Heart Health | 4 min read
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: 4 Important Things You Must Know
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Diabetes, obesity, and thyroid disease are the dilated cardiomyopathy causes
- Dilated cardiomyopathy symptoms include fatigue, blood clots, heart murmurs
- Medication and lifestyle changes help with dilated cardiomyopathy treatment
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a medical condition that affects your heart muscle. It begins in the heart's left ventricle, the main pumping chamber. It occurs when your heart's ability to pump blood is decreased due to a weakened and enlarged left ventricle. It can affect other chambers over time too.
The term ‘cardiomyopathy’ is referred to illnesses that affect the heart muscles. Dilated cardiomyopathy is the most common form of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. Many people in India make emergency visits to doctors due to dilated cardiomyopathy. However, this condition is often misdiagnosed as asthma or COPD, making patients undergo wrong courses of treatment for a long time [1].
Although dilated cardiomyopathy can develop at any age, it is usually diagnosed in adult males [2]. This condition may occur due to various underlying medical conditions. It is also the most common cause of heart failure [3]. Read on to know about dilated cardiomyopathy causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Additional Read: Myocardial InfarctionDilated cardiomyopathy symptoms
Some people may not experience any symptoms in the early stages. However, they may develop the symptoms quickly or gradually over time. Here are the common dilated cardiomyopathy symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Chest pain
- Fainting
- Blood clots
- Sudden death
- Weakness
- Weight gain<span data-ccp-props="{"201341983":0,"335559739":160,"335559740":240}">
- Heart murmurs
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Cough and congestion
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Decreased ability to exercise
- Arrhythmia - abnormal heart rhythms
- Edema - Swelling of the ankle, leg, feet, and abdomen
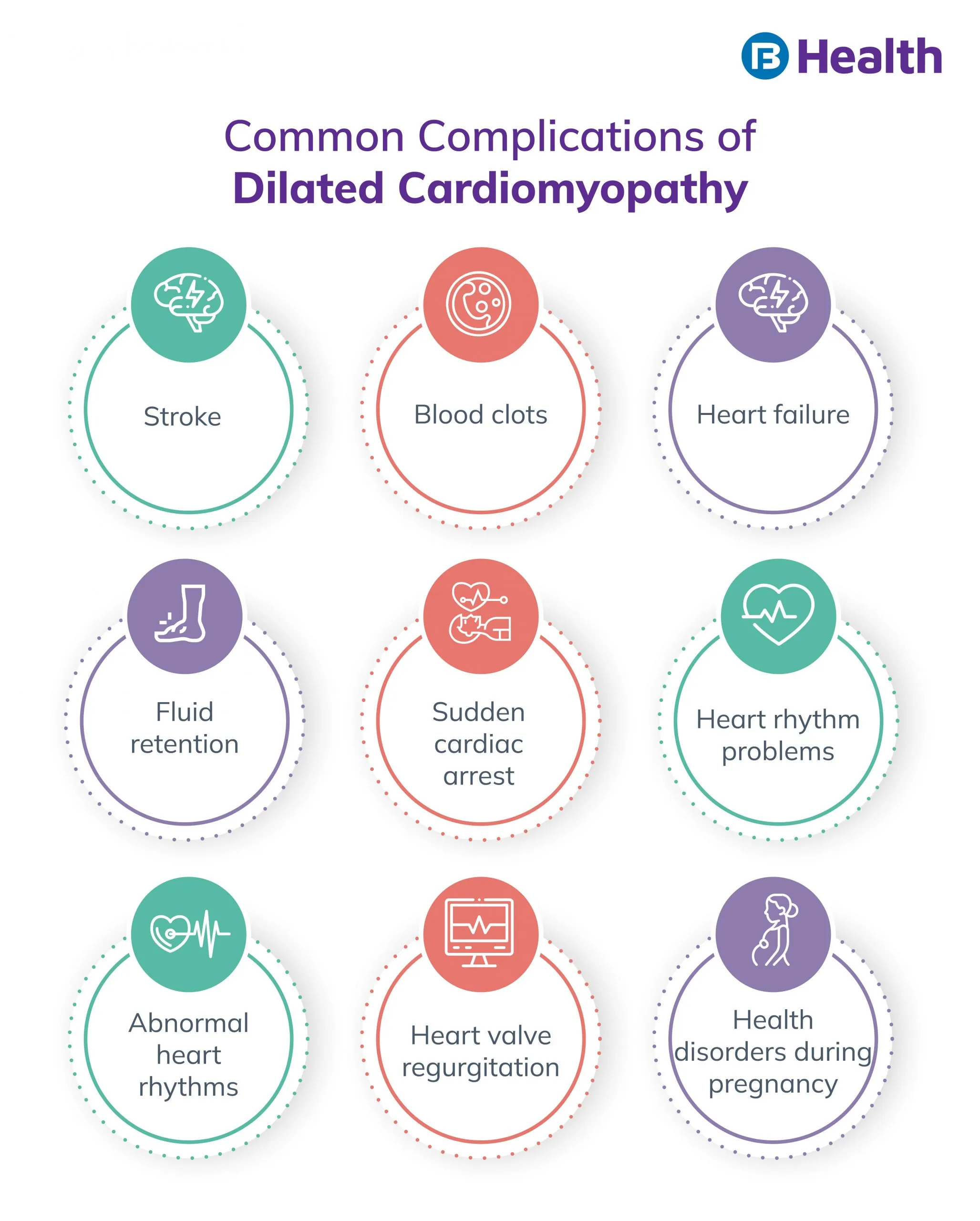
Dilated cardiomyopathy causes
In most cases, dilated cardiomyopathy causes are idiopathic, i.e., the exact cause is unknown. Some other factors that may include:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Viral infections
- Alcohol abuse
- Thyroid disease
- Exposure to toxins
- Cancer medications
- Hemochromatosis
- High blood pressure
- Women after childbirth
- Autoimmune disorders
- HIV and Lyme disease
- Heart valve disease
- Neuromuscular disorders
- Pregnancy complications
- Arrhythmia - irregular heartbeat
- Cocaine and other illegal drugs
- Nutritional or electrolyte problems
- Inflammation of the heart muscle
- Muscular dystrophy and other genetic conditions
- Family history of heart diseases
Dilated cardiomyopathy diagnosis
The diagnosis of it depends on a physical exam, your medical history, and specific tests. The tests for it include a blood test, chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI scan, cardiac catheterization, exercise stress test, electrocardiogram, and echocardiogram. A myocardial biopsy may also be performed to determine dilated cardiomyopathy causes.
