top 10 global killers [1]. Bone TB is uncommon but difficult to diagnose and, if neglected, can have serious consequences.
Types of Tuberculosis
Extrapulmonary tuberculosis describes TB when it spreads (EPTB) to other areas such as the abdomen, skin, joints, etc. Tuberculosis of the bones and joints is one type of EPTB. The spine, long bones, and joints are all affected by bone tuberculosis
Tuberculosis of the lungs is often known as pulmonary tuberculosis. The infection may result in lung issues, breathing difficulties, and chest pain
What Causes Bone Tuberculosis?
Sometimes, tuberculosis can spread to your bones and cause bone TB. TB can also spread between people through airborne transmission. The disease can spread from the lymph nodes or lungs into the bones, spine, or joints once you develop tuberculosis. Bone TB frequently develops in the dense vascular supply in the middle of the long bones and vertebrae.
The long bones are particularly vulnerable to tuberculous infection, which are similar to benign tumours, locally aggressive tumours like giant cell tumours, and occasionally even malignant tumours like osteogenic sarcoma or chondrosarcomas. As a result, it leads to bone cancer.
List of Factors that May Cause Bone Tuberculosis
Incorrect treatment
The illness may spread to your lungs and other organs if you are not diagnosed on time. Therefore, appropriate care is needed before the situation worsens. Early signs of bone TB are noticeable and should be treated as soon as possible.
Transmission
It is an infectious illness that spreads swiftly from one person to another. Once it enters the human body, it will affect the lungs, lymph nodes, thymus, and bones. Therefore, patients should recognise the symptoms and signs of bone TB to begin therapy as soon as possible. Patients with a history of active TB are more likely to develop osteoporosis and experience bone fractures. It’s essential to check our bone health periodically.
Additional Read: Leg Fracture: Symptoms and TreatmentsTypes of Bone TB
Bone tuberculosis can affect you in many different forms, such as:
- Upper extremity tuberculosis
- Ankle joint tuberculosis
- Knee joint tuberculosis
- Elbow tuberculosis
- Hip joint tuberculosis
- Spinal tuberculosis
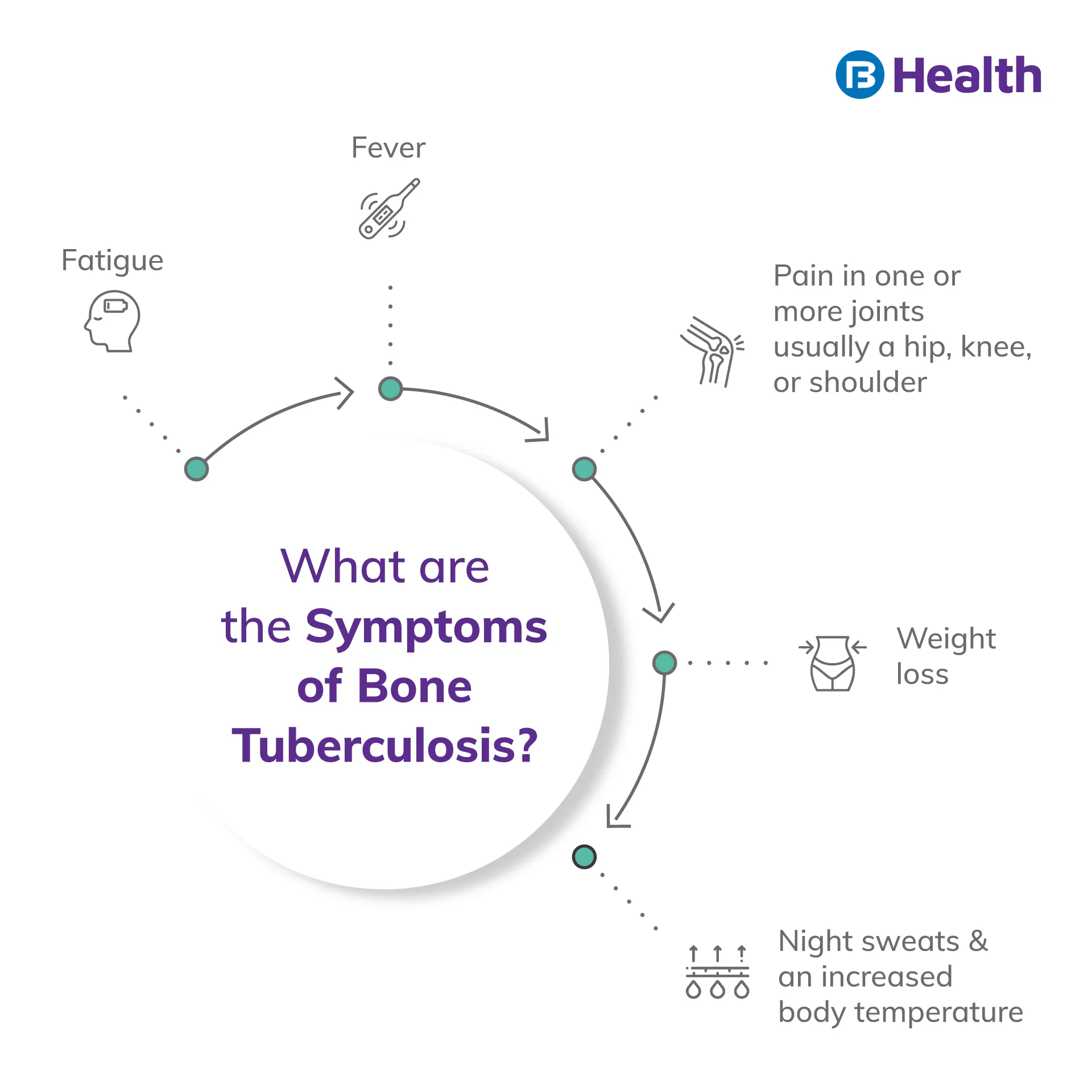
Symptoms of Bone Tuberculosis
Bone TB, mainly spinal TB, is painless in the early stages, and the patient may not display any symptoms making it difficult to detect. However, the signs and symptoms of bone TB are typically fairly advanced when it is ultimately detected.
In rare cases, the illness can lie latent in the lungs and spread without the patient knowing they have any tuberculosis. However, there are a few signs to look out for if a patient has developed bone TB:
- Back and joint stiffness
- Inflamed joints
- Back pain that is severe and ongoing
- Bone pain
- Abnormal blood loss
- Appetite loss
- Ongoing fever, especially one of low grade
- Extreme chills
- Sweating at night, feeling exhausted all the time
- Cough with blood
- Sharp chest ache
- A strong, three- or longer-lasting cough
