General Physician | 4 min read
Important Facts You Need to Know About the Different Immunity Types
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- The immune system fights against harmful viruses, bacteria, and pathogens
- Active immunity provides lifelong protection due to the immunological memory
- Herd immunity helps to prevent the spread of pathogens that cause infections
Microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, and fungi can enter the body and cause infections as they are present everywhere. The body’s immune system prevents such unwanted microbes from entering the body by fighting against them. It is made up of cells, tissues, and proteins that collectively protect your body. Learn more about various immunity types.
A weak immune system is susceptible to infections whereas a strong immune system protects against pathogens. Strengthening your immune system is essential for the prevention of several diseases. Exercising and eating a healthy diet help you to improve your immunity. However, were you aware that there are different immunity types? Read on to learn more about various immunity types and their role in defending the body.
What is Immunity?
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and proteins. It acts as a guard against pathogens like viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa from invading your body. The immune system plays a vital role in preventing infections and diseases. It helps your body recognize and differentiate between its own cells, proteins, tissues, and chemicals from that of the pathogens. It also helps in removing infected and dead cells from the body.
Additional Read: Important Symptoms of Weak Immunity and How to Improve It
Immunity Types: Know about Immunity
Innate immunity
Innate immunity is your body’s inborn or natural defense mechanism developed at the time of birth. Its primary function is to attack any pathogen that has entered the body and produce an immune response either immediately or after few hours. It also alerts adaptive immunity to be ready to fight against the invasion. Innate immunity has two lines of defense known as an external and an internal component. The external component is the first defense that prevents the entry of germs into the body. The internal component is the second line of defense that fights the pathogens after they have entered the body.
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive or acquired immunity develops throughout your life as you encounter different pathogens. It takes time to build and fight against specific pathogens. This level of immunity destroys pathogens that evade innate immunity. Adaptive immunity offers long-term protection from specific pathogens with the help of immunological memory. Acquired immunity types include active or passive immunity.
Active Immunity
Your body depends more on active immunity than passive immunity. It is formed by your own immune system as and when a pathogen enters the body. Apart from protecting against pathogens, this lasts longer in the form of immunological memory. Your body forms immunological memory that consists of lymphoid cells known as T lymphocytes (T cells) and B lymphocytes (B cells). These lymphoid cells from the memory react when the same pathogen enters the second time. Active immunity can be further classified as natural or artificial in nature.
Passive Immunity
Passive immunity is provided externally to protect against specific pathogens. It provides readymade antibodies and is given to patients who are at high risk of specific infections or to patients with immune deficiency. However, this immunity is short-lived as it doesn’t create lymphoid cells that form immunological memory. Thus, passive immunity can’t protect against the same infections and may need to be administered again.
Passive immunity can be natural or artificial in nature. Antibodies gained by newborn babies from the mother’s immune system are an example of natural passive immunity. In artificial immunity, antibodies from plants, other people, or artificially developed antibodies are introduced in a person’s blood to fight the infection. For example, artificial antibodies may be given to AIDS patients to fight the infection.
Community or Herd Immunity
Herd immunity is when people not immune to certain infections or diseases also get protected because of the people around them who are immune to a specific disease. The immune people may have developed immunity through vaccination or previous illnesses. As most people are immune, it prevents the spread of the infection thereby protecting those who are not immune. However, it should be noted that this type of immunity may not always be effective. You may need to take other necessary precautionary measures for protection.
