Health Tests | 5 min read
Troponin Test: What It is , Normal range and High Level Causes
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Your doctor may suggest several troponin tests to detect damage to your heart muscle and diagnose your cardiac condition. Treatment for heart problems lower high troponin levels in your blood.
Key Takeaways
- Troponin test detects troponin proteins released in your blood
- High troponin found in the troponin test indicates a heart attack
- Troponin levels are reduced by treating heart issues like blood clots
Whether you experience a minor stroke or a heart attack, your doctor will prescribe you the troponin test. This test determines the severity of your heart problems by detecting the levels of troponin in your blood. Experts suggest that your risk of chronic heart disease increases if you have suffered from COVID-19 and are at risk of developing cardiac ailments. This is why lab tests like the troponin test are part of post-COVID screenings.
Ensuring that your results fall within the troponin test normal range is important also because elevated levels of troponin in your blood can lead to serious heart problems like coronary ischemia. Read on to learn more about the troponin test, the troponin test normal range, and the reason why these levels spike.
What is the Troponin Test?
A troponin test checks mainly the levels of two types of troponins in your blood, troponin T and troponin I [1]. These proteins are present in your heart muscles and can be found in your blood. Troponin I helps in heart muscle contraction, whereas troponin T helps to bind the troponin proteins to the muscles. This activity allows these proteins to regulate your heart muscles.
A troponin test is done using your blood samples and examining them to check the levels of troponin T and I. Your doctor prescribes the troponin test several times within 24 hours when you experience or are suspected of having a heart attack. The levels of troponin detected in your blood are assessed to diagnose your heart condition and its severity.
Additional read: Important Tests to Check Your Cardiac Profile
What is the Troponin Test Normal Range?
Different labs cite the troponin test normal range differently. It is measured in nanograms or milliliter (ng/ml) of blood. The normal range for the troponin test is generally considered 0.04 ng/ml for troponin I and 0.01 ng/ml for troponin T. When your troponin test results in higher values, it indicates heart risk in terms of damage or an attack.
What Causes High Levels of Troponin in Your Blood?
When there’s a blockage in your heart muscles, you have a higher chance of a heart attack. This causes damage to your heart muscles, which then release the troponin proteins in your blood. The troponin test is usually done after a heart attack where the levels of troponin proteins can be detected. With more damage to your heart muscles, the levels of troponins also increase.
High levels of troponin can occur in both heart patients and normal people. The potential reasons for it include the following.
