Cancer | 8 min read
Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Types, Treatment and Risk Factor
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Prostate cancer is the 2nd most frequent malignant cancer among men
- Some types of prostate cancer are harmless and may not need treatment
- Prostate cancer causes include risk factors like old age and gene mutation
When it comes to the most frequent malignant cancers among men worldwide, prostate cancer, meaning abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland, holds the second position, just after lung cancer [1]. The prostate gland in men is located just below the bladder. Note that while some types of prostate cancers are harmless and require no or minimal treatment, a few types are malignant in nature and may require aggressive treatment.
To know important facts regarding prostate cancer causes, types, and treatment methods, read on.
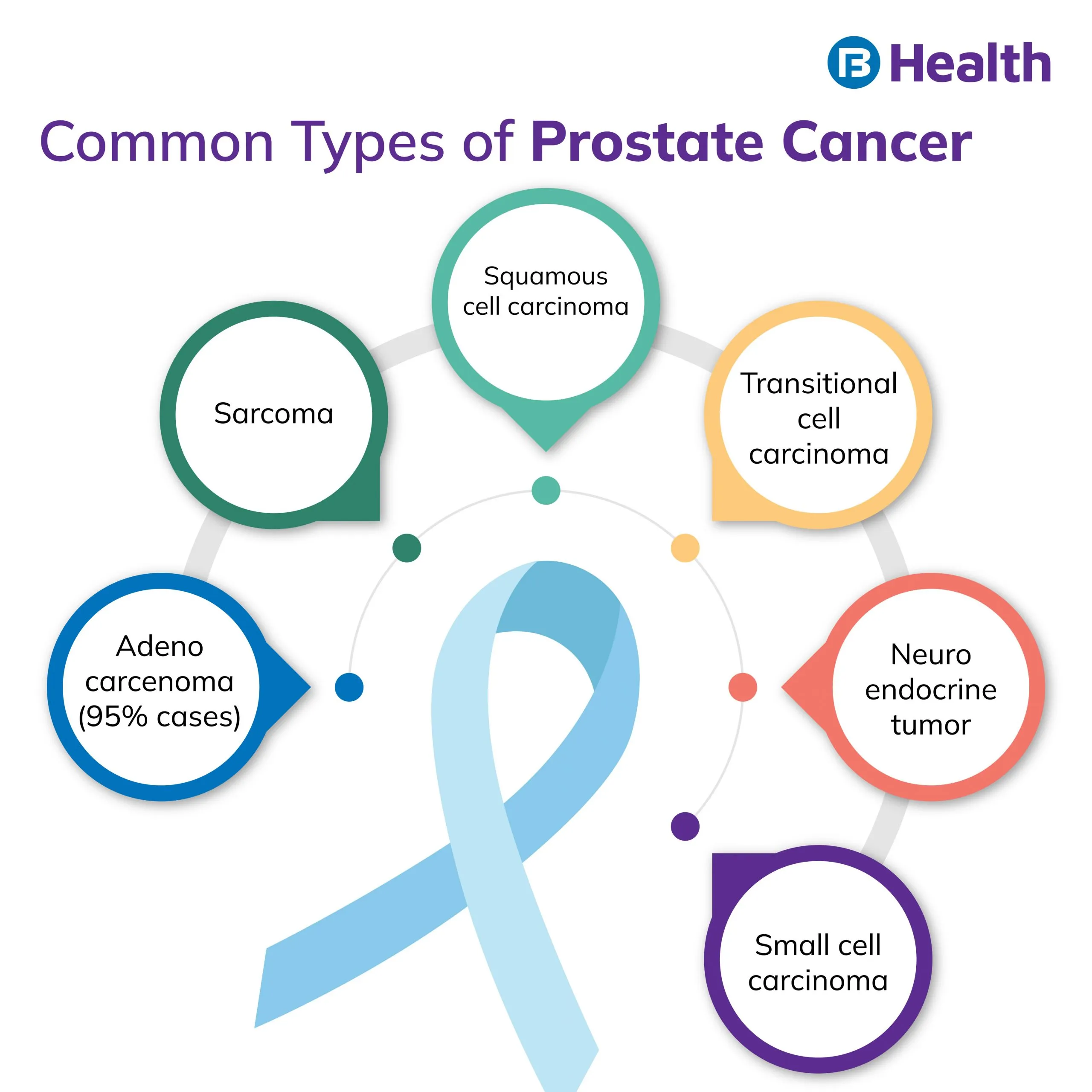
Types of Prostate Cancer
There are several different types of prostate cancer. The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which means that it starts in the glandular tissue of the prostate, which is a gland located in the pelvis. This type usually occurs when there are high testosterone levels or male hormones. Although, there are several more types of cancer included in it. Types of prostate cancer include the following. They most often start in an abnormal cell called carcinoma, which is made up of cells that have become abnormal and are growing out of control.
