Mental Wellness | 4 min read
Catatonia: Means, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Catatonia is a subtype of depression that manifests itself through unusual behaviour governed by withdrawal syndrome. Find out all about catatonia, including major symptoms and treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- Catatonia is a subtype of depression which may accompany related conditions
- Common symptoms include speech difficulty, grimacing, agitation and more
- Doctors can diagnose catatonia by checking for waxy flexibility and catalepsy
Individuals suffering from depression often experience different types of associated conditions. Catatonia is one such condition that may accompany depression, where people don’t acknowledge what is happening around them. The word catatonia originated from two Greek words, kata (meaning down) and tonas (meaning tone). Read on to know all about catatonia as this blog discusses catatonic depression, catatonic symptoms, as well as diagnosis and treatment of the condition.
What is Catatonic Depression?
A subtype of depression, catatonia may become visible with withdrawal syndrome and atypical behaviors. For example, people suffering from catatonia may not speak or appear blank for a long time. Now, research has identified that catatonia can accompany mental health conditions such as mood swings, depression, bipolar disorder, catatonic schizophrenia, and other personality disorders [1]. However, do note that catatonia can also affect an individual without any associated condition.
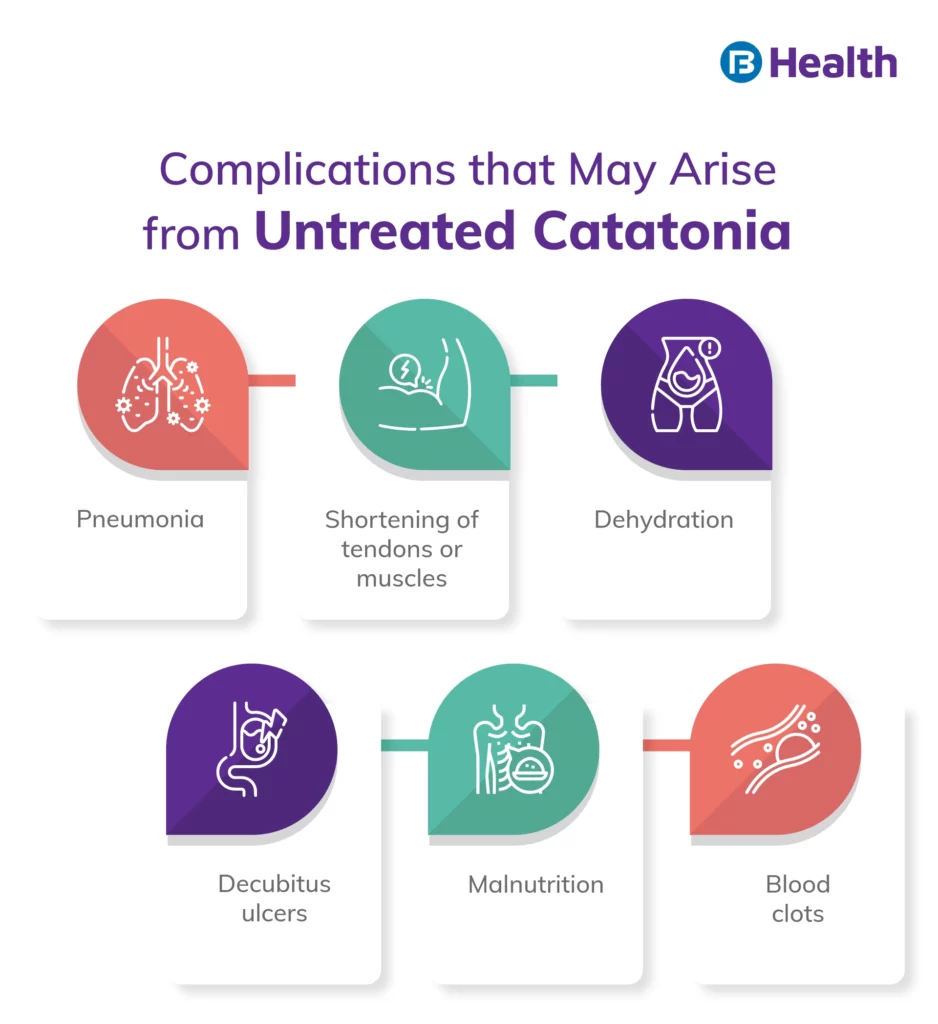
Catatonia Symptoms
The most common symptoms of this condition are remaining silent for a long time and a catatonic stupor (the condition of being in a daze). Other signs of catatonia are as follows:
- Grimacing
- Negative reaction as opposed to a stimulus
- Unnatural postures
- Trouble speaking
- Irregular movements
- Automatic obedience
- Imitation of another person’s movements
- Agitation
An individual with any three of these catatonia symptoms may be diagnosed as catatonic [2].
Additional Read: What is Autumn AnxietyCauses of Catatonia
No particular cause has been identified yet for catatonia. However, there are certain conditions which can lead to catatonia or a catatonic state. They include autoimmune conditions, stroke, Parkinson's, metabolic abnormalities, medication or substance use complications, infections, and more. Catatonic behaviour may also be a symptom of depression. The causes of the condition are as follows:
- Genetic link where people in your family have a history of mental health conditions
- Changes in brain functioning
- Significant changes in life caused by death or separation
- Certain medical conditions such as sleep disorder, severe pain, ADHD, and more
How to Diagnose Catatonia?
One of the most effective methods of diagnosing catatonia is through physical examination. Two factors in determining the condition include waxy flexibility and catalepsy. In the case of waxy flexibility, the patient's limbs refuse to move at first, despite the doctor's efforts and then become loose slowly. Catalepsy will be diagnosed if a patient holds a specific posture after being pushed to it.
