Hypertension | 4 min read
Pulmonary Hypertension: The Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- PAH is a lung disorder that can be fatal if left untreated
- The normal pulmonary artery pressure is 8-20 mm Hg at rest
- Fatigue is one of the most common pulmonary hypertension symptoms
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening lung disorder. It is another name for high blood pressure in your lung arteries and differs from regular hypertension. You may know that lung arteries or pulmonary arteries carry blood from heart to your lungs. Pulmonary hypertension occurs when your pulmonary arteries become narrow, which makes blood flow through the vessels difficult. As a result, it becomes hard for the heart to pump blood, and it starts working harder. This can eventually lead to heart failure, which can be fatal. Though this disease is more common among women than in men [1], it is important for all to watch out for it.
Normal pulmonary artery pressure should be 8-20 mm Hg at rest. Pulmonary hypertension is diagnosed if the pulmonary artery pressure is above 25 mm Hg at rest [2]. Read on to know what indicates PAH, its causes, and how to treat arterial hypertension in your lungs.
Additional Read: Idiopathic Intracranial HypertensionPulmonary Hypertension Symptoms
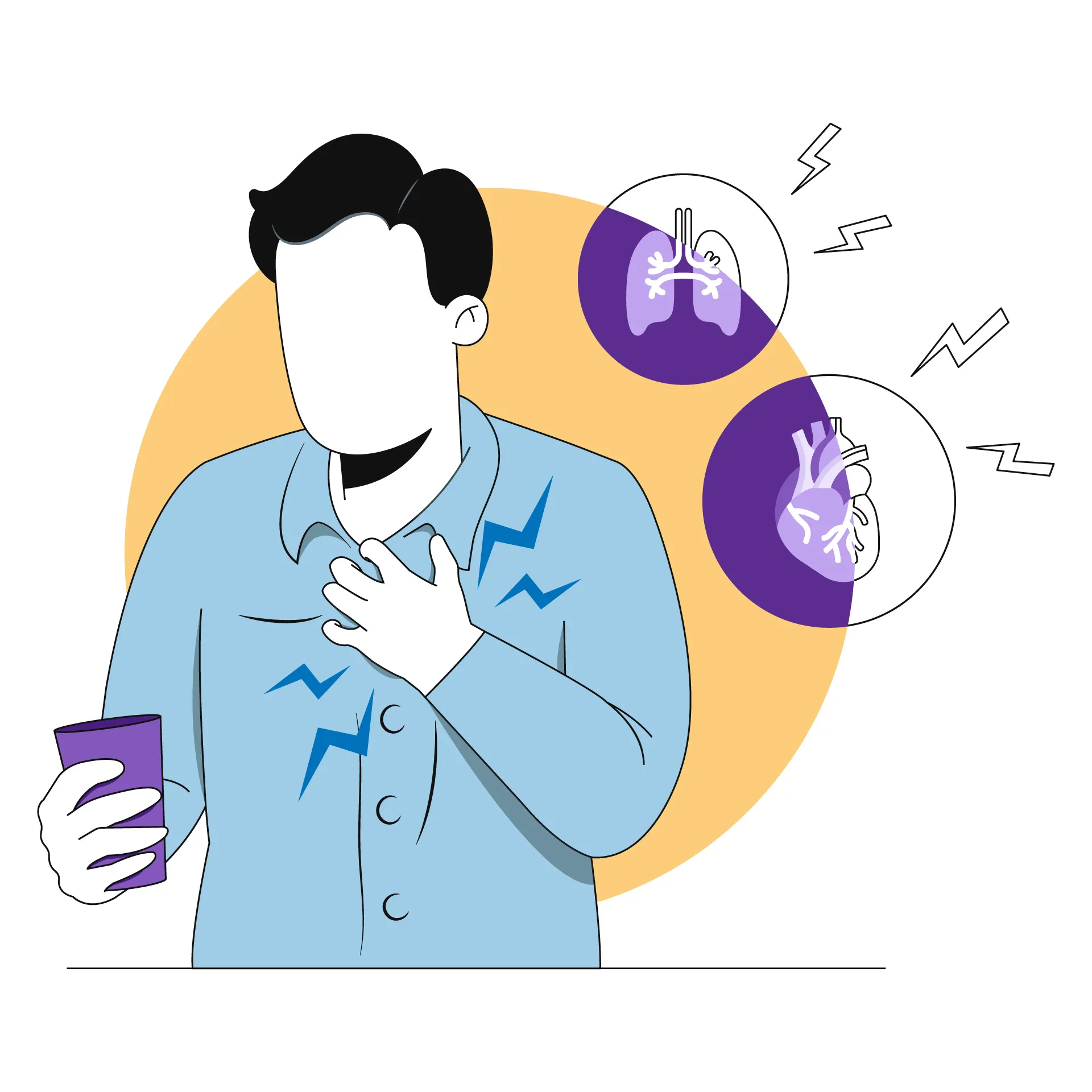
A few common PAH symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Fainting
- Chest pain
- Racing pulse
- Bluish lips or skin
- Dizziness or passing out
- Swelling in the ankles, abdomen, or legs
- Heart palpitation or irregular heartbeat
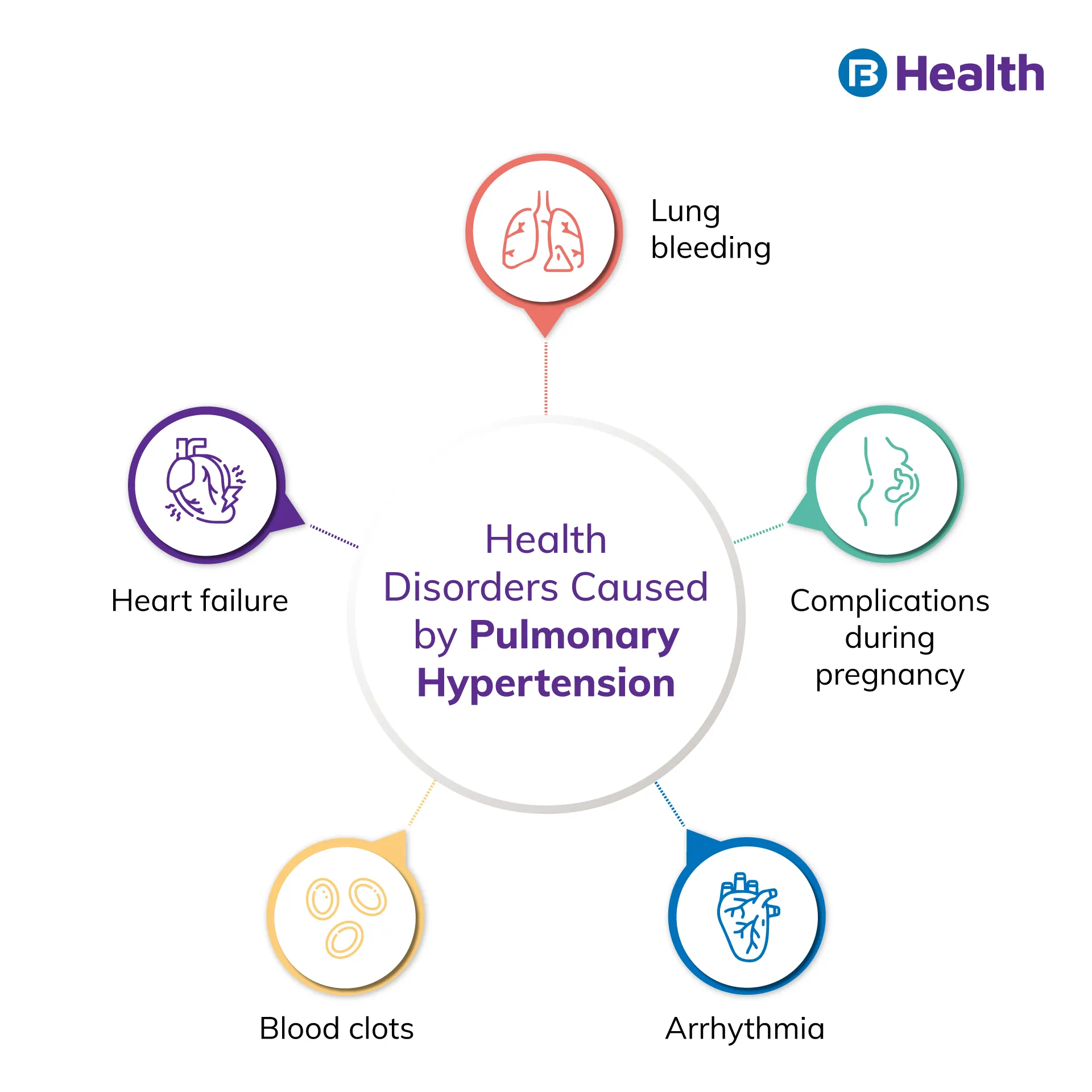
Pulmonary Hypertension Causes