When your condition is at an advanced stage, other symptoms will manifest. The following are the signs of advanced bone TB:
- Bone malformations
- Limb shortening in children
- Paralysis
- Neurological issues
Treatment for Bone Tuberculosis
Bone tuberculosis has a high mortality rate if untreated.
However, bone tuberculosis damage can be reversed using the following treatments:
Medicines
Anti-tuberculosis medications include rifampicin, streptomycin, kanamycin, isoniazid, prothionamide, cycloserine, and pyrazinamide. They can go inside the cerebral fluid and start fighting the germs. The recovery from bone TB may take six to twelve months
Corticosteroids
These drugs may be recommended to avoid issues, including inflammation around the heart or spinal cord
MDR
Antitubercular medications are taken as part of MDR treatment. It is the most advantageous course of treatment to get rid of the symptoms in the bone
DOTS Treatment
Direct Observed Treatment is another name for it. Patients with signs of bone TB are strongly advised to take it
Surgery
Surgery may be required to remove an infected portion if you have advanced bone tuberculosis
Diagnosis of Bone Tuberculosis
It is frequently diagnosed using the following techniques:
Bacterial cultivation
You most likely have a lung infection if you have bone tuberculosis. Your doctor may take a sample of your blood or sputum for testing for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Biopsy
Your physician would prescribe a biopsy, which entails removing a sample of affected tissue and testing it for infection. Bone marrow biopsy can help test for spinal TB lesions.
Examination of bodily fluids
To examine your lungs for infections, your doctor may take a sample of the pleural fluid surrounding and protecting them. For example, they could remove cerebrospinal fluid from the region surrounding your spinal cord or synovial or joint fluid for testing to check for bone or joint TB.
Complications of Bone Tuberculosis
Although spinal TB is uncommon (1–3% of the time), it is a disorder that can be fatal once discovered. The severity might increase the longer it remains untreated. In addition, the severity might increase the longer it remains untreated. Typical difficulties include:
- Vertebral collapse resulting in back rounding or bending (kyphosis)
- Compressed spinal cord
- The development of a cold abscess in the cervical area
- Severe infection that might spread to the mediastinum or trachea and other areas and possibly result in the creation of sinuses
- Severe neurological issues
- No movement in the lower body
Bone tuberculosis poses a greater danger in developing countries. Although the threat of TB is reduced in affluent countries, bone tuberculosis is nevertheless a concern. Drugs can be used to treat this condition once it has been recognised, and in more complex situations, medication can be used in combination with surgical intervention.
Visit Bajaj Finserv Health to get a doctor consultation if you experience any bone TB symptoms or have more queries.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3691411/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.