Psychiatrist | 8 min read
Bipolar Disorder: Symptoms, Types, Risk Factor, Diagnosed
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Bipolar disorder was formerly known as manic depression
- Know the bipolar disorder types and symptoms to be aware
- Use a natural way to reduce anxiety for your mental well-being
Bipolar disorder is a mental disorder that was previously known as manic-depressive illness or manic depression [1]. It can cause rapid mood swings including emotional lows (depression) and highs (hypomania or mania). While depression makes you feel sad, hopeless, and lose interest in activities, hypomania or mania makes you feel euphoric and full of energy.
These unusual mood swings affect your
- Energy level
- Thoughts
- Activities
- Behavior
In 2017, India had reported 6.9% cases of bipolar disorder [2]. This mental disorder may occur rarely or multiple times a year. Although some patients experience certain common mental illness symptoms, others may not. You can manage lifelong bipolar disorder complications by following the right treatment plan. Read on to understand more about bipolar disorder types, symptoms, and treatments.
Additional Read: What Is SchizophreniaBipolar Disorder Symptoms
Mania and Hypomania Symptoms
These two distinct types of episodes that have similar symptoms. Here are the common ones.
- Euphoria
- Impaired judgment
- Abnormal anxiety
- Underperformance
- Increased libido
- Racing thoughts
- Taking rapidly or in an unusual manner
- Distraction or boredom
- Affected decision-making skills
- Reduced sleep without feeling tired
- Increased energy, agitation, or aggression
- High levels of self-confidence and self-importance
- Major depressive episode symptoms
A depressive episode includes five or more of these symptoms:
- Extreme sadness
- Sense of guilt
- Loss of interest
- Irritability
- Pain and physical uneasiness
- Change in appetite
- Weight loss or weight gain
- Insomnia or sleeping problems
- Anxiety, fatigue, and tiredness
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing
- Suicidal thoughts
- Feeling of gloom, despair, and hopelessness
Bipolar Disorder Types
Bipolar I Disorder
A person is diagnosed with bipolar I disorder when they have experienced at least one manic episode. This refers to a period of eccentric and abnormal behavior stemming from high energy. Major depressive or hypomanic episodes may take place before or after this. In certain situations, mania may take you away from reality by triggering psychosis [3].
Bipolar II Disorder
When you have one or more episodes of depression, at least one hypomanic episode, but no manic episodes, it may indicate bipolar II disorder. It involves patterns of hypomania, but depression is often more common.
Cyclothymic Disorder
This is when you experience multiple periods of hypomanic symptoms as well as depressive symptoms for at least 2 years as an adult. For children and adolescents, the duration is at least 1 year. Depressive symptoms are usually less severe than major depression. They do not meet the diagnostic requirements to be categorized as a hypomanic episode or a depressive episode.
Bipolar Disorder Causes
Here are some bipolar disorder risk factors that may be the main causes.
Genetic Factors
If you have a first-degree relative such as a sibling or a parent with this condition, your risk of developing this increases. People with certain genes have higher chances of getting this disease than others. Researchers are learning more about genes to develop new treatments.
Biological Factors
Researchers are of the view that the brains of people with this may differ from those who don’t have any mental disorder. The imbalances in hormones or neurotransmitters affecting the brain may play a role in causing this condition.
Environmental Factors
Certain life events including the loss of a loved one, traumatic experiences, mental stress, and drug or alcohol abuse can trigger bipolar disorder.
Bipolar Disorder Symptoms in Women Vs Men
Bipolar illness is diagnosed in nearly equal amounts of males and women. However, depending on your gender and the sex you were given at birth, the disorder's primary symptoms may change.
Bipolar illness in women is often diagnosed later in life, typically in their 20s or 30s. However, sometimes people may become aware of symptoms for the first time during pregnancy or right after delivery. Additionally, bipolar II rather than bipolar I am more likely to be the diagnosis.
Bipolar Disorder Symptoms in Women
- Milder manic episodes
- Fast cycling between manic and depressed episodes, or four or more episodes of mania
- Depression in a year or more co-occurring disorders
- Relapses may occur more frequently
Bipolar illness in women may be partially brought on by hormone changes associated with menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Relapsing is defined as experiencing a mood episode after a period of time without doing so in terms of bipolar disorder.
