Gynaecologist and Obstetrician | 5 min read
What is Ovulation: Its Process and 4 Tips to Track It
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Knowing your menstrual cycle is the key to understanding what is ovulation
- Bloating, cramps, tender breasts, light bleeding are symptoms of ovulation
- The place of your ovulation pain depends on which ovary releases the egg
The female reproductive system is a complex system because of its vital purpose. Females produce eggs and provide a safe environment like uterus for fetal development. Knowing about ovulation and the menstrual cycle, in general, is important to understand how the female reproductive system works.
Wondering what is ovulation and how is it a part of the female reproductive system? The menstruation cycle is divided into four phases
- Menstrual
- Follicular
- Ovulation
- Luteal
Ovulation is the period when your ovary releases an egg for fertilization. It is the phase of your menstrual cycle during which you can conceive. Read on to understand what is ovulation, its process, and its symptoms.
What is ovulation?
To understand what is ovulation, it is important to learn about the different organs of the female reproductive system. It consists of 5 major organs that include
- Fallopian tubes
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Ovaries
- Cervix
The ovaries are responsible for producing and releasing eggs. These are transported to the fallopian tubes for fertilization. The release of eggs from your ovaries is known as ovulation.
After fertilization, the egg moves to the uterus and implants itself in the lining of the uterus. If not fertilized, the uterine lining starts shedding from your body. This shedding process is also the start of menstruation. It occurs every month during the reproductive life of a woman.
Additional Read: What is Vaginal DrynessOvulation and your menstrual cycle
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is released by your hypothalamus, a portion of your brain, to start the ovulation process. Your brain's pituitary gland secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) in response to GnRH.
- The day your menstrual flow starts, your menstrual cycle resets. The follicular phase, during which the egg develops and is later released during ovulation, begins at this time.
- The follicular phase is when your body releases a hormone called follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which helps the egg in your ovary mature and get ready to be released.
- When the egg is fully developed, your body produces a large amount of luteinizing hormone (LH), which causes the egg to be released. Around day 14, between 28 and 36 hours after the LH spike, ovulation typically takes place.
- Latinization occurs after ovulation. In the event of pregnancy, hormones will prevent the lining from shedding. If not, bleeding will begin on or around day 28 of the cycle, starting the following cycle.
Ovulation, conception, and pregnancy
The route that your egg takes after ovulation is through your fallopian tube. The union of your egg and sperm to create a fertilized egg occurs in your fallopian tube. If conception occurs, the fertilized egg travels from your sperm-fertilized egg to your uterus. After about a week, your uterus lining and the fertilized egg, which is now a blastocyst, merge. The term for this is implantation. The endometrium thickens due to the released hormones progesterone and oestrogen, which gives the blastocyst the nutrition it needs to develop into a baby. Hormones inform your body that a baby is growing inside your uterus while cells continue to divide, some of which become the foetus, and others become the placenta. Additionally, it instructs your uterus to maintain its lining, delaying the start of your period. The absence of menstruation is typically the first indication of pregnancy.
When does ovulation occur?
In a typical 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation takes place roughly 14 days before the start of your subsequent period. Your cycle duration may be longer or shorter, so the precise timing varies. It is useful to keep track of your menstrual cycle with a calendar or a phone app. This can assist you in figuring out when ovulation is most likely to happen. No matter how long their overall cycle is, most people will start bleeding 14 to 16 days following ovulation.
