Skin & Hair | min read
Anthrax Disease: A Guide on its Causes, Symptoms and More
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Anthrax is a bacterial infection that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It happens when the bacterium Bacillus anthracis affects both humans and animals. This blog covers everything you need to understand about Anthrax disease, including its causes, symptoms, types, treatment, and precautions.
Key Takeaways
- Anthrax is a rare but serious infection that can affect humans and animals
- The symptoms of Anthrax can range from mild to severe, and early diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment
- Precautions such as vaccination, proper handling of animal products, and avoiding contact with contaminated materials ca
What is Anthrax Disease?
Ever wonder what is Anthrax meaning?
Anthrax disease is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. This bacterium produces spores that can survive for years in soil and animal products such as wool, hides, and hair. Anthrax can affect both animals and humans, and it is commonly contracted through contact with infected animals or animal products. In humans, Anthrax can affect the skin, lungs, or digestive system and can be fatal if left untreated.
Anthrax disease symptoms to look out for
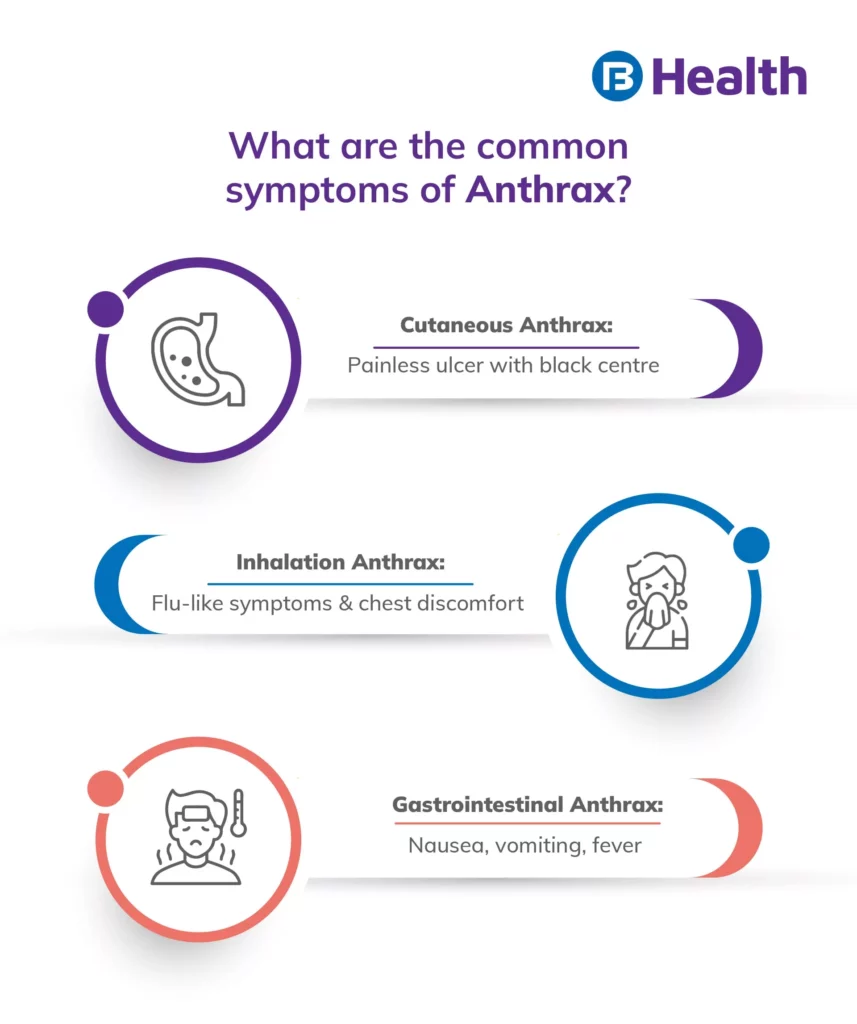
The symptoms of Anthrax disease can vary depending on the type of infection, as previously mentioned. The three types of Anthrax are cutaneous, inhalation, and gastrointestinal.
Cutaneous Anthrax
It is the most common form of Anthrax disease and affects the skin. It typically begins with a small, painless sore that develops into a blister within 1-2 days. The blister then forms a black, scab-like lesion that is usually painless but may be itchy. The lesion can range in size from a small bump to a large ulcer. There may also be swelling in the surrounding area.
Inhaled Anthrax
It affects the lungs and is usually contracted by inhaling the spores of the bacterium. Initial symptoms may be similar to the flu, including fever, cough, and chest discomfort. The symptoms may progress further to severe breathing problems, shock, and meningitis. Inhaled Anthrax disease is rare but can be life-threatening.
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
It affects the digestive system and is usually contracted by consuming contaminated meat. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Gastrointestinal Anthrax disease is also rare but can be fatal if left untreated.
It is essential to note that symptoms of Anthrax can take anywhere from 1-7 days to appear after exposure, depending on the type of infection. Therefore, early treatment is critical for a successful recovery.
