Health Tests | 4 min read
Why is it Important to Know When Your WBC Count is High or Low?
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Treatment of WBC count disorders depends on the underlying conditions
- Certain medications like chemotherapy drugs can cause a low WBC count
- The normal WBC count for men is 5,000 to 10,000 per microliter of blood
White blood cells make up a mere 1% or less of your total blood [1]. They are produced in the bone marrow and are stored in the blood and lymphatic system to fight infections. A WBC count essentially measures the number of white blood cells in your body. A high WBC count may indicate that your immune system is fighting an infection. In contrast, a low WBC count may mean that a health condition is destroying your WBCs or that your body is producing fewer WBCs. Both the WBC blood test and RBC blood test are usually a part of the Complete Blood Count (CBC) tests.
Since white blood cells play an important role, you should know that there are five major types of WBCs in your body. These are basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils. Read on to know what a normal count is and what a low and a high white blood cell count indicates.
What Is the Normal White Blood Cell Count?
Here is the normal white blood cell count per microliter of blood (mcL).
- Newborns under the age of 2 weeks, should have a WBC count ranging from 9,000 to 30,000 WBC per mcL.
- Infants and adolescent children, should have a WBC count ranging between 5,000 and 10,000 WBC per mcL.
- Women, the normal count is 4,500 to 11,000 WBC per mcL.
- Men, WBC normal range is 5,000 to 10,000 WBC per mcL.
Symptoms of High and Low White Blood Cell Count
A high WBC count often doesn’t cause any symptoms. However, it depends on the underlying conditions as high white blood cell count causes usually display their own symptoms. Some people do not experience any symptoms of white blood cell disorders at all. If symptoms occur for low WBC count, they may include infections, fever, body aches, headaches, and fatigue.
Causes of High White Blood Cell Count
Leukocytosis or high WBC count is caused by the following conditions.
- Reduction in the efficacy of the immune system
- Infections caused by bacteria
- Allergic reactions
- Injuries
- Asthma
- Pregnancy
- Cigarette smoking
- Exercising excessively
- Emotional stress
- Bone marrow tumors
- Burns and other tissue damage
- Spleen removal surgery [2]
- Bone marrow or immune disorder
- Acute or chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Rheumatoid arthritis, allergy, bowel disease, and other inflammatory conditions
- Medications like corticosteroids, heparin, and epinephrine
