Cancer | 9 min read
Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Stages, Symptoms, Prevention, Diagnose
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare type of head and neck cancer
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma affects the upper part of throat
- A nasopharyngeal mass is more common in men than in women
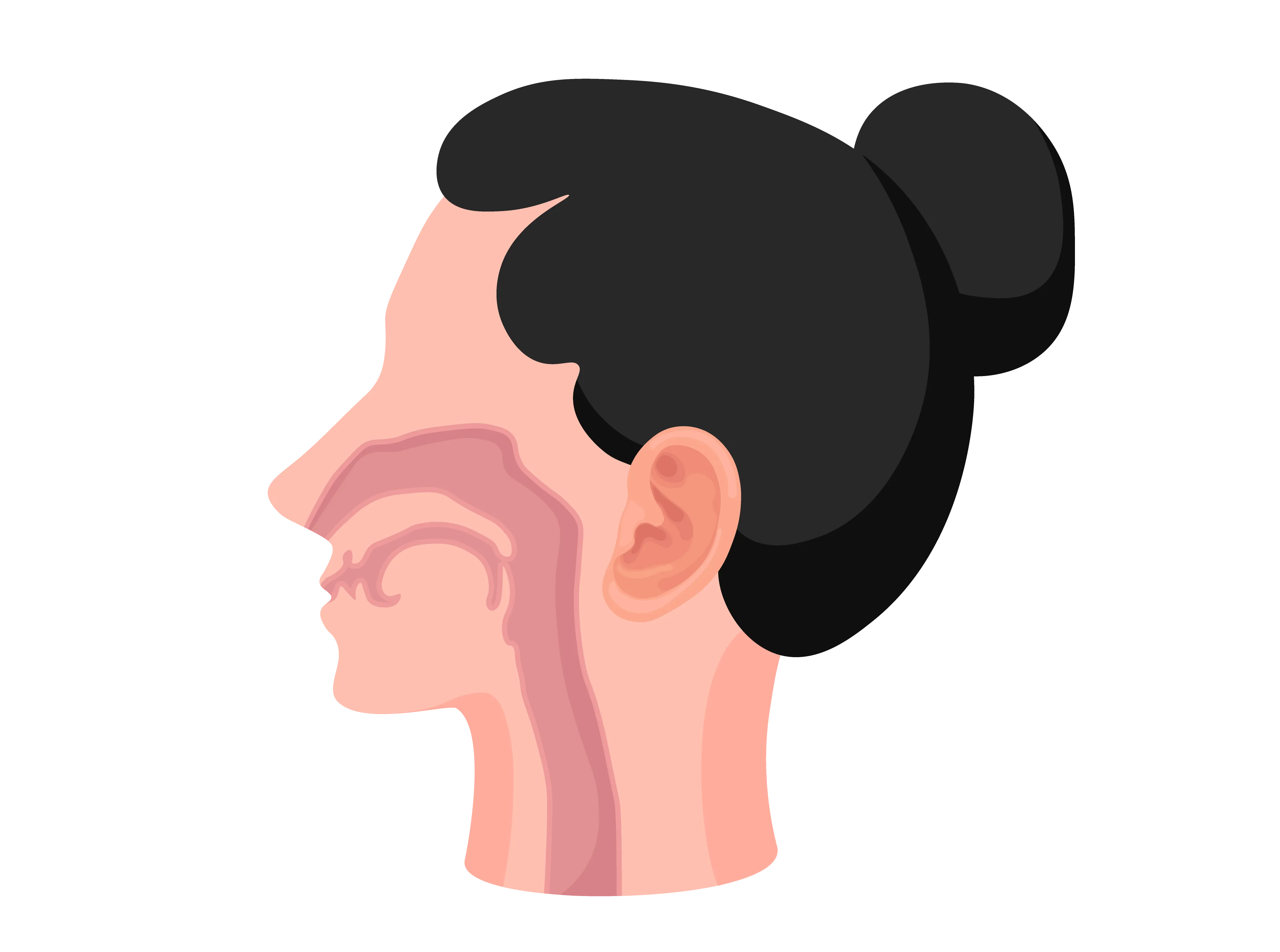
Nasopharyngeal cancer is also known as nasopharyngeal carcinoma. It is a rare type of head and neck cancer that starts in the nasopharynx. This refers to the upper part of the throat behind the nose and near the base of the skull [1]. The air you breathe flows through your nose, nasopharynx, throat, and then to your lungs. Nasopharyngeal cancer occurs when the cells at the upper part of your throat grow out of control.