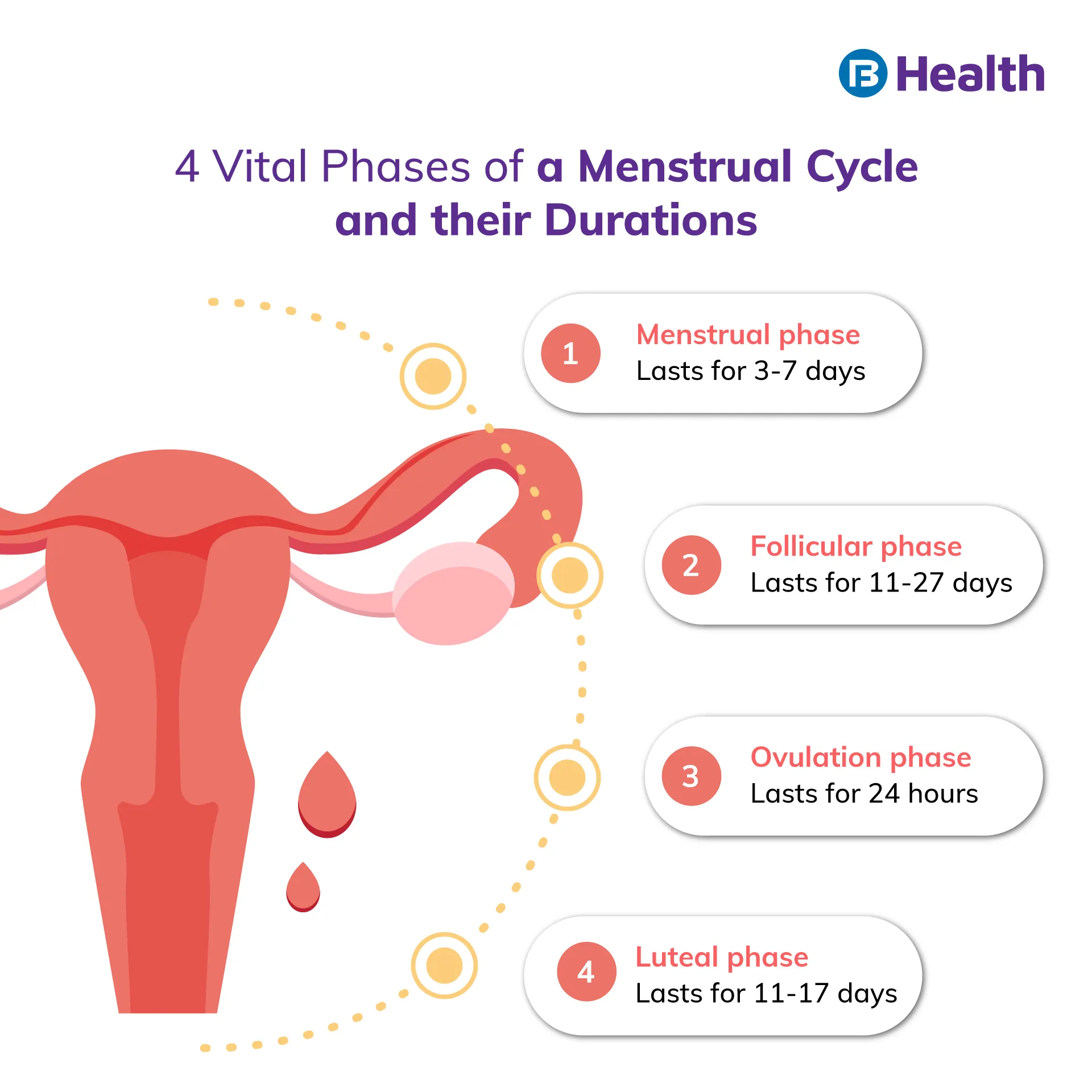
Do you understand what is ovulation in a usual 28-day cycle?
Between 6-14 days of your menstrual cycle, follicles in your ovaries begin to mature. This is a result of follicle stimulating hormones being released in the follicular phase. During 10-14 days, one of the follicles form a mature egg. On day 14, a rise in luteinizing hormones causes your ovaries to release the egg.
Once released, the egg is transported to the fallopian tube. This phase is luteal phase and lasts till the end of your cycle. It usually lasts from day 15-28 of your cycle. During this phase, the progesterone level of your body rises. This helps in thickening of your uterine lining and prepare your uterus for pregnancy.
When fertilized, the egg will implant itself on the uterine lining and start developing. In case your egg is not fertilized, your uterine lining will start shedding. The shedding takes place through menstruation, which usually lasts for 5 days. It also marks the start of your menstrual cycle.
