Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation | 9 min read
Hives On Skin: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Hives on skin look like raised and itchy, red bumps that may hurt or sting
- Hives causes include allergic reactions, physical triggers, health conditions
- Treatment of hives include medication or natural and home remedies
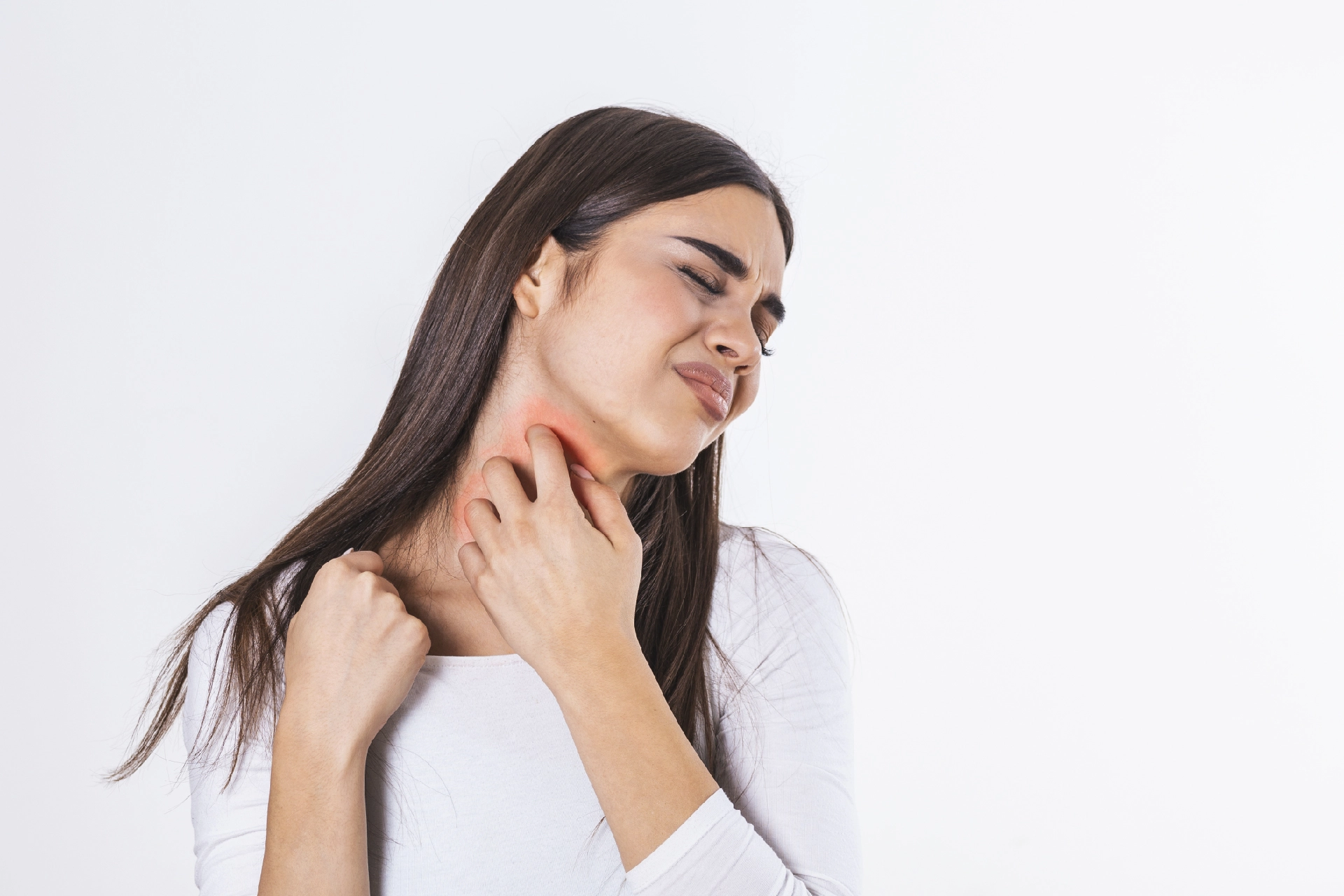
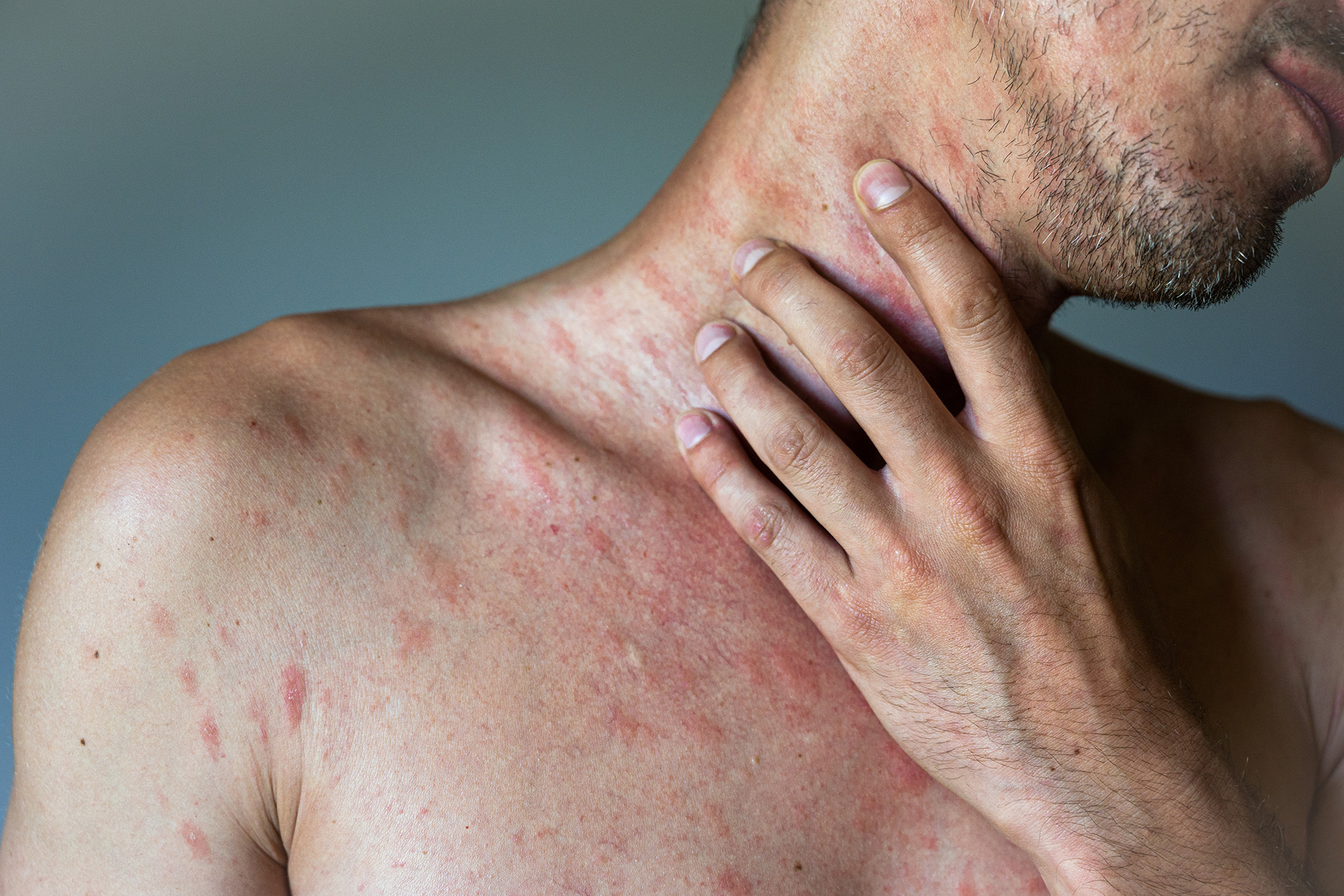
Hives affect around 15-20% of the population during a lifetime [1]. In medical terms, hives are also known as urticaria. In India, the lifetime prevalence for hives is said to be 7.8% to 22.3%. Of these, almost 4%-33% cases are physical urticaria [2]. Hives on skin appear as raised, itchy rashes that are red or flesh-colored and may sometimes hurt or sting.
Dry Skin itching causes a feeling of discomfort and may interfere with your daily activities. Hives allergy is generally caused by allergic reactions or physical factors including an underlying health condition.
Read on to learn more about hives’ causes, symptoms, types and treatment.
What Are Hives?
