Thyroid | 11 min read
Thyroid Cancer: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factor
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Thyroid cancer is a benign disease as it has a survival rate of 98%
- Lump, hoarseness, pain, cough are common thyroid cancer symptoms
- Radiotherapy & chemotherapy fall among thyroid cancer treatments
The thyroid gland is a part of your endocrine system. It is a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of your neck. The thyroid gland is responsible for producing hormones that help regulate metabolism. Thyroid hormones also control your blood pressure, body temperature, and heart rate. Thyroid cancer is the cancer that affects this gland.This includes knowing thyroid cancer symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and causes.
Thyroid cancer is common after the age of 30 and affects women thrice as much as men. It is a highly treatable form of cancer and has a survival rate of 98% if diagnosed at an early stage [1].
For timely diagnosis and best treatment options, it is important to understand different aspects of thyroid cancer. Read on to know more.
What Is Thyroid Cancer?
Thyroid cancer begins in the thyroid, a tiny, butterfly-shaped gland that sits at the bottom of your neck. This gland secretes the hormones that regulate your metabolism. Thyroid hormones help manage the temperature in the body, heart rate and blood pressure. Thyroid cancer is a kind of endocrine cancer which is generally very treatable and has a high cure rate.
Additional Read: This World Cancer DayTypes Of Thyroid Cancer
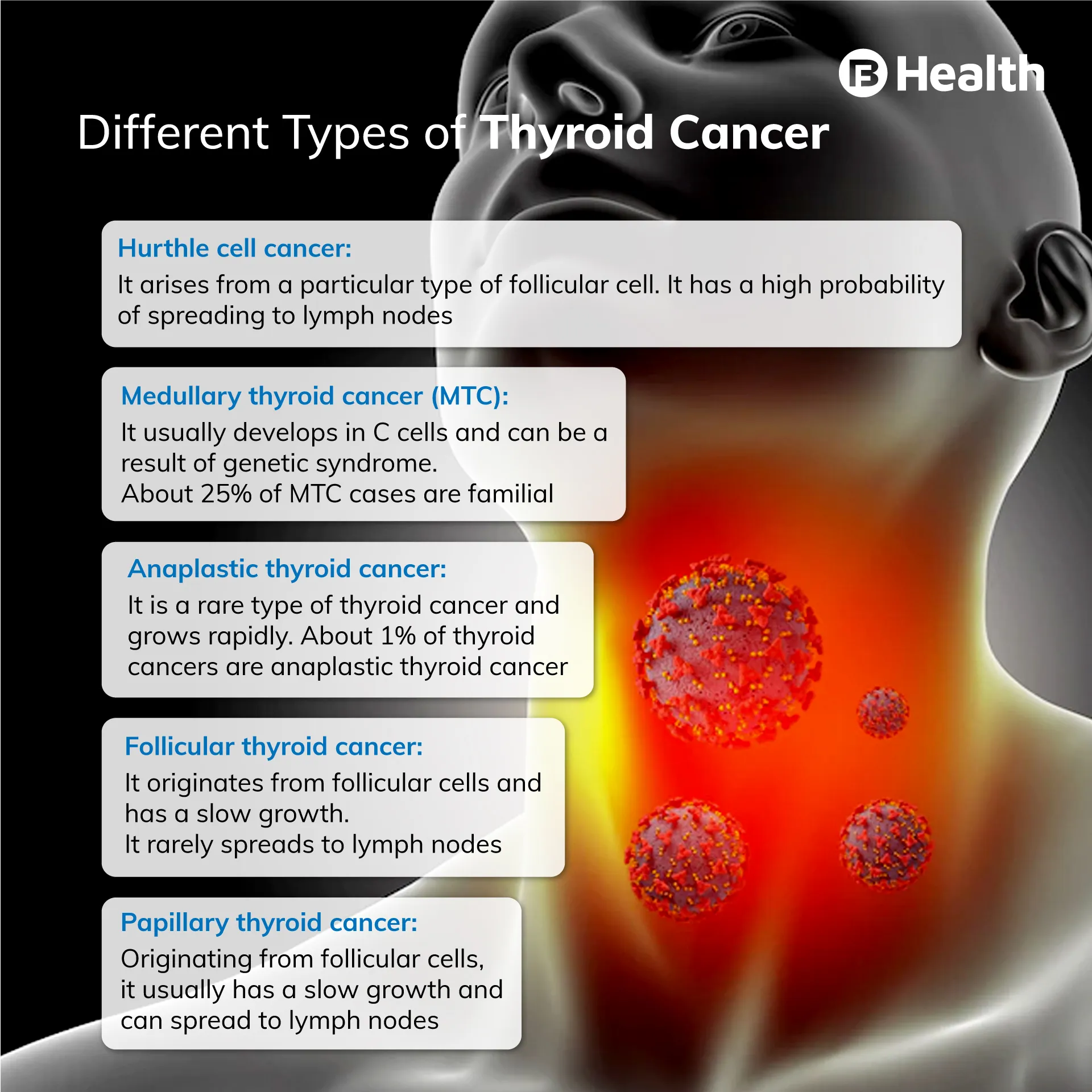
Researchers have identified four primary categories of thyroid cancer:
Papillary thyroid cancer:
This is the most prevalent type of thyroid cancer. Up to 80% of thyroid cancer cases are of this type. Even though it usually spreads slowly, it commonly spreads to the lymph nodes present in the neck. Yet, the prospects for a complete recovery are high [1]
Follicular thyroid cancer:
Besides spreading into the blood vessels more easily, this type of thyroid cancer can also spread into the lymph nodes
Medullary cancer:
4% of thyroid cancer cases are reported to have medullary cancer. [2] There is a good chance of discovering it early as it generates calcitonin, a hormone that doctors look for in the results of blood tests
Anaplastic thyroid cancer:
The most dangerous type of thyroid cancer is Anaplastic thyroid cancer, which spreads quickly to other body areas. It is rare and the most challenging to treat
Stages Of Thyroid Cancer
Medical professionals use a staging system to ascertain whether and to what extent thyroid cancer has spread. The lymph nodes and nearby structures are typically the first places where thyroid cancer cells spread when they metastasize. The malignancy could then spread to other lymph nodes, organs, or bones.