In ovulation, conception can happen during the fertile window. Fertile window is the time period before ovulation during which you can get pregnant. It is 6 days before ovulation, including the day of ovulation. The duration is of 6 days because the sperm may be in the fallopian tubes for several days. When the egg reaches fallopian tubes, it is fertile for 24 hours after which it cannot be fertilized.
What are the common symptoms of ovulation?
Since each person is different, only some experience ovulation symptoms. The most prevalent symptoms during ovulation are the following:
- Supple breasts
- Bloating
- Minor abdominal or pelvic pain
- Spots of light bleeding
- Changes in your cervix's location and stiffness
- Heightened sex desire
- Enhanced taste, smell, or visual perception
- Mood shifts
- Appetite shifts
What are the common symptoms of ovulation?
As you near the day of ovulation, you may start experiencing more vaginal discharge than usual. Apart from this, you may also experience the following symptoms of ovulation.
- Spotting or light bleeding
- Increased sex drive
- Breast tenderness
- Bloating
- Cramps
During this, pain is also a common symptom. Around 40% of women experience discomfort or pain [1]. Depending on the ovary that releases the egg, you may feel pain in the right or left side of your abdomen. If the pain is severe, consult a doctor so that you can get some relief. In rare cases, ovulation pain may be a symptom of one of the following underlying conditions.
- Scar tissue
- Endometriosis
- Sexually transmitted infections (STI)
How do I know I’m ovulating?
Calendar approach
People who use a calendar to estimate ovulation look at six months of menstrual cycles to see when they are fertile. You need to determine your shortest and longest cycles over six months to determine when you might be ovulating. Your longest cycle is shortened by 11 days and your shortest by 18 days. These two numbers indicate the most fertile days during your cycle. If your cycle lengths are 31 and 18, your fertile period would be from day 10 to day 20 of your cycle.
Breast Tenderness:
Period-related breast discomfort typically:
- Starts up to two weeks before a period and gets worse before disappearing after the period
- Affects both breasts and occasionally spreads to the armpit
- Feels dull, heavy, or hurting
- Pain in Tummy:
Period pain is a common symptom of the menstrual cycle. It happens to the majority of women at some point in their lives.
- It usually presents as terrible stomach cramps that move to the back and thighs on occasion
- Pain can vary in intensity from acute and spasmodic to dull but persistent
- Additionally, it could change over time. While some periods are painless, others might be rather unpleasant
- Even when you are not on your period, you may occasionally experience pelvic pain
How to know if you are ovulating?
Once you know what is ovulation, it is easy to track it. There are different ways through which you can track your ovulation. The conventional way of tracking your ovulation includes ultrasound imaging and blood tests. There are other ways too. You can determine whether you are ovulating with the help of following.
Menstrual cycle
Usually, it takes place in the middle of your cycle. A menstrual cycle can last for 21-35 days but in general it lasts for about 28 days. Tracking your cycle for a few months will help you get a fair idea on how long your cycle lasts.
Body temperature
It is normal for your body temperature to increase after ovulation takes place. This rise can range between 0.3-0.7°C [2]. Checking your temperature every morning will help you notice the changes.
Vaginal discharge
It is common for you to experience more discharge just before the ovulation. Note that during this time the discharge is clearer (like egg whites) and slippery.
Ovulation predictor kits or fertility monitors
These OTC kits help you track your ovulation at home. They work by either tracking the LH or estrogen hormones from your urine. It gives you a brief idea about your fertility window. The fertility monitors can track more than 4 fertile days with an accuracy of 99%.
Can you have irregular ovulation?
You can discover that you are not ovulating on a regular basis or, in some situations, not ovulating at all if you monitor your ovulation from one month to the next. This is a solid cause to see a doctor.
The exact day of ovulation varies from month to month based on factors such as stress or food. Furthermore, certain conditions, such as thyroid abnormalities or polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), can cause ovulation to become unpredictable or stop completely.