Hives are red raised pimples or dark spots on the skin. They are a form of an inflammation on the layer of your skin that occurs when your body reacts to an allergen. When your immune response comes into touch with an allergen, it produces allergic responses. Allergic reactions are substances that are normally safe for most individuals but produce allergic reactions in those who are susceptible to them.
Hives are frequently itchy, but you may also experience burning or stinging. They can range in size from a fingertip to a dinner plate. Hives are medically known as urticaria.
Hives' welts can sometimes combine together to form bigger regions known as plaques. Hives often diminish within 24 hours; however, they may be visible for a few days or weeks.
Difference Between Hives And Rash
A rash is a skin ailment characterized by unusual features such as patches, swelling, itching, or redness. A rash can be hives, although not all rashes are hives.
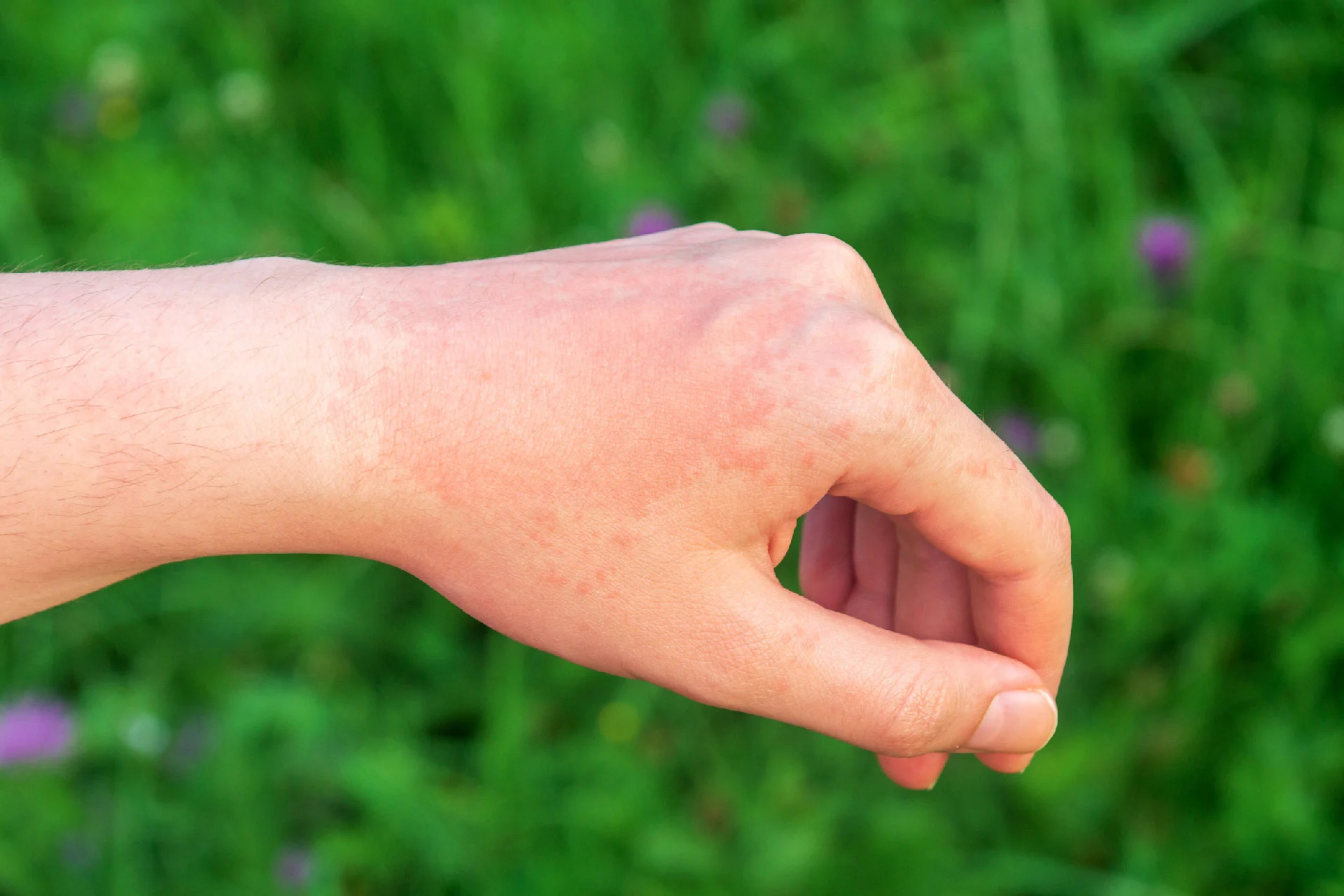
Symptoms of Hives on Skin
- Skin lesions on any part of the body that may appear in batches
- The lesions may be red, pink, or skin colored and cause itching
- When pressed, the color of the hive may fade or turn white
- The welts can either be ring-shaped or random
- They may also grow larger, spread, or change shape
- The size of lesions vary between a pinprick to several inches across
- The bumps or lesions may usually disappear in 24 hours but may reappear
- Instead of bumps you may see blotches, thin raised lines, or tiny spots
Causes of Hives on Skin
Hives can develop as an allergic response to various triggers or due to some physical condition or health condition. In some cases, the reason for you to get hives may be unclear. The following are the most common hives causes diagnosed by doctors.