The stages of thyroid carcinoma vary from one (I) to 4. (IV). Simply put, the bigger the number, further the cancer has spread. Please speak with your healthcare professional to understand more about cancer staging and how it fits your individual diagnosis.
What Factors Lead To Thyroid Cancer?
Doctors are not sure why certain cells turn cancerous and attack the thyroid. A number of elements, including radiation exposure, a low-iodine diet, and defective genes, can raise the risk. Additional risk factors are as follows:
- Thyroid enlargement (goitre)
- Thyroid cancer or thyroid disease in the family history
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland)
- Endocrine illnesses are caused by gene mutations (changes). Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A(MEN2A), and type 2B (MEN2B) syndrome are examples
- Low iodine consumption
- Obesity
- Radiation therapy for cancer of the head and neck, particularly in childhood
- Radiation exposure from power plant accidents or nuclear weapons
Thyroid cancer develops when your thyroid cells experience a mutation. This allows the cells to multiply and grow at a rapid pace. These cells also lose their ability to die and start accumulating. This accumulation of abnormal cells leads to formation of tumor. The abnormal thyroid cells can invade tissues nearby and spread to other body parts. This spread is also known as metastasizing.
Other than this, there are also certain risk factors than can be its causes.
Thyroid Cancer Risk Factors
The risk factors of thyroid cancer can be mainly classified into 2 categories. Ones that you can control and ones that you cannot control.
- Controllable thyroid cancer risk factors
- Diet and weight
Having an adequate iodine intake from your diet is essential. A high or low intake may increase your risk of follicular or papillary thyroid cancer.
Your weight also plays a role in determining your risk of thyroid cancer. People with a higher BMI have a higher risk of this condition, and as the BMI increases, the risk does too. [2]
- Radiation
Radiation is one of the known thyroid cancer risk factors. The sources of such radiation include cancer treatments, and exposure to nuclear weapons or power plant accidents.
- Non-controllable thyroid cancer risk factors
- Age and gender
Women are three times more likely to have thyroid cancer diagnosis than men. Other than this, women are also at risk from an earlier age. For women, the risk peaks in their 40s-50s and for men it usually peaks when they are in their 60s-70s.
- Hereditary conditions and family history
There are some cases where thyroid cancer is a result of inherited conditions. These may include Medullary Thyroid Cancer, familial adenocarcinoma polyposis, or Cowden’s syndrome. If you have a first-degree relative, you may be at a higher risk of thyroid cancer.