Other methods of diagnosing catatonia by applying the Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale include the following:
- Observing how the patient behaves during normal conversation
- Doctors scratch their heads aggressively to check whether the patient imitates them
- A doctor stretching out their hands for handshakes but telling the patient not to shake their hand
- Examining how the patient's grasp reflex is
- Checking for vitals signs of agitation [3]
Usually, patients suffering from catatonia cannot answer random questions aimed at them. Therefore, while diagnosing catatonia, doctors try to rule out other related conditions by checking the patient's medical history. They may also order imaging studies to check whether a brain tumour is causing the catatonia symptoms.
Additional Read: Narcissistic Personality Disorder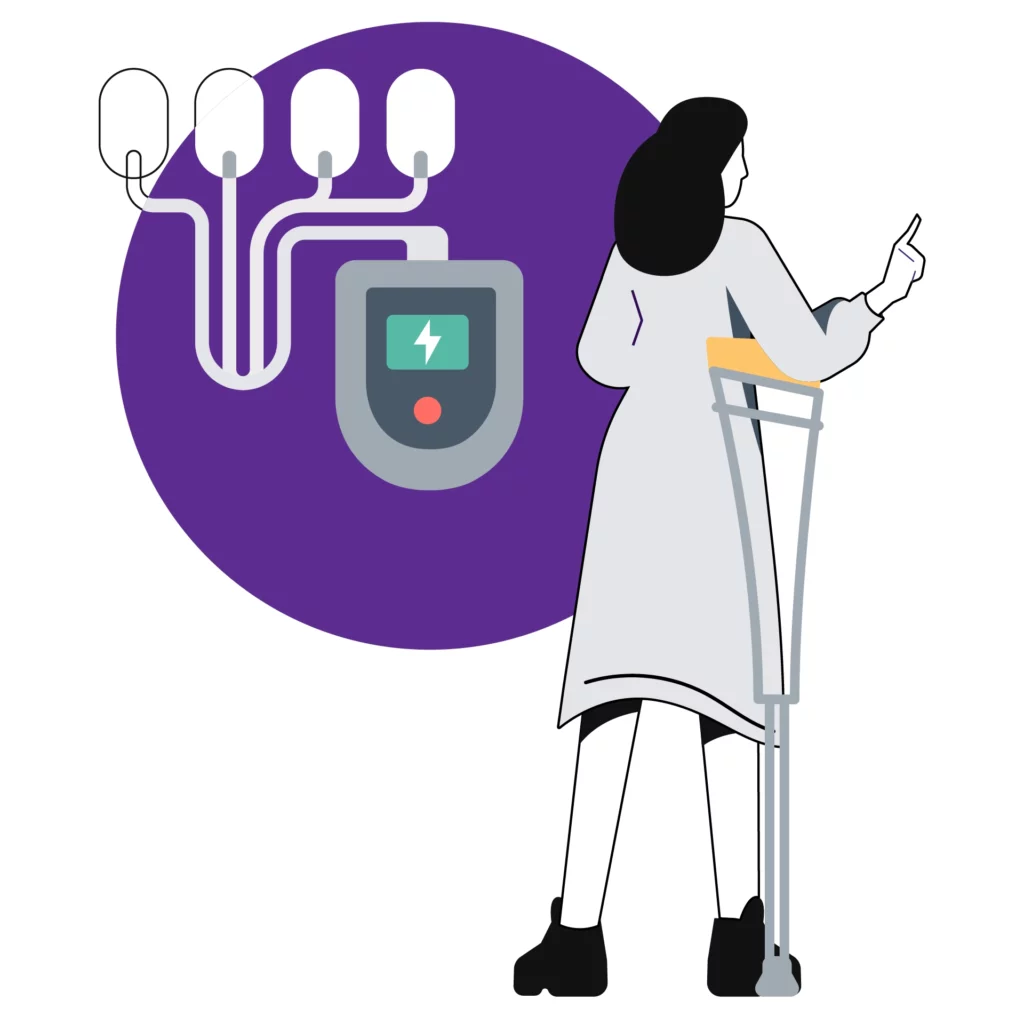
Treatments For Catatonia
In cases where catatonia is associated with schizophrenia or other depressive disorders, doctors focus on treating the underlying health issue. Once the underlying health issue improves, the treatment focus can be returned to catatonia. Treatment of catatonia can be divided into benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Benzodiazepines
Doctors often prescribe this psychoactive drug to treat anxiety and panic disorders. In some cases, they help manage depression. To treat catatonia, doctors usually recommend lorazepam, a type of benzodiazepine. The drug is given as intravenous injections, and the dose is lowered with time.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
In case lorazepam doesn't work out, doctors may prescribe ECT, which is another effective treatment for catatonia. During ECT, doctors attach electrodes to the head and stimulate the brain with electrical impulses, which triggers a generalized seizure. Today, ECT is regarded as a safe and effective procedure for treating a range of mental health conditions, including depression. As per a 2016 study, ECT worked for 80%-100% of cases of different types of catatonia [4].
Conclusion
While catatonia can affect your mental health in different forms, remember that there are treatments available for each. Start seeing a mental health expert if you are experiencing catatonia symptoms or signs of associated conditions. For a quick consultation, you can book an online or offline appointment with a doctor on Bajaj Finserv Health. Keep your health above everything to fly high with self-belief!
FAQs
What is a typical example of catatonic behaviors?
One suffering from catatonia may stare without expression and not respond to communication. However, they may keep repeating whatever you say.
Is catatonia caused by anxiety?
Catatonia is associated with an extreme form of anxiety and depression.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4695780/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5183991/
- https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/19014
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4473490/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.