- Allergic reactions
When your body reacts to an allergen, it may cause hives. Such reactions occur when you touch or eat something that you are allergic to. This is when your body releases histamine and the capillaries leak fluid. The fluid accumulates in your skin and causes inflammation as well as a rash.
Hives caused by an allergic reaction is known as contact urticaria. Some common allergens that may cause hives are
- Medicines
- Latex
- Fruits such as banana, kiwi, mango, or chestnut
- Plants like poison ivy, poison oak, or nettles
- Food allergy like eggs, nuts, or seafood
- Physical factors
Apart from allergies there are also some physical factors that may trigger hives. These triggers are
- Exposure to sun light or UV rays from a tanning bed
- Changes in temperatures or extreme temperatures
- Adrenaline released during heat exposure, stress, or exercise can lead to stress hives
- Rubbing, scratching, or pressure on the skin
- Health conditions
Underlying health issues are also one of the common hives causes. These conditions may be
- Bacterial or viral infections
- Autoimmune hypothyroidism
- Intestinal parasites
- Other autoimmune conditions
- Conditions that may cause blood vessel inflammation
Types of Hives on Skin
Anaphylaxis
It is a severe allergic reaction in which hives usually accompany nausea, vomit, swelling, breathing issues, and dizziness.
Dermatographism
A form of acute hives, this is a mild condition caused by scratching and pressure on the skin. It usually goes away on its own and may not require medical treatment.
Chronic hives
Also known as chronic urticaria, these are recurring and don’t have an identifiable cause. These usually last over 6 weeks. They may also be a sign of underlying conditions such as type 1 diabetes, celiac, or lupus.
Temperature-induced hives
If you are sensitive to temperature changes, you may experience this type of hives. Depending on the temperature you are exposed to, you may experience cold-induced hives, solar hives, or exercise-induced hives.
Infection-induced hives
Bacterial or viral infection may also lead to hives. Common infections that may cause it are strep throat, urinary tract infection, and colds. Mononucleosis and hepatitis viruses can also be the reasons for these hives to form.
Allergic hives
Caused by an allergic reaction, this type is usually treated with allergy medicines and avoiding the triggers. Common allergens are foods, pollen, dust mites, medication, insect bites, or pet dander.