Thyroid Cancer Warning Signs
You or a healthcare provider may feel a thyroid nodule, which is a bump or enlargement in your neck. If there is a thyroid nodule, don't become frightened. Nodules are often benign (not cancer). Just around three out of every twenty thyroid nodules are found to be cancerous (malignant).
Other symptoms of thyroid cancer include:
- Breathing or swallowing difficulties
- Voice loss (hoarseness)
- Neck lymph nodes that are swollen
Common Thyroid Cancer Symptoms
Here are some common thyroid cancer symptoms.
- Lump or swelling in your neck
- Pain going from the front of your neck to your ears
- Trouble swallowing or breathing
- Persistent hoarseness and voice changes
- Cough that is not related to cold
What Is The Procedure For Diagnosing Thyroid Cancer?
The doctor might suggest one or more of the following tests for those who have a thyroid nodule that is enlarged or other symptoms of thyroid cancer:
Blood test:
A thyroid blood test evaluates levels of hormones and assesses if your thyroid is operating appropriately
Biopsy:
Your healthcare professional takes cells from your thyroid in a fine-needle aspiration biopsy to check for cancer cells. If cancer cells have progressed to lymph nodes, a sentinel node biopsy could be used to determine it. Ultrasound technologies used by your provider may guide these biopsies
Radioiodine scan:
This scan can find thyroid cancer and establish whether it has spread. You take a tablet that contains a small quantity of radioactive iodine (radio iodine). The thyroid gland absorbs iodine over a few hours. A specific gadget is used by the healthcare professional to determine the quantity of radiation present in the gland. Further testing is required to confirm the existence of cancer in areas with lower radioactivity
Imaging scans:
Radioactive iodine, computed tomography (CT), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans can identify thyroid cancer and cancer spread
If you have any of the above thyroid cancer symptoms, doctors may advise one or more of the following tests. These tests will help them reach an accurate thyroid cancer diagnosis.
- Blood test
- Imaging scan
- Radioiodine scan
- Biopsy
Five Treatments For Thyroid Cancer
Treatment will be determined by the type of cancer, the tumour size, and whether or not it has spread or metastasized.
Surgery
- The preferred course of treatment for malignant tumours ranging from 1 to 4 cm involves partial or complete thyroid removal. Doctors may remove any problematic lymph nodes as well
- The surgery may impact your body's ability to generate thyroid hormones. If so, thyroid hormones can be replaced with oral supplements
- Following surgery, a laryngoscopy might be done to check if your vocal cords are functioning properly
Radioiodine treatment
- The majority of the body's iodine is absorbed by the thyroid gland. Doctors may employ that thyroid function to destroy cancer cells by administering radioactive iodine
- After surgery, doctors may employ radioiodine therapy to remove any remaining thyroid tissue or to treat thyroid cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes
External beam radiation therapy
Cancer cells can be eliminated by external radiation waves directed at the thyroid gland. This kind of treatment is most often used by doctors for anaplastic and medullary thyroid malignancies.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer-fighting drug that is injected into the vein or taken orally.
Targeted drug therapy
- Scientists have created newer medications that can tackle the alterations inside cells that lead them to become malignant
- These drugs are also called kinase inhibitors. These may assist in preventing protein kinase from directing the growth of other cells. These medications can also prevent tumours from establishing new blood vessels required for their growth
- For people with anaplastic thyroid cancer, doctors may combine this with radiation therapy
Management of thyroid cancer depends on the type and size of the tumor. Common thyroid cancer treatments include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgery
- Radioiodine therapy
- Hormone therapy
What Are Some Complications?
Most cases of thyroid cancer are treatable, but in rare cases there may be complications. Some possible thyroid cancer complications are
- Hoarseness or injury to your voice box after surgery
- Cancer getting spread to other body parts such as lungs or bones
- Accidental removal of parathyroid gland resulting in a low calcium level
- A condition where you need to take thyroid hormone replacement therapy for the rest of your life
Tips For Preventing Thyroid Cancer
It is challenging to prevent thyroid cancer since the cause of many cases is unknown. However, if you are aware of your potential risk for thyroid cancer, you might be able to follow these recommendations:
Preventative (prophylactic) surgery: Genetic testing can reveal whether you have a gene mutation that raises your risk of developing multiple endocrine neoplasias or medullary thyroid cancer. If you possess the faulty gene, you may opt for a preventive (prophylactic) surgery to remove the thyroid gland before cancer arises.Potassium iodide: If you've been exposed to radiation from a nuclear disaster, like the 2011 Fukushima, Japan incident, consuming potassium iodide within 24 hours after exposure can reduce your risk of developing thyroid cancer in the future. Your thyroid gland is prevented from receiving too much radioiodine by potassium iodide. As a result, the gland stays healthy.Changing or avoiding the controllable risk factors is one the best ways for its prevention. Make sure you adapt to the following.