Lung cancer
A type of cancer that begins in the lining of your lungs.
Pancreatic cancer
A type of cancer that begins in the lining of your pancreas.
Kidney cancer
A type of cancer that begins in the lining or tissue of your kidneys.
Sarcomas
Sarcomas are cancers that can occur anywhere in the body where there is soft tissue, including bone, cartilage, fat tissue, tendon, and muscle.
Prostate Cancer Causes and Risk Factors
A variety of distinct risk factors can cause prostate cancer. Some of them consist of obesity, smoking, drinking, being exposed to chemicals like the herbicide Agent Orange, prostate inflammation, and sexually transmitted diseases.
Every type of cancer has its own set of risk factors. Multiple studies to find potential causes have found the following as the risk factors.
Diet:A diet that is high in fat and low in fibre content can increase your risk of getting prostate cancerEthnicity
As per data, It is more common among Caribbean men of American origin and African-American men. It is a rarer occurrence among men of Hispanic, Latino, or Asian American origin. However, the exact reasons for this remain unclear.
Family Background
In some families, there are instances of cancer among men across generations. However, in most cases of prostate cancer, family history has no role to play.
Gene Mutation
In rare cases, prostate cancer causes are linked to inherited changes in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes. Inherited gene mutations also lead to Lynch syndrome, which can be another cause of prostate cancer.
Old Age
This cancer is less common among men aged below 40. However, once they reach 50 years, the probability of having this cancer increases significantly. On average, 6 out of 10 cases of prostate cancer cases are linked to men aged over 65.
Habitat
Major cases are found on the Caribbean islands and in the north-western parts of Australia and Europe, and North America. In continents like Asia, Central and South America, and Africa, there is a lesser number of instances. However, the exact reasons behind this dissimilarity are not clear.
Apart from these, there are a few minor risk factors for prostate cancer whose exact effects remain unclear. Here’s a look at them:
- Exposure to chemicals
- Dairy and calcium diet
- Obesity
- Vasectomy
- Tobacco addiction
- STIs
- Inflammation of the prostate gland (prostatitis)
Common Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Its symptoms can be hard to recognize at first, so it's important to watch for them. Prostate cancer is a disease that mostly affects men, and it's the second leading cause of cancer death among men in the United States. The symptoms of prostate cancer can vary from person to person. Some people may have no signs or symptoms at all, while others may experience the following symptoms:
Urinary Problems
You may notice that you're having trouble getting or maintaining an erection or getting a strong stream of urine. You might also notice blood in your urine or a change in how often you pass urine.
Sexual Problems
You may notice an inability to achieve orgasm or ejaculation, pain during sex, or difficulty reaching an orgasm.
Pain and Numbness
You may notice pain in your back, hips, thighs, or testicles, numbness in your hands or feet, or tingling sensations all over your body.