Cases of this cancer are mostly found in Southeast China, some parts of North Africa, and the Middle East [2]. Nasopharyngeal cancer is more frequent in men than women and is the 23rd most common cancer around the world [3]. Although around 50% of the cases happen in people below 55 years, this cancer can occur at any age, even during childhood. Read on to know more.
Common Nasopharyngeal Cancer Causes
Although the exact cause of the cancer is not known, it is linked to several factors including:
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) [4]
Contracting this virus causes glandular fever and mononucleosis. Even though the virus is associated with nasopharyngeal cancer, not all people diagnosed with EBV develop it. Although researchers are still finding how the virus causes cancer, it may be linked to genetic material from the virus that affects the cells of the nasopharynx.
Diet rich in salt-cured fish and meat
Having such foods increases your risk of developing this cancer.
Tobacco and alcohol
Although the link between tobacco and alcohol with this cancer is not clear, heavy smoking and consumption of alcohol can increase your risk.
Age, race, and gender
Most nasopharyngeal cancer cases are diagnosed in people between the ages of 30 and 50. However, it can occur at any age. Also, people living in Southeast Asia, South China, and North Africa are at a higher risk than others. As far as gender is concerned, it is found that men are two to three times more likely than women to develop this cancer.
Occupation
Certain types of jobs can put you at risk of this cancer. People who are constantly exposed to hardwood dust or formaldehyde may be at an increased risk of developing cancer.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
People affected with HPV sometimes have an increased risk of developing nasopharyngeal cancer [5].
Family history
Having a family member with a history of this type of cancer or having certain genes related to cancer development can put you at a higher risk.

Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of this disease is difficult as they are similar to those of other less severe diseases. In most cases, people don’t experience any symptoms until the cancer reaches a serious stage. Here are some common symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer.
Lump in neck
Stuffy or blocked nose
Hoarse voice
Loss of hearing
Bleeding from the nose
Blurred or double vision
Rapid weight loss
Facial pain or numbness
Ringing in the ears
Difficulty in breathing, speaking as well as swallowing
A feeling of fullness in the ears
Stages of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
When a nasopharyngeal cancer diagnosis is made, the doctor will probably list the stage and kind of your cancer. A doctor's staging of your cancer can assist you and the other patients on your treatment team in understanding your prognosis.
The phases often depend on the size of a tumour and whether it has spread to neighbouring tissues. The phases of nasopharyngeal carcinoma are described in the following concise manner:
Stage 0:
This stage, also known as "carcinoma in situ" by medical professionals, denotes the appearance of abnormal cells in the lining of the nasopharynx. These cells are not malignant now, but they could develop into cancer
Stage 1:
Only the nasopharynx is affected by stage 1 cancer. However, it may have progressed to the oropharynx or nasal cavity
Stage 2:
The disease has progressed to one or more lymph nodes on either one or both sides of the neck in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Stage 3:
One or more lymph nodes on both sides of the neck have been affected by cancer. Cancer's spread may have also affected the oropharynx, nasal cavity, parapharyngeal space, surrounding muscles, or the bones at the base of the skull. Typically, the lymph nodes are 6 millimetres (cm) or smaller at this stage
Stage 4:
Stage 4 is divided into stage 4A and stage 4B by doctors.
In stage 4A, cancer has progressed to the hypopharynx, salivary gland in front of the ear, cranial nerves, brain, or other parts of the face. The lymph nodes might be more than 6 cm in size at this point
The lymph nodes in the lungs, armpit, or groyne are distant from the neck lymph nodes where the disease has progressed in stage 4B. Because they indicate that the disease has spread to other body areas, the final stages of nasopharyngeal cancer are typically the most severe.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
When deciding on a course of therapy for nasopharyngeal cancer, a doctor will consider several variables. These elements might consist of the following:
- The stage of the disease, mainly whether it has spread
- The size of the tumour
- Blood tests reveal the existence of EBV antibodies
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are the most often used nasopharyngeal cancer therapies.
Radiation therapy may be suggested as the only treatment for stage 1 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiation treatment and chemotherapy are frequently used to treat malignancies that are stage 2 and above.
Treatments for nasopharyngeal cancer may influence a person's quality of life. These consist of the following:
- Dry mouth exhaustion
- Loss of hearing
- Hypothyroidism swallowing issues
- It's crucial to discuss how to reduce these adverse effects with a doctor
Doctors may ask you several questions regarding your symptoms, medical history, and family history. They may also do a physical test for the diagnosis. You may be further referred to an otolaryngologist. The doctor may also feel your neck for any lumps. A nasopharyngoscopy may also be performed where flexible tube with light and camera is inserted through your mouth or nose to get a better view of the nasopharynx. With it, doctors can find any abnormal growths or bleeding. If your result is abnormal, you may be asked to get a biopsy.