- Consume a healthy diet to build immunity
- Maintain an active lifestyle
- Go for regular preventive health check-ups
Impacts Of The Treatment For Thyroid Cancer
Like all medical treatments, thyroid cancer treatment also has potential side effects. Here are various complications one should be mindful of if undergoing treatment:
Thyroid Surgery Risks
Among the dangers of thyroid surgery are the following:
Laryngeal nerve damage: The nerve may be shocked, or one voice cord may not move like the other. This issue affects about 5% of people momentarily and 1% permanently. Vocal rehabilitation techniques are available, and an ENT professional can help the patient with this processHypoparathyroidism: Surgeons sometimes remove one or more of the parathyroid glands, which are four microscopic glands found near the rear of the thyroid that regulates calcium levels. There is a 10% chance of parathyroid problems in patients undergoing thyroid surgery through a central neck incisionVagus nerve issues: According to a doctor, lateral neck incisions run the danger of impacting the vagus nerve. Due to the fact that the laryngeal nerve starts near the vagus nerve, this may have an impact on the tongue, shoulder, or voiceDysfunction of the thyroid: You will most likely need to take tablets your whole life after surgery to replenish thyroid hormones lost. In addition, if the parathyroid glands are removed, you might have to take vitamin D and calcium supplementsThyroid Hormone Therapy Adverse Effects
The thyroid hormone pills themselves normally do not have any adverse effects, yet it may take some time to find the perfect dosage, and you might suffer hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism symptoms till you and your physician determine the appropriate dosage. (Your thyroid hormone levels will be monitored via blood testing.)
Symptoms of an excess of thyroid hormone include
- Increased heart rate
- Loss of weight
- Chest pain
- Cramps
Some symptoms of insufficient thyroid hormone are
- Gaining weight
- Fatigue
- Dry hair and skin
If you are exhibiting any of the symptoms mentioned above, consult your doctor right away so that the dosage can be modified.
Radioactive Iodine Treatment Adverse Effects
Radioactive iodine (RAI) side effects might include
- Slight nausea on the first day
- Pain and swelling in the neck area where thyroid cells persist
- Dry mouth
- Short-term loss of taste and scent
Furthermore, high RAI doses can induce fertility issues (more common in women than men). They may also kill healthy thyroid cells in addition to malignant ones, necessitating the need for thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
There are also claims that repeated RAI procedures can raise your risk of developing certain cancers, including leukemia.
External Beam Radiation Treatment Side Effects
The following side effects may result from radiation to the neck, depending on the dose:
- Dry and sore mouth and throat
- Hoarseness
- Swallowing difficulty
- Fatigue
Chemotherapy adverse effects
Chemotherapy, which is often solely used to treat anaplastic thyroid cancer, can have various adverse effects depending on the drug used, how much is given, for how long it is taken, and other factors. Among the possible side effects are the following:
- Hair loss
- Mouth sores
- Appetite loss
- Vomiting and nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Elevated risk of infections (because of the low counts of white blood cells)
- Easy bleeding or bruising (because of low blood platelet counts)
- Fatigue (owing to low counts of red blood cells)
Now that you know what is thyroid cancer, be sure to keep an eye on signs your body shows. Early and timely diagnosis will increase the possibility of the best treatment. Apart from this, you should also look out for signs of an underlying condition such as hashimoto's thyroiditis. This condition may lead to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland). You can follow our guide on thyroid cancer symptoms to able to stay on top on your health.
Additional Read: Thyroid SymptomsWhen you see signs of a health condition, contact a doctor immediately. Book an online doctor consultation on Bajaj Finserv Health to get timely treatment. You can also choose from the affordable test packages that will help you stay ahead of underlying health conditions.
References
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/cities/kochi/2018/may/29/look-out-for-thyroid-cancer-1821080.html
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/thyroid-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.