General Health | min read
Typhoid Fever: 6 Important Things you Must Know About It
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Typhoid fever, a chronic bacterial infection that impacts your gut, can be prevented with timely measures. Read on to learn about the causes and symptoms of the condition, preventive measures as well as the usual treatment method.
Key Takeaways
- Typhoid fever is different from paratyphoid fever
- Leaving typhoid untreated can increase your health risk
- Follow safe food practices like maintaining cleanliness to prevent typhoid
What is Typhoid Fever?
Typhoid fever is a chronic bacterial infection that impacts your gut. Salmonella Typhi (S. Typhi) is the bacterium responsible for this infection. Infection by this bacterium leads to conditions such as stomach aches and high fever. Note that this fever is also known as enteric fever.
People often link paratyphoid fever with typhoid. However, remember that it is not so, as paratyphoid is caused by a different bacterium, Salmonella Paratyphi (S. Paratyphi), and its symptoms are milder.
WHO’s 2019 data shows that an estimated 90 lakh people fall sick every year due to typhoid, leading to about 1,10,000 deaths per year [1]. Read on to learn about the various causes and symptoms of typhoid fever, as well as typhoid fever diagnosis and treatment.
Typhoid Fever Causes
The human body gets infected with S. Typhi from contaminated water and food. Once it enters your body, it reaches your intestines and eventually into your blood. Then the blood carries them to your body's different organs and systems. Commonly affected body parts include the spleen, liver, gallbladder, and lymph nodes.
Individuals may also become long-term carriers of the S. Typhi bacteria, releasing them in their stools. Therefore, people in close contact with such individuals are at a high risk of typhoid fever infection.
Additional Read: Widal Test Normal Range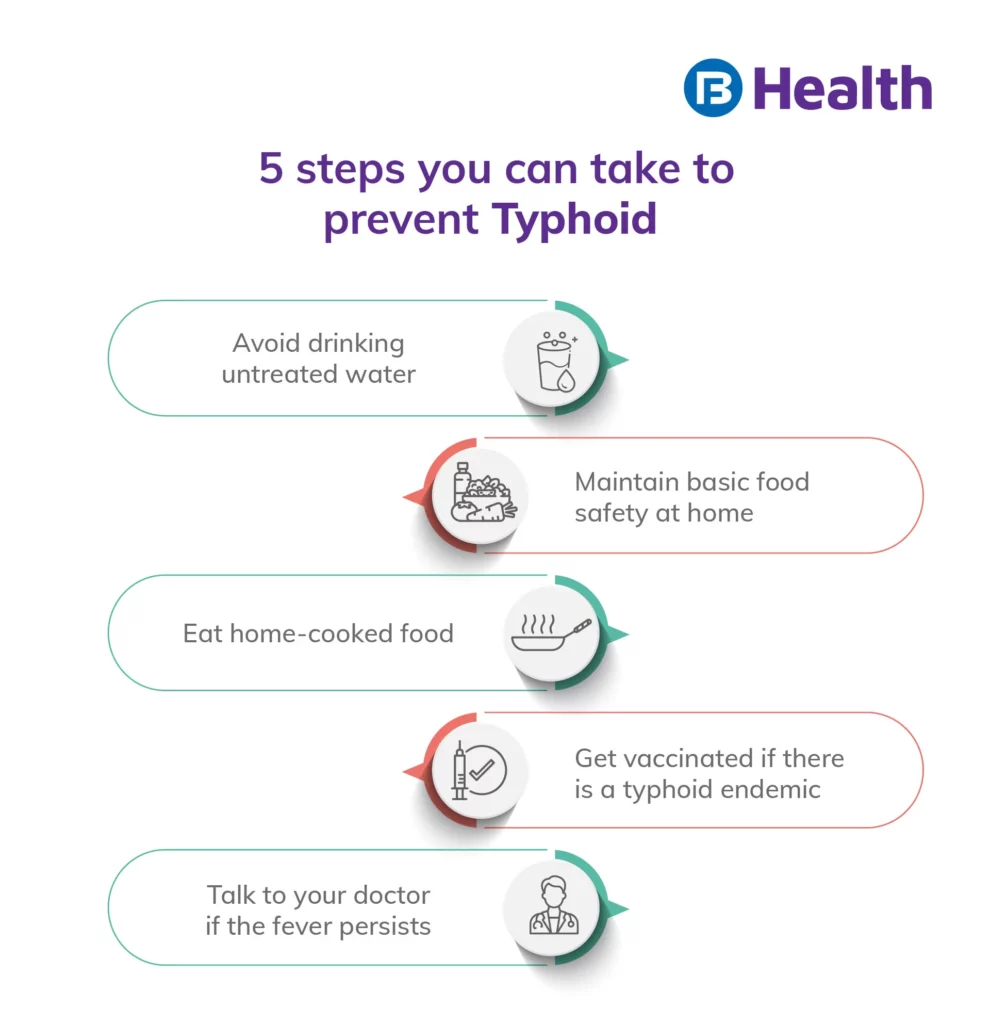
Symptoms of Typhoid Fever
The most common symptom of typhoid is a high fever that continues for weeks if not medically intervened. If you are infected with the S. Typhi bacteria, a delay in treatment can put your health at high risk. So it is important to visit your doctor if the fever continues for more than a week and the usual medicines for the fever do not work.