Additional Read: What is Cold UrticariaHives On Different Parts Of The Body
Hives can occur anywhere on the body, for example, on the:
- Legs
- Arms
- Trunk
- Face
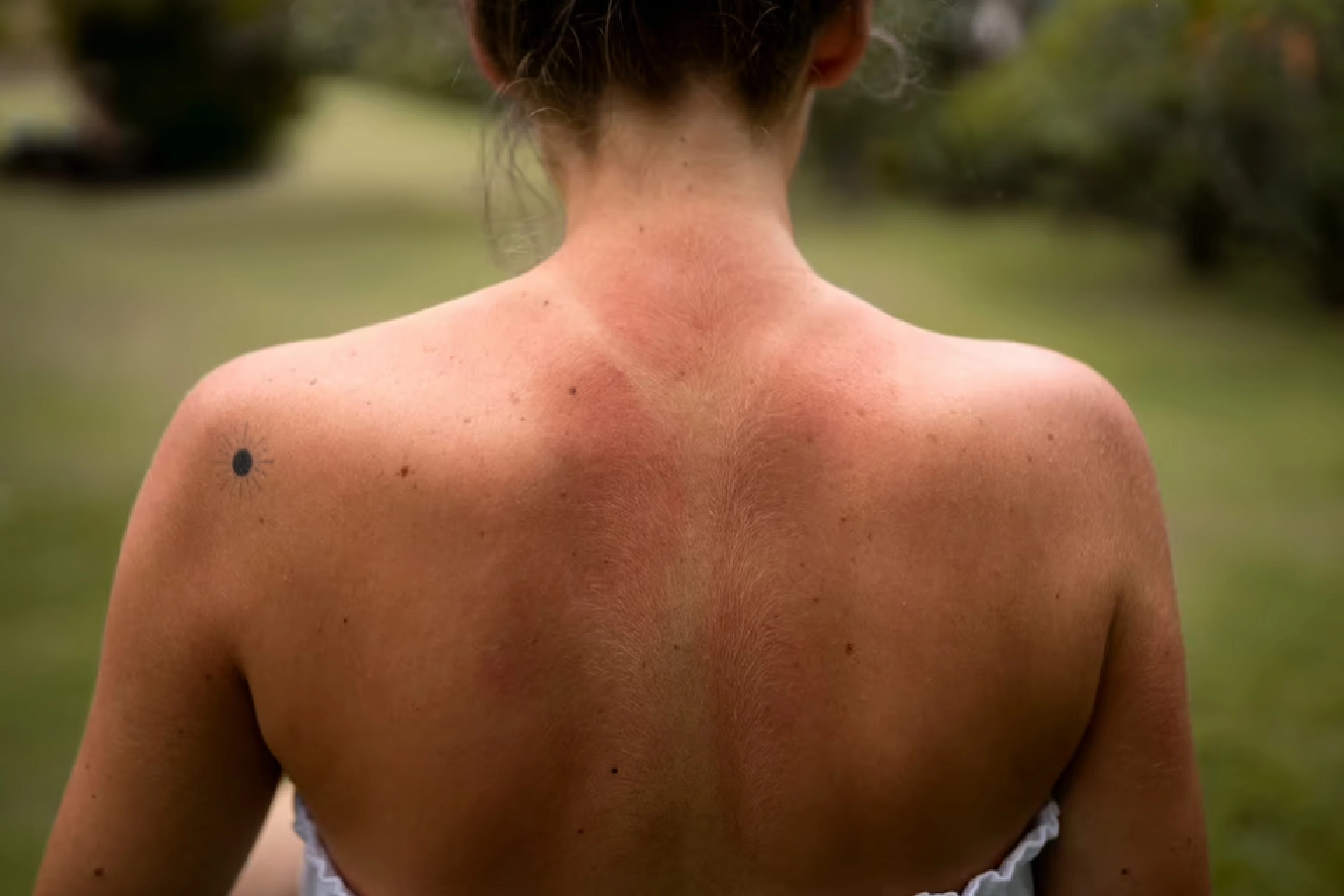
Hives on legs
In response to the bug or spider bites, some people develop "papular urticaria." It is more common in youngsters who have not yet gained immunity to these bites. Lesions can appear everywhere. However, they most usually appear on the legs.
Some typical characteristics are as follows:
- The uncomfortable red pimples, known as papules, appear in groups
- Each papule has a center point and is 0.2 to 2.0 centimeters wide
- They might be liquid-filled
- As existing papules dissolve, new ones may emerge
- Papules may recur as a result of a fresh insect attack
Hives on face
Hives caused by an allergic or sensitivity reaction can substantially impact appearance, for example, by generating puffiness in the lips.
The swelling may spread and impair the mouth, throat, and airway. In this instance, the individual may have difficulty breathing. This is an issue, and the individuals need immediate medical attention. They are in danger of getting anaphylaxis, a potentially fatal illness.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic response that affects the entire body.
It can cause severe respiratory difficulties as well as loss of consciousness. It is a life-threatening emergency that can be lethal if treated late.
If an individual develops hives, they should be on the lookout for any additional symptoms that might signal an anaphylactic response.
If the person has any of the following symptoms, get medical treatment immediately.