Imaging tests such as chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI, and ultrasound can also help detect nasopharyngeal cancer. Your doctor may also order CBC and EBV testing for proper diagnosis. If you are diagnosed with nasopharyngeal cancer, you will be required to undergo other tests to check its spread. This process is called nasopharyngeal carcinoma staging. The cancer is staged from stage 0 to stage IV where stage 0 is the earliest stage and Stage IV is the most advanced stage.

What Is the Treatment for Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
The stage of cancer determines the specific treatment. After diagnosing you, the doctor team will review your treatment choices. Treatment options for nasopharyngeal cancer include:
Radiation treatment:
High-energy X-rays are used in this procedure to either delay or destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is frequently utilized to treat nasopharyngeal cancer since the illness is highly responsive to the treatment.
Chemotherapy:
Anti-cancer medications are used intravenously or orally. Chemotherapy is effective for malignancies that have spread to other body areas because it crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Chemoradiation:
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are frequently used to treat nasopharyngeal cancer. This may intensify the effects of radiation while increasing its adverse consequences.
Surgery:
The tumour may occasionally be removed surgically. Surgery isn't generally the primary form of therapy, though, because the nasopharynx is a challenging location to operate on. However, in rare cases, neck lymph nodes that have not responded to conventional therapies are removed surgically.
Specific pharmacological treatment:
Certain cancers can be targeted by some medications. Cetuximab injections can help those with nasopharyngeal cancer. A synthetic version of an immune system protein is called cetuximab. Most frequently, chemotherapy or radiation therapy is coupled with targeted medication therapy.
Immunotherapy:
This therapy strengthens your immune system to help find and eliminate cancerous cells. It is still primarily experimental right now.
A combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is often used to treat nasopharyngeal cancer. Doctors generally don’t suggest surgery as it becomes difficult for surgeons to access the affected area. Other treatments include:
biologic drugs
palliative therapy
targeted drug therapy
Immunotherapy is also used to strengthen your immune system in order to detect and fight cancer cells. However, it still remains experimental.
Side Effects Of Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treatment
The side effects you experience from your nasopharyngeal cancer therapy differ. The most frequent adverse effects of each form of therapy are listed below:
Radiation treatment
- Inflammation or redness of the skin
- Long-term dry mouth
- Nausea
- Tiredness
- Mouth ulcers
- Having trouble swallowing
- A bone ache
- Dental decay
- Alterations in taste
- Loss of hearing
Chemotherapy
- Tiredness
- Vomiting and nauseous
- Long-term mouth drying
- Hair fall
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Decrease in appetite
- Loss of hearing
Chemoradiation
- Tiredness
- Mouth ulcers
- Influenza-like symptoms
- Anaemia
- Vomiting and nauseous
- Hair fall
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Loss of hearing
Surgery
- Nerve harm
- Due to a fluid accumulation, swelling
Certain medication treatments
- Diarrhoea
- Liver issues
- Elevated blood pressure
- Clotting issues in the blood
- A rash or dry skin
Immunotherapy
- Skin coloration
- Influenza-like symptoms
- Headaches
- Muscle pain
- Respiration difficulty
- Nasal congestion
- Diarrhea
- Hormone alterations
- The legs swelling
- Cough
Remember that even if you receive the same treatment as someone else, you can experience distinct symptoms. It's crucial to inform your healthcare professional of any problems because side effects might differ. They may discover approaches to lessen your symptoms.
Can Nasopharyngeal Cancer Be Prevented?
Although you cannot prevent many occurrences of nasopharyngeal cancer, the following actions may help reduce your risk:
- Avoid meats and fish that have been salted
- Avoid smoking
- Don't overindulge in alcohol consumption
Although many cases of nasopharyngeal cancer cannot be prevented, it is better to avoid smoking, cut down on alcohol, and quit having salt-cured fish and meats to lower the risk. Celebrate Nasopharyngeal Cancer Awareness Month in April every year to spread awareness about nasopharyngeal mass and other types of cancer. Another way to stay healthy and avoid diseases is to take preventive steps. Consult with the top doctors and specialists on Bajaj Finserv Health. This way, you can get the best advice on nasopharyngeal carcinoma and other conditions. If you want to protect yourself from Nasopharyngeal cancer you can avail cancer insurance.
References
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/nasopharyngeal-cancer/about/what-is-nasopharyngeal-cancer.html
- https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/nasopharyngeal-cancer/statistics
- https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/nasopharyngeal-cancer-statistics/
- https://www.cdc.gov/epstein-barr/about-ebv.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25265358/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.