Other symptoms of typhoid infection that can accompany fever are as follows:
- Reduced or no appetite
- Chills
- Headache
- Diarrhoea and vomiting
- Rashes
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Blood in stool
- Cough
- Nosebleeds
- Attention-deficit disorder
Precautions to Lower your Risk of Typhoid Fever
It’s wise to get vaccinated if your area is getting infested with typhoid disease or you are travelling to a country infested with the same. Here’s a look at the two vaccines to choose from:
Live typhoid vaccine
This vaccine is available in the form of oral capsules and is recommended for people aged six years and older. In this course, an individual must consume four capsules every alternate day as per the typhoid vaccine schedule.
If you are getting immunized for your travel plans, ensure that the last vaccination dose is taken at least a week before your journey. A booster dose is given every five years for individuals who remain at risk.
Inactivated typhoid vaccine
This typhoid vaccine is intended for anyone above the age of 2 years and is administered via injection. Taking the shot at least two weeks before your travel plans is wise. Usually, this vaccine consists of a single dose. However, if you have a serious reaction after your first dose, it is wise to consult a healthcare professional to get another shot. A booster dose is given every two years for individuals who remain at risk.
Additional Read: Common Waterborne DiseasesSafe food practices
Besides immunization, you can follow safe food practices to protect yourself from the S. Typhi bacteria. Here are the measures you can take:
- Don't prepare food for other people if you are not well
- Sanities your hands or wash them with soap and water before and after cooking and eating
- Clean your hand with sanitizer or soap and water after using the washroom
- Wash or sanities surfaces used for food preparation
- Cleanse the utensils after use
- Consume well-cooked foods prepared at home for maximum safety
- Avoid drinking untreated water
Typhoid Fever Diagnosis
Doctors will assess your symptoms and travel history and recommend a few lab tests if they suspect typhoid. You may need to get the samples of your blood, urine, stool, bone marrow, and skin checked as part of this process. Treatment is initiated if the results show the presence of the S. Typhi bacteria.