- Heart infections
- Inflammation in the heart or myocarditis
- Chronic kidney diseases
- Sepsis or infection in your bloodstream [2]
- Blood clot or blockage in arteries
- High blood pressure
- Heart damage from chemotherapy
- Heart injuries from accidents
Elevated levels ranging higher than 0.04 ng/ml indicates heart problems. Usually, heart patients show high levels in troponin test results within a span of 6 hours after having a heart attack. Experts suggest that high levels of troponin stay for 1 to 2 weeks after having a heart attack. When your troponin test results in no detection, your doctor assesses your heart condition as normal.
Additional read: Sepsis Meaning, Symptoms, Causes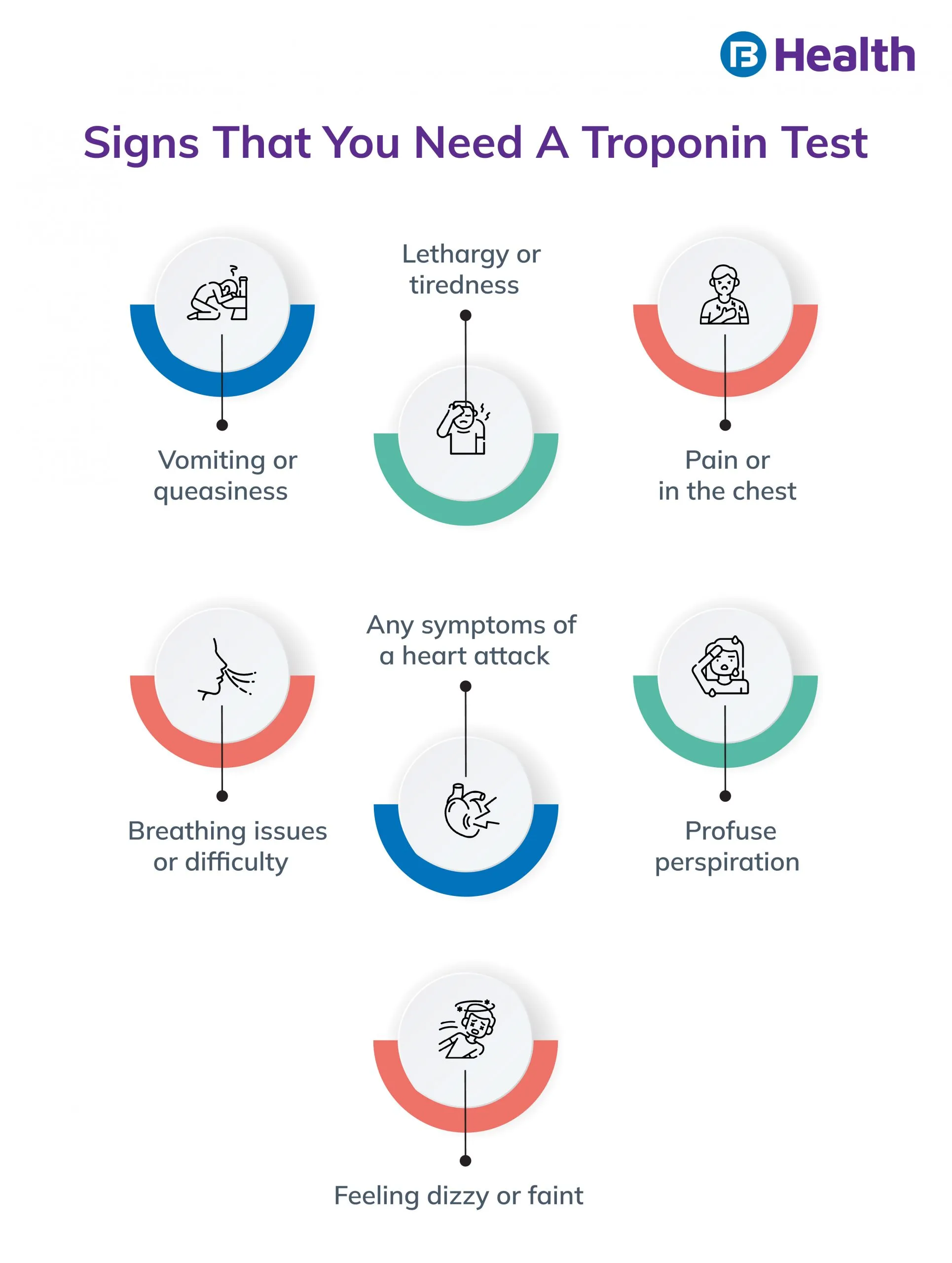
How Can You Lower High Levels of Troponin?
You can bring your levels to the troponin test normal range by maintaining your heart health. There are many treatments you can get to treat heart conditions and ensure a low risk of heart attacks in the future. These include
- Medicines that dissolve blood clots in your heart muscles
- Inserting a stent (a tube of wired mesh) in your heart muscles to open the blockage in your arteries during angioplasty
- Destroying heart cells with radio waves, known as ablation
- Bypass surgery to clear the blood flow pathway through your heart muscles
- Opening blood clots in the primary arteries of your heart
Your doctor may suggest the last option if you have had a heart attack recently and to avoid any damage to your heart cells in the future. In all these ways, your troponin levels decrease gradually along with improvement in your heart muscles.
You can minimize high troponin levels with a few lifestyle changes, such as
- Exercising regularly
- Shedding extra body weight
- Eating a healthy low-fat diet
- Stopping your smoking habit
Now that you know the important facts about the troponin test. Book lab tests to keep a check on your heart health. You can book this blood test with ease on the Bajaj Finserv Health platform and avail a lab test discount too! With blood samples being collected from the comfort of your home, this is both convenient and affordable. On the Bajaj Finserv Health app or website, you can also book other heart-related lab tests such as an HDL and LDL cholesterol test, a set of 5 test as cardiac risk marker, a hemoglobin test, and more.
If you have a history of heart problems or have been diagnosed with cardiac issues, secure your medical needs with a health insurance plan. Choose insurance coverage from Aarogya Care and manage your medical expenses smartly. The Complete Health Solution plan, for instance, offers you up to 180 free online doctor consultations as well as reimbursements for lab tests and in-person doctor visits. Sign up now and take care of your heart health.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1277047/
- https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/10.1164/rccm.202103-0613OC
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.