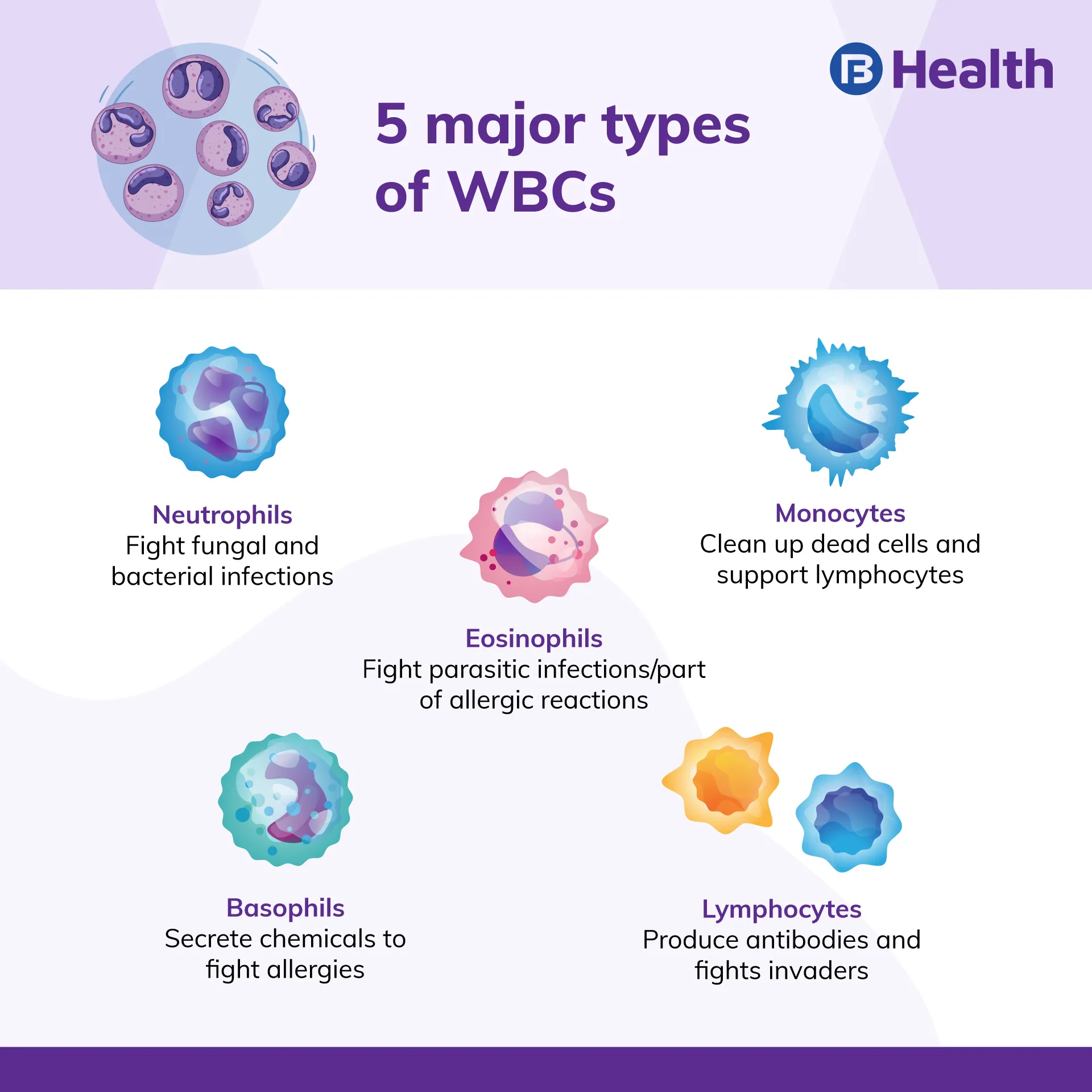
Causes of Low Blood Cell Count
Leukopenia or low WBC count is caused by the following conditions.
- Bone marrow failure or deficiency due to tumor or infection
- Bone marrow cancers
- Liver or spleen disease
- Severe bacterial infections
- Emotional or physical stress
- Radiation therapy for treating cancer
- Cancer of the lymphatic system
- Mononucleosis (mono) [3] and other viral illnesses
- HIV infection
- Systemic lupus erythematosus and certain other autoimmune disorders
- Medications such as antibiotics, captopril, and chemotherapy drugs
Common WBC Count Disorders
- Leukocytosis, which refers to an increase in WBC count caused by bacterial or viral infections, smoking, and genetic conditions among other causes.
- Leukemia, cancer of the cells in the bone marrow responsible for producing white blood cells.
- Autoimmune neutropenia, which is associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cyclic neutropenia, a disorder due to genetic mutation.
- Chronic granulomatous disease, which occurs when multiple types of WBCs like neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes fail to function properly.
- LAD syndromes, a rare condition in which white blood cells struggle to travel to infected areas [4].
Treatment of Abnormal White Blood Cell Count
Doctors may ask you to take a CBC test as part of the diagnosis or if they suspect a white blood cell disorder. They may also specifically prescribe a WBC count test for you. The treatment of any WBC count disorder largely depends on the type and the underlying condition. Doctors may prescribe antibiotics to treat and prevent further infections. You may also be given medications to stimulate the production of white blood cells. In some cases, stem cell transplantation is recommended, which transplants healthy stem cells into your bone marrow or blood. However, treatment through white blood cell transfusion is rarely used.
While there are no visible symptoms of high white blood cell count, the best way to prevent yourself from an abnormal count is to maintain proper hygiene and invest time in self-care. Make the WBC count test a part of your healthcare routine by doing regular check-ups. You can now book lab tests online on Bajaj Finserv Health and track your health with ease.
References
- https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/patient-education/facts-about-blood-and-blood-cells
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/14614-splenectomy
- https://www.cdc.gov/epstein-barr/about-mono.html
- https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/leukocyte-adhesion-deficiency-syndromes/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.