Cancer | 9 min read
Oral Cancer: Causes, Types, Stages and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- India contributes a third of all oral cancer cases globally
- Men over age 50 and tobacco users are at risk of developing oral cancer
- Early diagnosis of oral cancer symptoms can lead to cure
Oral cancer is one of the most common types of cancers globally, and India contributes to almost 33% of all global oral cancer cases. The high number of oral cancer cases can be attributed to a lack of awareness, unhygienic oral habits, and tobacco and alcohol consumption.
Annually, India reports approximately 77,000 oral cancer cases and 52,000 deaths due to oral cancer, making it a potent health risk to the country's population.
While early diagnosis and treatment can cure oral cancer, making it less fatal, it can have lasting effects if left untreated. To help you increase your awareness of this condition, here is a brief overview of the oral cancer symptoms, treatment, and preventive,
What is Oral Cancer?
Cancer causes a mutation in cells, making them multiply uncontrollably. These cells finally outgrow the number of healthy cells in the body and form a mass or lump called a tumor. Finally, they invade or metastasize, spreading to other healthy tissues or organs in the body.
In oral cancer, tumors and unexplained growth occur in mouthparts such as the tongue, lips, cheeks, sinuses, the base of the mouth, the pharynx, and the hard and soft palate.
Additional Read: Types of Childhood CancerTypes of Oral Cancer
Different types of Oral Cancers can happen in:Cancers of the oral include:
- Lips
- tongue
- Cheek's internal lining
- Gums
- Mouth's bottom
- Soft and hard palates
Oral cancer symptoms are frequently initially identified by your dentist. By visiting the dentist every two years, you can inform your dentist about your mouth's condition.
Oral Cancer Symptoms
Early diagnosis and treatment of the condition can provide complete relief from oral cancer. Therefore, if you notice or experience any of the following oral cancer symptoms, rush to your doctor or dentist for immediate medical diagnosis and treatment.
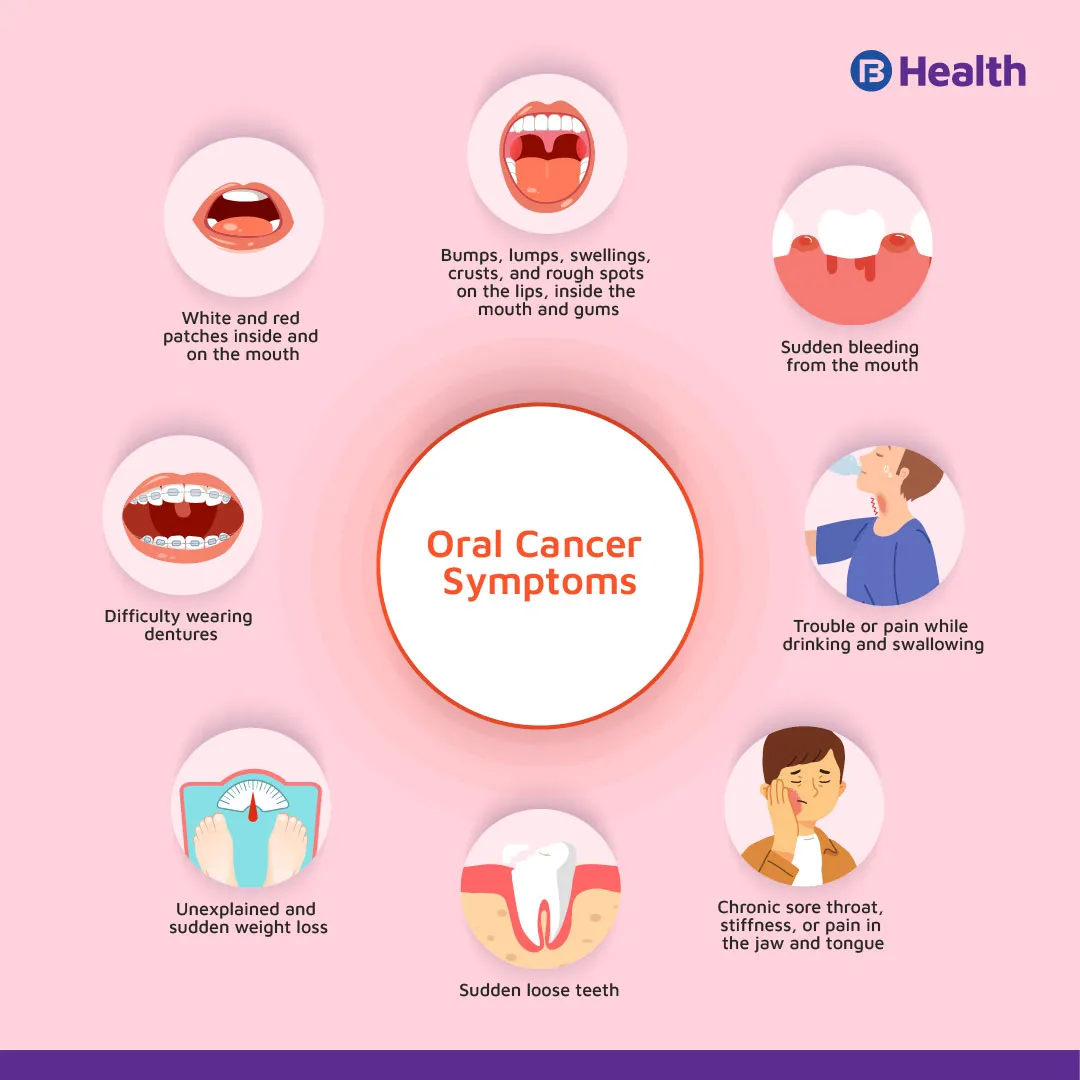
- Development of patches that are white and red in colour and feel like soft velvet inside and on the mouth
- Unexplained presence or occurrence of bumps, lumps, swellings, crusts, and rough spots on the lips, inside the mouth and gums that do not heal
- Sudden bleeding from the mouth
- Trouble or pain while drinking and swallowing
- Sudden loose teeth
- The feeling of having a lump in your throat at all times
- A sudden earache that won't subside
- Unexplained and sudden weight loss
- Sudden hoarseness or change in voice
- Difficulty wearing dentures
- Chronic sore throat, stiffness, or pain in the jaw and tongue
Some of these oral cancer symptoms can also be signs of other illnesses and conditions; therefore, there is no need to panic. However, if you experience oral cancer symptoms for long with no sign of healing, contact your dentist or family doctor at the earliest.
Oral Cancer Causes