Additional Read: How To Increase Immunity in Kids: 10 Efficient Ways
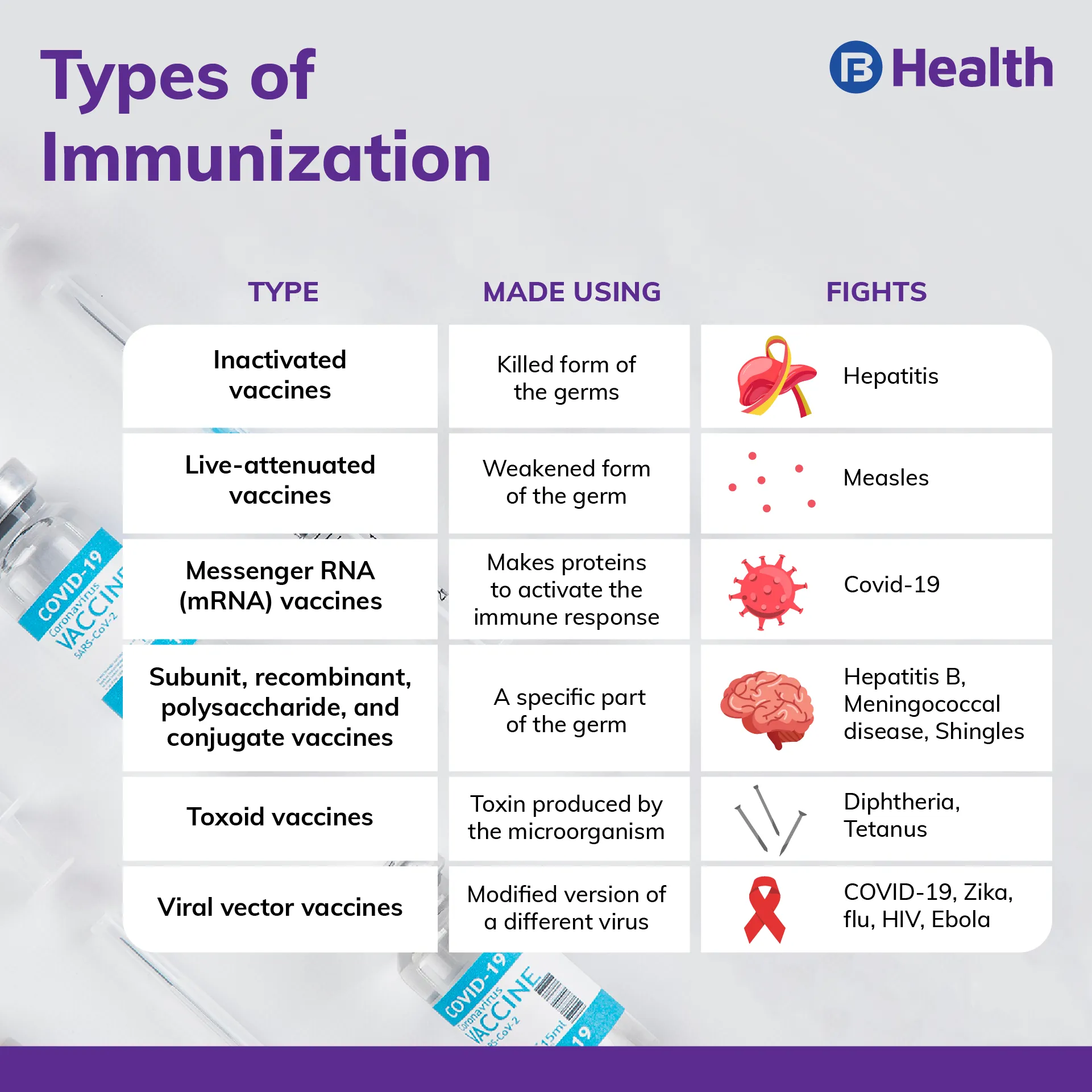
Types of Immunization
Different types of vaccines make you resistant to specific diseases by helping your immune system. Below are the various kinds of vaccines.
- Inactivated vaccines
- Live-attenuated vaccines
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines
- Subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide, and conjugate vaccines
- Toxoid vaccines
- Viral vector vaccines
Now that you know the different immunity types, remember that a strong immune system is your ticket to good health. A healthy lifestyle helps you build a strong immune system. Eat healthy, exercise, quit smoking, get adequate sleep, and maintain your weight for good health. Get regular health check-ups as part of your healthcare routine and book an online doctor consultation on Bajaj Finserv Health if you notice any signs of infection.
References
- https://www.rush.edu/news/weakened-immune-systems-during-covid-19
- https://medlineplus.gov/immunesystemanddisorders.html
- https://www.jhsph.edu/covid-19/articles/achieving-herd-immunity-with-covid19.html
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.