Its primary stages may not show any signs and symptoms. Once it reaches an advanced stage, you may experience the following:
- Chronic pain in bones
- Rapid weight loss
- Difficulty urinating
- Lack of trust in the flow of urine
- Presence of blood in semen and urine
- Frequent night-time urination or nocturia
- Erectile dysfunction
Diagnose Prostate Cancer
Oncologists diagnose prostate cancer in two steps. At first, they perform the following screening tests to understand whether the results indicate significant signs of this cancer:
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test
- Digital rectal exam (DRE)
In case doctors detect an abnormality in these tests, they may further perform the following tests:
- MRI
- Ultrasound
- Prostate biopsy
Early Detection of Prostate Cancer
Early detection of prostate cancer is important because it provides a chance to treat the disease before it causes any harm. If you have symptoms of prostate cancer, you should see your doctor as soon as possible so that you can start treatment. Here are a few methods of detecting cancer in its early stage.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein in the prostate gland that helps detect cancer. PSA levels increase when there is an abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. PSA levels can be measured at any time after men notice changes in their symptoms. Men should get their tests done until they know whether or not they have cancer. If you are going to have a biopsy, it is important to know your PSA level because it will help determine how promptly the biopsy should be done.Digital rectal exam (DRE)
A digital rectal exam (DRE) is a simple, painless procedure that can help detect prostate cancer early. It involves inserting a gloved finger into your anus and gently pressing on the prostate gland. If you have any symptoms that suggest you may have prostate cancer, your doctor may recommend repeating DREs every five years.
Prostate Imaging
If you have had a prostate exam and have not felt any changes in your prostate, then it is unlikely that you have cancer. However, if you have noticed any changes in the size or shape of your prostate or if you have experienced any pain during urination, seek immediate medical attention.
Prostate biopsy
Prostate biopsy is a type of medical examination that involves removing tissue from the prostate gland. It is used to detect cancerous tumours or other abnormalities in the prostate. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Prostate Cancer Treatment Methods
Your doctor will create a suitable treatment plan based on your age, health, and cancer stage.
Non-aggressive
Non-aggressive prostate cancer is a condition that refers to the use of non-invasive treatments for prostate cancer. These treatments don't involve surgery.
Non-aggressive prostate cancer may be treated with radiation therapy, which involves directing high-energy rays at specific body areas. Radiation therapy can often be used alone or together with other approaches, such as hormone therapy or surgery. This form of treatment is generally less invasive than surgical approaches, but it doesn't always lead to the complete removal of cancerous tissue in all patients.
If non-aggressive prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland, it may be treated with hormone therapy or chemotherapy. Hormone therapy and chemotherapy are typically used together to treat this type of aggressive cancer more effectively than either treatment alone.
Aggressive
More aggressive cancers may be treated by doctors using different techniques, such as:
- Surgery
- Cryotherapy
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Immunotherapy
- Hormone treatment
Your bones may have been affected by bone metastasis if your cancer is particularly aggressive and has spread. The aforementioned treatments and others may be applied to bone metastases.
Once it is diagnosed, doctors decide on the treatment to be followed based on the degree of malignancy. Here are the usual ways to treat:
- Active surveillance in low-risk cases
- Heating of freezing affected prostate tissue
- Radiotherapy for cancer
- Prostate removal surgery
- Therapy with targeted drug
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- Immunotherapy
Prostate Cancer Prevention
You have no control over some of the risk factors for prostate cancer, including age and family history. Others, though, you could handle:
- Diet: It is often linked to diet, with research showing that a high fat and low-fiber diet can increase the risk of prostate cancer. The American Cancer Society recommends eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. In addition to decreasing your risk of prostate cancer, it also reduces your risk of developing other types of cancer.
Though 100% cure is not possible in the case of any cancer, you can successfully manage the symptoms if it is diagnosed at a primary stage.
Note that it is not possible to prevent, but you can take some precautionary measures to lower the risks. Limit your calcium and dairy intake, watch out for obesity, and remain physically agile to reduce the chances of prostate cancer. To know facts regarding other types of cancer, you can observe World Cancer Day on February 4 every year and get all the information you want through the various events held. If you are experiencing any signs related to this or have any other health concerns, get a doctor consultation on Bajaj Finserv Health and clarify all your doubts remotely. Talk with the top specialists in your locality and follow their advice to lead a life stress-free!
References
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.