Other symptoms connected to changes in hormone levels may also be brought on by these disorders, such as:
- Acne
- Increased face or body hair growth
- Infertility
Yes, irregular ovulation can happen and sometimes you might not ovulate at all in certain cases. If your notice no or irregular then talk to a doctor. There several factors that may cause a change in your period. Consulting a doctor will help you identify and tackle these issues. Some common factors than can cause no or irregular ovulation are
- Stress
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid conditions
Ovulation pain
It's not unusual to feel pain during ovulation. Up to 40% of women who ovulate experience some discomfort near the menstrual cycle midpoint. In German, the term "mittelschmerz" (literally, "middle pain") is also used to describe this illness. Every month, the pain generally manifests. Depending on which ovary is producing an egg that month, you'll feel it on the left or right side of the lower abdomen. Little to severe pain is possible. The sensation could be dull or sharp, like a cramp.
Consult a doctor if the discomfort is severe. Options to lessen your discomfort might be available. A doctor can also decide whether additional examinations or medical care are required.
Rarely, pain during ovulation may be a symptom of one of the following conditions:
- Sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- Endometriosis
- Scar tissue in the abdomen
What happens if I'm not ovulating?
Ovulation may be affected by some medical issues or life circumstances, or it may halt altogether. Among them are:
- Hyperprolactinemia or breastfeeding
- Menopause
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Primary insufficiency of the ovaries
- Factors including high or low body fat, extreme stress, exhaustion, or exercise bring on Amenorrhea
You could not have been ovulating if your cycle is erratic or you go months without having one. If this is the case, speak with your healthcare practitioner right away so they can rule out any serious illnesses.
Tracking ovulation at home
You have options for monitoring ovulation at home, even though an ultrasound or hormonal blood tests prescribed by your doctor are the most accurate way to do so.
- OPKs, or ovulation predictor kits: These are typically sold over-the-counter at your local pharmacy. They find LH in your urine, which often indicates that you may ovulate shortly
- Pregnancy Trackers: They are also sold over the counter. They monitor oestrogen and LH to determine your reproductive window. The cost of fertility monitors may be higher than that of LH-only options. Some monitors assert they can reliably identify four or more fertile days each month
Always adhere to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure you're using at-home trackers to their full potential. Then, choose the right one for you by speaking with a doctor or a chemist.
Knowing about your fertility cycle is important whether you are trying to conceive or not. Talking to a gynecologist will help you know what measures you need to take. Book online doctor consultation with top gynecologists on Bajaj Finserv Health. This way, you can ease your worries. Start prioritizing your reproductive health without delay!
Frequently asked questions
How many days after your period do you ovulate?
Your menstrual cycle lasts from the first day of your period to the first day of your subsequent period. You are most fertile during ovulation, which normally takes place 12 to 14 days before the beginning of your subsequent period.
How long does ovulation last?
While ovulation only lasts 12 to 24 hours, the six days before and after ovulation are when you have the highest chance of becoming pregnant.
Can you ovulate twice a month?
According to Canadian experts, assuming that women ovulate only once a month is incorrect. Instead, they may ovulate twice or even three times per month. [1]
Is ovulation the only time you can become pregnant?
No. While the sperm can only remain in the reproductive canal under ideal conditions for roughly five days, the egg can only be fertilized in the first 12 to 24 hours after it is released. Therefore, you run the risk of getting pregnant if you have intercourse in the days prior to or on the actual day of ovulation.
The most secure course of action is to use contraception at all times of your cycle if you do not want to get pregnant.
Can you ovulate more than once in a given cycle?
It may be unclear if this would have any further implications for fertility. According to a 2003 study, some women may be able to ovulate twice or three times within a single menstrual cycle. However, other experts dissented, pointing out that there is only one fertile ovulation per cycle.[2]
It is possible for more than one egg to be released during one ovulation. Multiple eggs might be released naturally or as part of infertility therapies. In this circumstance, fraternal multiples, such as twins, may be produced if more than one egg is fertilized. Fraternal (nonidentical) twins comprise about two of every three sets of twins.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31747229/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33123618/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1126506/
- https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn3927-women-can-ovulate-more-than-once-a-month/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.