- Vomiting and nausea
- Swelling of the mouth, tongue, lips, and throat, resulting in trouble breathing, chilly, clammy skin, and a fast pulse
- Lightheadedness or faintness
- A surprisingly strong sensation of anxiety
Treatment for Hives
For the overwhelming majority of the time, hives resolve on their own. However, your doctor may offer drugs and at-home care to help you feel better and reduce your chances of getting hives again. Treatment options include:
Allergy drugs
Antihistamines are medications that prevent the effects of histamine. They can be administered orally (a pill) or topically (put on the affected skin). Antihistamines decrease itching caused by hives and reduce the severity of allergic responses. Some antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine, have a rapid onset of action. Depending on the severity of the hives, your doctor may prescribe daily allergy drugs such as loratadine, fexofenadine, cetirizine, or levocetirizine.
Allergy shots
If you have difficult-to-treat persistent hives, your doctor may recommend monthly injections of medications that inhibit allergic responses. People who have severe allergies produce an excessive amount of IgE. These injections prevent your immune system from producing IgE.
Treatments at Home
Take a chilly bath or shower, wear loose-fitting clothing, and apply cold compresses to ease hives. Itching and swelling can be relieved with over-the-counter (OTC) hydrocortisone or antihistamine lotion.
Oral steroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can reduce hive symptoms that do not respond to antihistamines or topical steroids.
Epinephrine
Severe acute allergic responses can result in a potentially fatal condition known as anaphylaxis. Hives, facial, mouth, or throat swelling, shortness of breath, wheezing, vomiting, and low blood pressure are some of the symptoms. Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening response that requires an emergency epinephrine injection (EpiPen®) to open a swollen airway.
The best way to treat hives is to identify and treat the trigger that caused it. Depending on the cause and the types, you may get one or a combination of the following as a treatment.
Over the counter options such as
- Medicines like Prednisone, leukotriene-receptor antagonists, omalizumab, dapsone
- Antihistamines such as fexofenadine, cetirizine, loratadine
- Calamine lotion to relieve itching
- Benadryl to reduce itching, rash, and other symptoms
Home and natural remedies for relief from hives are
- Using witch hazel or aloe vera
- Cold compress or bath with anti-itch solution
- Avoiding products and factors that irritate the skin and increase your body temperature
How Are Hives Diagnosed?
By examining your skin, your doctor can identify hives and angioedema. Allergy testing can assist in determining what is causing a response. However, this is mostly true for acute hives. Knowing the reason might assist you in avoiding allergies and the hives that accompany them. The following allergy tests can be used to identify hives:
Skin tests:
Throughout this test, healthcare experts examine your skin for allergies. If your skin becomes red or swollen, it indicates that you are allergic to that chemical. A skin prick or scratching test is another name for this sort of allergy test. Skin testing is seldom performed for persistent hives.
Blood tests:
A blood test looks for particular antibodies in your blood. Your body produces antibodies to combat allergies. Hives and swelling might occur if your body produces too many antibodies.
Complications Of Hives
Anyone with a severe acute allergic response may experience life-threatening swelling of the airways, including the throat and lungs. Anaphylaxis is the medical term for this syndrome. It has the ability to block the airways, resulting in death.
Anaphylaxis is frequently caused by a severe allergic reaction to a specific food, such as peanuts and tree nuts, or by a bee sting. If you have anaphylaxis, you need epinephrine right away, such as injectable epinephrine.
Epinephrine relaxes blood vessels, increases blood pressure, and relieves hives and edema. If you use epinephrine outside of a medical environment, go to the emergency department and be monitored. Anaphylaxis symptoms may reappear when the adrenaline wears off.