Dilated cardiomyopathy treatment
The dilated cardiomyopathy treatment aims to reduce symptoms, improve cardiac function, and treat the causes of heart failure. Here are the few things your doctor may suggest.
Medication
Doctors may prescribe medication to treat symptoms, improve cardiac function, and prevent complications. You may take ACE inhibitor and beta-blocker medications even when you do not experience dilated cardiomyopathy symptoms. Take diuretics, digoxin, and aldosterone inhibitors when symptoms develop or worsen.
Doctors usually prescribe medications to treat the causes. For instance, you may be prescribed medication to control the heart rate if you have a heart arrhythmia. Similarly, blood thinners may be suggested to prevent blood clots.
Lifestyle changes
Making lifestyle changes helps control certain dilated cardiomyopathy symptoms. For instance, reducing salt intake is important if you develop symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath. Make sure you follow a low-sodium diet even if your symptoms subside. Your doctor may also recommend aerobic exercises.
Implantable devices
In serious cases, cardiac resynchronization therapies such as biventricular pacing and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD) are used. Biventricular pacing reduces symptoms, improves survival, and increases tolerance capacity in people with advanced heart failure.
The pacemaker also maintains heart rate in people with slow heart rates or heart block. ICD-monitored heart rhythms are recommended for patients who are at risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias or sudden cardiac death. When the ICD detects a fast, abnormal rhythm, it shocks the heart muscle, making the heartbeat normal.
Surgery
Your doctor may suggest surgery in serious cases. Surgeries are done to treat the heart muscle after cardiac arrest, valve disease, and congenital malformations. Left ventricular assist device insertion also proves beneficial for some patients. Other surgical options for heart failure include heart transplants.
Additional Read: 4 Types of Valve Replacement SurgeryManage your stress, stay physically active, eat healthy, maintain your weight, quit tobacco, and get quality sleep to prevent various types of heart diseases including congenital heart disease. Also, get preventive health check-ups done to avoid fatal consequences. You may book online consultation with doctors and heart specialists on Bajaj Finserv Health. It is the easiest way to keep your overall health under check.
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269740232_Epidemiological_study_of_dilated_cardiomyopathy_from_eastern_India_with_special_reference_to_left_atrial_size
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000168.htm
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/joim.12944#:~:text=DCM%20is%20one%20of%20the,the%20prevalence%20is%20quite%20difficult.
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.