If you have been exposed to Anthrax or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Additional Read: Skin Disease ConditionCauses of Anthrax
Note that Anthrax is caused by a type of bacteria called Bacillus anthracis. It is commonly found in soil and can infect animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. Humans can contract Anthrax disease by coming into contact with infected animals, their products (such as wool or hides), or soil that contains the spores of the bacterium.
Anthrax disease can also be spread through the intentional release of the bacterium, as it has been used as a bioterrorism agent in the past. The spores of the bacterium can be released into the air, water, or food supply and can be inhaled or ingested, thereby leading to an infection.
It is important to note that Anthrax is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
Additional Read: Red Spots on Skin
Treatment of Anthrax Disease
Early anthrax treatment is critical for a successful recovery. Here are some treatment options for anthrax disease:
- Antibiotics are the primary treatment for Anthrax disease. Depending on the kind of infection and the severity of symptoms, different antibiotics may be used
- In addition to antibiotics, other medications may be used to manage symptoms, such as pain relievers and fever reducers
- Cutaneous Anthrax can often be treated with antibiotics taken orally, while severe cases may require intravenous antibiotics
- Inhalation and Gastrointestinal Anthrax are more serious and require aggressive treatment with intravenous antibiotics and other supportive measures, such as oxygen therapy and fluid replacement
- Treatment for Anthrax disease may need to be continued for several weeks to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria
- People who have been exposed to Anthrax may also be given a vaccine to help prevent infection
- It is important to follow the treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare provider and to continue taking antibiotics as directed, even if symptoms improve, to prevent a relapse of the infection
Additional Read: White Spots on Skin
Precautions to Take to Avoid Getting Anthrax Disease
Here are some precautions that can be taken to avoid getting Anthrax disease:
- Avoid contact with animals that may be infected with Bacillus anthracis, such as sick or dead livestock
- Do not handle animal products, such as wool, hides, or bones, from areas where Anthrax disease is known to be present
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and thoroughly with soap and water, especially after handling potentially contaminated animal products
- If you work in a high-risk occupation, such as handling animal products or in a laboratory setting, follow all safety procedures and wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves and masks
- If travelling to an area where Anthrax disease is known to be present, take precautions such as avoiding contact with sick or dead animals and wearing appropriate protective clothing
- If you have been exposed to Anthrax or are experiencing symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Early treatment is critical for a successful recovery
It is important to note that while Anthrax is a rare disease, it can be very serious and potentially life-threatening. By taking appropriate precautions, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting Anthrax.
Additional Read: Fungal Skin Infection
Diagnosis of Anthrax
The diagnosis of Anthrax disease typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Here are some methods commonly used for the diagnosis of Anthrax:
- Clinical evaluation: A healthcare provider will evaluate the patient's symptoms and medical history, as well as any potential exposure to Anthrax, to determine if the disease is likely
- Blood tests: A blood sample may be taken to look for the presence of antibodies to Bacillus anthracis, which can indicate an active infection
- Culture tests: Samples of blood, skin lesions, or other body fluids may be cultured in a laboratory to see if Bacillus anthracis is present
- Imaging tests: X-rays or CT scans may be used to evaluate the lungs or other organs for signs of Anthrax infection
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests: This type of test can detect the DNA of Bacillus anthracis and may be used to confirm a diagnosis
It is important to avail of medical attention urgently if you suspect you may have been exposed to Anthrax or are experiencing symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment are critical for a successful recovery.
Early Anthrax Symptoms you Should Not Miss
The early symptoms of Anthrax can vary depending on the type of infection, but they typically develop within a few days of exposure to Bacillus anthracis. Here are some common early symptoms:
- Cutaneous Anthrax: The earliest symptom of Cutaneous Anthrax is a small, painless sore or blister that develops at the site of exposure, such as a cut or scratch on the skin. The sore may then develop into a black, ulcerated lesion surrounded by swelling and redness
- Inhalation Anthrax: The early symptoms of Inhalation Anthrax can resemble those of a cold or flu, including fever, fatigue, cough, and muscle aches. These symptoms can persist for several days before progressing to more severe respiratory symptoms, such as shortness of breath and chest pain
- Gastrointestinal Anthrax: The early symptoms of Gastrointestinal Anthrax can include nausea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal pain. These symptoms can be followed by severe gastrointestinal symptoms, such as bloody diarrhoea and inflammation of the intestines
It is important to go see a medical practitioner immediately if you suspect you may have been exposed to Anthrax or are experiencing any symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment are critical for a successful recovery.
Anthrax is a serious disease caused by bacteria. Take precautions to avoid exposure and seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms. Get online doctor consultations on Bajaj Finserv Health for convenient and qualified care. You can also avail of a dermatologist consultation on the website. Read more health blogs on their website to stay informed and healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
References
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.