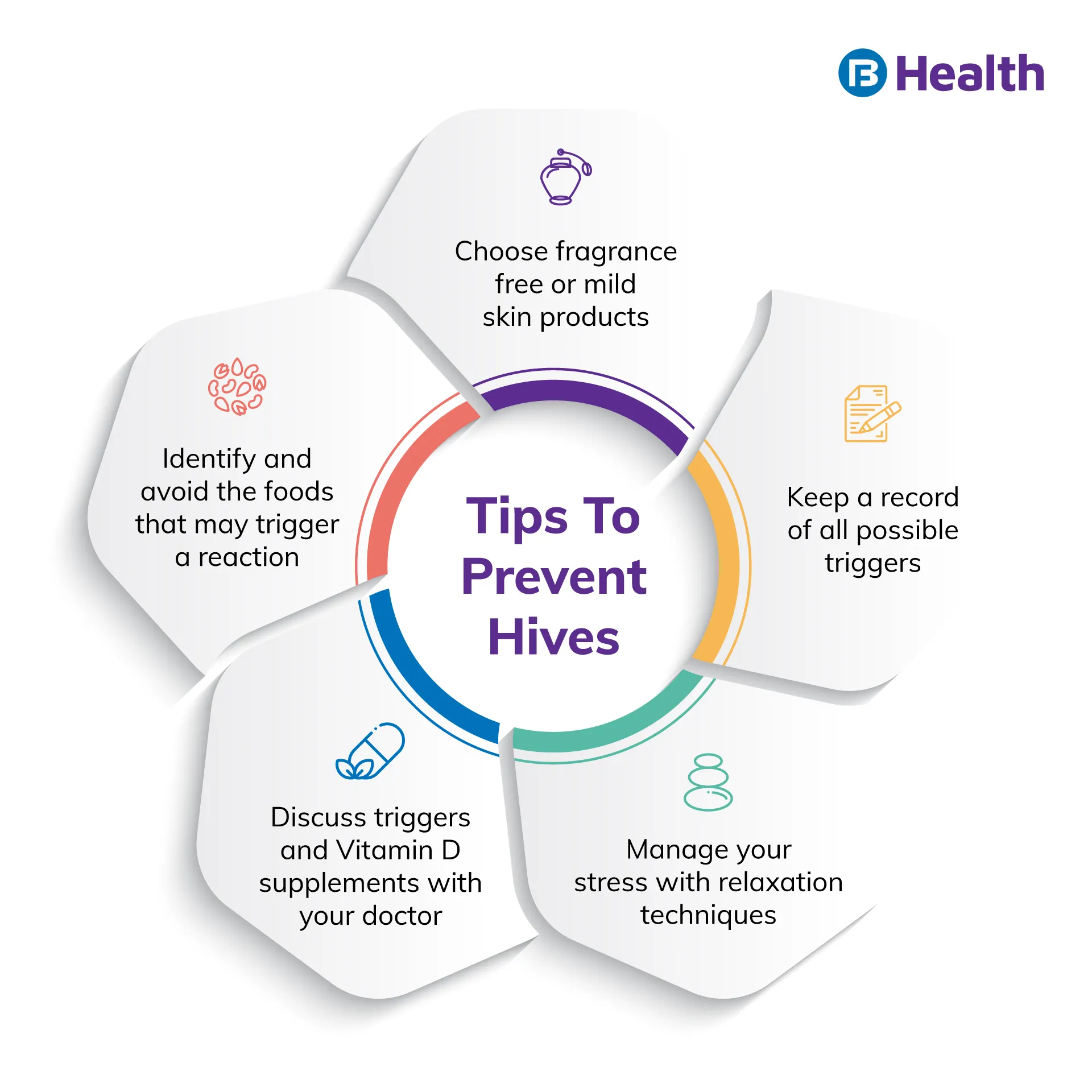
Prevention Tips For Hives
Severe hives
Your healthcare professional can utilize allergy test findings to assist you in determining which chemicals cause acute hives. You can avoid your triggers after you've identified them. You might want to:
- Remove specific foods from your diet
- Limit your exposure to airborne allergens
- Use scent-free and dye-free detergents and soaps
- Temperature swings should be avoided
- When you're stressed or overworked, relax and take a break
- Wear light, loose-fitting clothing
Some of these suggestions can also be used to treat chronic hives.
Hives that persist
Chronic hives may be impossible to avoid. Your provider may be unable to pinpoint the specific cause. They might also be symptoms of a larger medical disease affecting your immune system.
Although hives go away on their own in most cases, you can take allergy medications to ease the problem. But, if you have chronic hives or severe allergic reactions, it is best to seek medical attention. In rare cases, such chronic skin rashes cause further complications. If you have hives, allergy or any other health condition, book an online consultation from the comfort of your home on Bajaj Finserv Health. Get in touch with health experts on the platform for the best skincare tips.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3276885/#:~:text=Urticaria%20(from%20the%20Latin%20word,recur%20for%20months%20or%20years
- https://www.e-ijd.org/article.asp?issn=0019-5154%3Byear%3D2018%3Bvolume%3D63%3Bissue%3D1%3Bspage%3D2%3Bepage%3D15%3Baulast%3DGodse#:~:text=Lifetime%20prevalence%20for%20urticaria%20is,in%20India%20is%20not%20known
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.