As per research, men are twice more likely to develop oral cancer than women, especially men over the age of 50. Furthermore, compared to the West, more than 70% of oral cancer cases in India are diagnosed in the advanced stages. Therefore, it is important to take every measure possible to prevent any type of oral cancer. To this effect, here are some of the oral cancer causes and risk factors.
- Smoking tobacco, cigar, cigarettes can increase the risk of oral cancer by six times
- Individuals that use/ chew smokeless tobacco products have a 50 times greater chance of developing oral cancer
- Alcohol consumption, especially in conjunction with tobacco, increases oral cancer risk
- A family history of oral cancer can increase your likelihood of contracting oral cancer
- Overexposure to the sun and strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) can also cause different oral cancers
Oral Cancer Risk Factors
Tobacco usage is one of the largest risk factors for mouth cancer. This includes chewing tobacco, smoking pipes, cigars, and cigarette.
People who regularly use both cigarettes and alcohol are at much greater risk, especially when both are consumed in considerable amounts.
Other danger signs consist of the following:
- Infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Persistent sun exposure to the face
- A prior oral cancer diagnosis
- A history of oral or other cancers in the family
- A lowered immunological response
- Genetic disorders caused by insufficient nutrition
- Being a man
Oral cancer affects males twice as often as it does women.
Stages of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer develops in four phases.
Stage 1:
The tumour is less than 2 centimetres (cm) in diameter and has not disseminated to the lymph nodes.
Stage 2:
The tumour is 2-4 cm in size, and the lymph nodes are free of cancerous cells.
Stage 3:
Either the tumour is more than 4 cm in size and has not yet metastasized to the lymph nodes, or it is any size and has metastasized to one lymph node but not to other bodily parts.
Stage 4:
Tumors of any size that have migrated to neighbouring tissues, lymph nodes, or other areas of the body due to cancerous cells.
The National Cancer Institute reports the following five-year survival rates for cancers of the oral cavity and pharynx:
- Eighty-three per cent chances for locally contained (non-spreading) cancer
- Sixty-four per cent, when local lymph nodes have been affected by cancer
- Thirty-eight per cent, if cancer has spread to other bodily regions
Sixty per cent of persons with oral cancer will live for five years or more on average. The likelihood of survival following therapy increases with earlier diagnostic stages. In reality, stage 1 and stage 2 oral cancer patients often have a five-year overall survival rate of 70 to 90 per cent. Because of this, prompt diagnosis and treatment are even more crucial.
Recovering From Oral Cancer Treatment
Each form of treatment has a different healing process. Pain and swelling are common postoperative side effects, although small tiny tumor removal is typically free of long-term complications.
If bigger tumours are removed, you might not be able to chew, swallow, or communicate as effectively as you did before the operation. To replace the facial bones and tissues that were lost during surgery, you could also require reconstructive surgery.