Here are the common environmental and habitual causes of PAH.
- Genes or family history
- Asbestos exposure
- Drug abuse such as cocaine
- Living at a high altitude
- Consumption of specific weight-loss medicines or drugs
- Intake of drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for treating anxiety and depression
Certain health conditions can also increase your risk for this disease. They include:
- Congenital or acquired heart disease
- Liver disease
- Lung disease
- Sleep apnea
- Blood-clotting disorders
- HIV
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Certain autoimmune conditions
Stages of PAH
Based on the severity of the disease, PAH is classified into 4 stages.
- Class I: PAH with no symptoms during activity.
- Class II: No symptoms when you are resting, but you may experience shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain during activity.
- Class III: No symptoms during rest, whereas symptoms occur during activity.
- Class IV: You may experience symptoms both during rest and physical activity.
Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosis
If you have any PAH symptoms such as shortness of breath, doctors may enquire about your medical history. They may also order the following tests to make a proper diagnosis.
- CT scan
- Chest X-ray
- Ventilation-perfusion scan (V/Q scan)
- Exercise testing
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
Pulmonary Hypertension Treatment
PAH treatment is based on the factors pertaining to you. For instance, if you are at risk of developing blood clots that may cause hypertension, you will be prescribed blood thinners or other medications accordingly.