Additional Read: World Immunization Week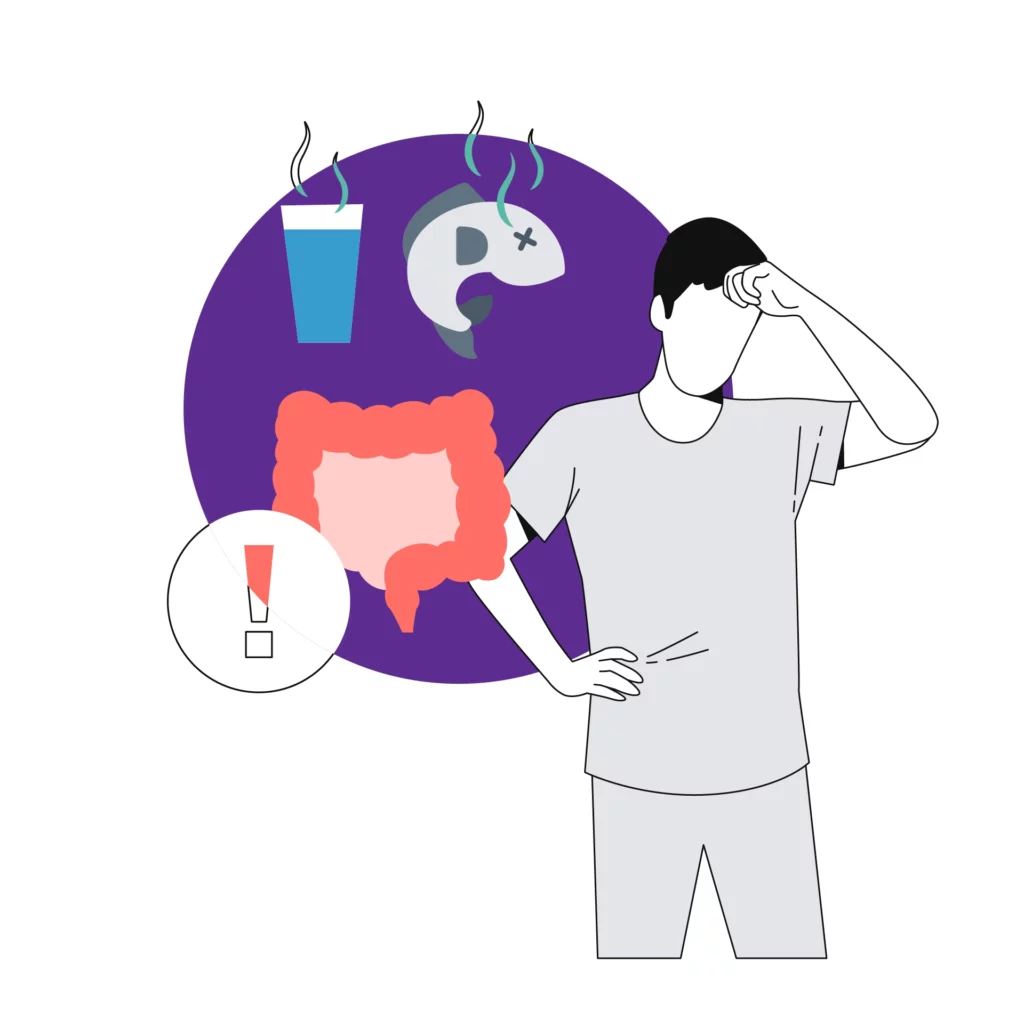
Typhoid Fever Treatment
Antibiotic treatment is common for typhoid. However, some new variants of the S. Typhi bacteria may survive the usual course of antibiotics. So, doctors prescribe different antibiotics as per the type of your infection. If your condition is severe, hospitalization may be required for additional treatments.
In less severe cases, doctors may also recommend the following home remedies for typhoid fever:
- Increase fluid intake
- Cold compress
- Basil
- Pomegranates
- Bananas
- Cloves
- Garlic
- Triphala churan
- Apple cider vinegar
Early Symptoms of Typhoid
For typhoid, all symptoms may not appear at once. Here’re the usual early symptoms from which you can suspect typhoid and get medical help:
- High fever with body temperature up to 104 degrees Fahrenheit
- Stomach ache
- Loose motion or constipation
- Tiredness
- Rashes
- Muscle aches
With all this essential information regarding typhoid fever at your disposal, you can take a quick and wise decision if a similar situation arises. If you have typhoid fever symptoms or other conditions such as dengue fever symptoms, you can consult a general physician on Bajaj Finserv Health. Get easy access to the health platform via the website or app, and book an online appointment to get started with your treatment!
References
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/typhoid
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.