The body may suffer as a result of radiation therapy. Radiation can have a number of negative impacts, such as:
- Throat or mouth sores
- Decrease of salivary gland function and dry mouth
- Decayed teeth
- Vomit and nausea
- Bleeding or sore gums
- Mouth and skin infections
- Jaw aches and stiffness
- Issues with wearing dentures
- Fatigue
- A modification to your sense of taste and smell
- Alterations in your skin, such as burning and dryness
- Loss of weight
- Thyroid alterations
Chemotherapy medications can be hazardous to non-cancerous cells that are dividing quickly. There may be negative impacts like:
- Hair fall
- Gums and mouth ache
- Mouth bleeding
- Extreme anemia
- Weakness
- Lack of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Lip and mouth sores
- Hand and feet numbness
Targeted therapy typically results in limited recovery. The following are possible adverse effects of this therapy:
- Fever
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- An allergy response
- Rashes on the skin
Even though these medicines can have adverse effects, they are frequently vital to defeating cancer. Your doctor will go through the side effects and assist you in weighing the benefits and drawbacks of the various treatments.
Prevention Tips For Oral Cancer
You may actively participate in avoiding oral cancer if you want to. The following advice can help you avoid oral cancer:
- Try giving up or reducing your tobacco usage if you smoke, chew, or use a water pipe. Ask your doctor about programmes to help you quit smoking.
- If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Don't forget your sunscreen. On your face, apply sunblock and UV-AB-blocking sunscreen.
- Get a human papillomavirus vaccine.
- Consume a balanced diet.
- Have routine dental exams. Every three years, between the ages of 20 and 40, oral cancer screenings are recommended, and beyond the age of 40, yearly checkups.
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
On spotting any signs and symptoms of oral cancer, the doctor or dentist will first conduct a thorough physical examination of the mouth to ensure that it is not caused by any other health condition. Once this is eliminated, the doctor may choose to conduct a biopsy. In this procedure, a part of the infected tissue is removed and examined under a microscope. The doctor may either opt for brush or tissue biopsy. Brush biopsy involves brushing cells from the infected tissues onto a slide, while tissue biopsy warrants removing a small, infected piece of the tissue for further examination.
Additionally, for further clarity, the doctor can administer the following diagnostic tests.
CT scan
To check for the presence of cancerous tumours in the throat, mouth, lungs and neck
X-rays
To detect the presence of cancer in the chest, jaw, and lungs
Endoscopy
This is done to detect the presence of cancerous tumours in the throat, nasal passage, windpipe, and trachea
MRI scan
This is done to assess the stage of the cancer and detect the clear presence of the cancer in the neck and head
PET scan
This diagnostic test is done to check how far cancer has spread to other organs and the lymph nodes
Using these tests, the doctor determines the presence of cancers, evaluates its stage and spread, and decides an appropriate treatment plan.
Oral Cancer Treatment
The treatment plan for oral cancer differs as per the location and cancer stage. Read on to know more about oral cancer treatment options.
Surgery
If oral cancer is diagnosed early, then surgery is the quickest and easiest treatment option. Here, infected, cancerous tissues are surgically removed to stop them from metastasizing further. Furthermore, as a precaution, surrounding tissues can be removed as well
Chemotherapy
This oral cancer treatment involves using drugs administered orally or via an intravenous line (IV) to kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy
Here, a high-energy beam is used to kill cancer cells by simply aiming it at the affected area. A combination of both chemo and radiation therapy is used to treat patients with advanced-stage oral cancer
Targeted therapy
This is a relatively new treatment option, still undergoing clinical trials. Here, the administered drugs bind with the cancerous cells and tissues and hinder their growth and spread
While oral cancer is not as fatal as other types of cancers and is completely curable if diagnosed early. Oral cancer treatment can have long-lasting effects on a person's overall health and lifestyle. Therefore, you must take every precaution possible to prevent oral cancer. Some basic precautions to prevent oral cancer include not smoking, drinking, or using tobacco and tobacco products. Likewise, take precautions while venturing out in the sun and maintain a healthy lifestyle by having a balanced diet and exercising regularly. Additionally, visit your dentist regularly to be on top of your oral health.
Additional Read: Breast Cancer SymptomsConclusion
To find a dentist with ease as well as to get treatment for oral cancer, use the Bajaj Finserv Health app. This digital tool helps you find the right specialists in seconds using filters related to your preferred area, consult timings and more. You can also get access to health plans and health cards here that offer you deals and discounts at reputed partner clinics to make healthcare more affordable. To explore all this and more, download the app for free today!
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7515567/
- http://www.idph.state.il.us/cancer/factsheets/oralcancer.htm
- https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh293/193-198.pdf
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.