Here is a look at the different ways doctors treat this disease.
Medication
Your doctor may prescribe you diuretics, potassium, anticoagulants, inotropic agents, bosentan, and IV drugs.
Dietary Changes
Your doctor may also advise you to make changes in your diet to control or manage PAH. Eat fruits and vegetables high in nutrients such as bananas, oranges, peanuts, and broccoli. Maintain your weight by limiting the consumption of unhealthy foods. When you shop, look for foods low in sodium. Avoid junk food such as smoked or canned meat products.
Lifestyle Changes
Quit unhealthy habits such as cigarette smoking and chewing tobacco. Avoid excessive consumption of alcohol and stay physically active to maintain or lose weight. Consult with doctors and take preventive measures such as annual check-ups to stay healthy.
Surgery and other Procedures
Surgical therapies are also done to treat severe PAH especially if there are blood clots that affect blood flow and lung functions. As part of medical therapy, doctors may suggest pulmonary thromboendarterectomy, lung and heart transplantation.
Although PAH is not curable, treatments can help ease symptoms and make your life better. Getting the best medical advice is equally important. Book an online doctor appointment on Bajaj Finserv Health and consult with top health professionals or specialists for best remedies.
References
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6530-pulmonary-hypertension-ph
- https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/the-facts-about-high-blood-pressure/pulmonary-hypertension-high-blood-pressure-in-the-heart-to-lung-system
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.