Bipolar Disorder Symptoms in Men
- Receive a diagnosis early in life
- Have more severe episodes, especially manic episodes, that are less frequent
- Display more anger when experiencing manic episodes and be more likely to additionally have a drug use disorder.
Women with bipolar illness spend more time sad than males. Women are also more likely to have physiological and mental health difficulties. Thyroid problems, migraines, and anxiety disorders are examples of medical concerns.
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens
Since children don't usually exhibit the same bipolar disorder symptoms as adults, diagnosing bipolar illness in youngsters is debatable. Additionally, their moods and actions might not match the criteria used by doctors to identify the illness in adults.
Many symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and other diseases that typically affect children coexist with those of bipolar disorder in children (ADHD).
During the previous few decades, doctors and mental health specialists have learned to detect the disease in youngsters. Children who need therapy might benefit from a diagnosis, but getting one can take weeks or even months. So it could be beneficial to seek treatment from a specialist in the care of young patients with mental health issues.
Children with bipolar illness have severe mood swings, much like adults. They may look extremely joyful and behave exuberantly, or they may come across as depressed, sad, and agitated.
While mood swings affect all kids, bipolar illness produces distinct and observable mood symptoms. Additionally, mood swings are typically more severe than those that frequently occur in children.
How Is Bipolar Disorder Diagnosed?
If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of bipolar disorder, consult your primary care physician or a psychiatrist. They will inquire about any mental disorders you or the individual you are concerned about have experienced, as well as any mental illnesses that run in your family. The individual will also have a comprehensive psychiatric assessment to determine whether they are likely to have bipolar disorder or another mental health problem.
The symptoms of bipolar disorder must be evaluated to see whether they are the product of another cause (such as low thyroid or mood symptoms caused by drug or alcohol abuse). How serious are they? How long did they last? How frequently do they occur?
The most striking signs are mood swings and changes in sleep, activity, thinking, and behavior.
Talking to the person's close friends and family may frequently assist the doctor in differentiating bipolar illness from major depressive disorder or other mental conditions that can cause changes in mood, thinking, and behavior.
You may be scared if you have recently been diagnosed with bipolar illness. The future may appear to be quite unpredictable. What does this mean for your life, family, and job?
However, receiving a correct diagnosis is really excellent news. It means you can finally obtain the care you require. Unfortunately, people with bipolar disorder are frequently misdiagnosed for roughly ten years.
Diagnosis of bipolar illness might be more difficult in children and teens. Their symptoms may be similar to those of adults, but they may be mistaken for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or simply poor conduct.
If you suspect your kid has a bipolar illness, ask your doctor to send you to a child psychologist specializing in bipolar disorder.
Bipolar Disorder Treatment
The treatment of bipolar disorder aims at improving a person’s mood and reducing the symptoms. It may include a combination of therapies.
Bipolar illness is treatable. It is a chronic ailment that needs continuous treatment. People who experience four or more mood episodes in a year or who also have drug or alcohol issues may have more difficult-to-treat types of the disorder.
Treatment can have a significant effect. You can feel better with a mix of factors such as appropriate medical care, medicine, talk therapy, lifestyle modifications, and the support of friends and family. There is currently no recognized cure for bipolar illness, often manic depression. It is a chronic health issue that must be managed for the rest of one's life. Many persons with this illness are successful; they have families, work, and live typical lives.
Medication
A doctor may prescribe mood stabilizers such as lithium, antidepressants and anticonvulsants to relieve mania. You may also take antipsychotics and medicines for sleep and anxiety.
Psychotherapy
Talk therapy or counseling uses various treatment techniques to help a person identify and manage triggers. It helps in changing one’s thoughts, emotions, and behavior.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain modifications in daily habits can also help with managing symptoms of bipolar disorder. Maintaining a regular schedule, eating a healthy diet, exercising, and getting enough sleep may help.
Other Treatments
Treatments such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), a brain stimulation procedure, and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) may also be used to treat bipolar disorder.
Additional Read: Beat Depression Without MedicationWhat Are Bipolar Disorder Risk Factors?
Bipolar illness is a genetic condition that affects both men and women equally. Some factors that increase your chances of having bipolar disorder include:
- Having a family member suffering from bipolar illness
- Going through a period of extreme stress or trauma
- Abuse of drugs or alcohol
- Certain medical conditions
When manic or sad, many persons with the disease misuse alcohol or other substances. Seasonal depression, co-occurring anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder are more common in people with bipolar disorder.
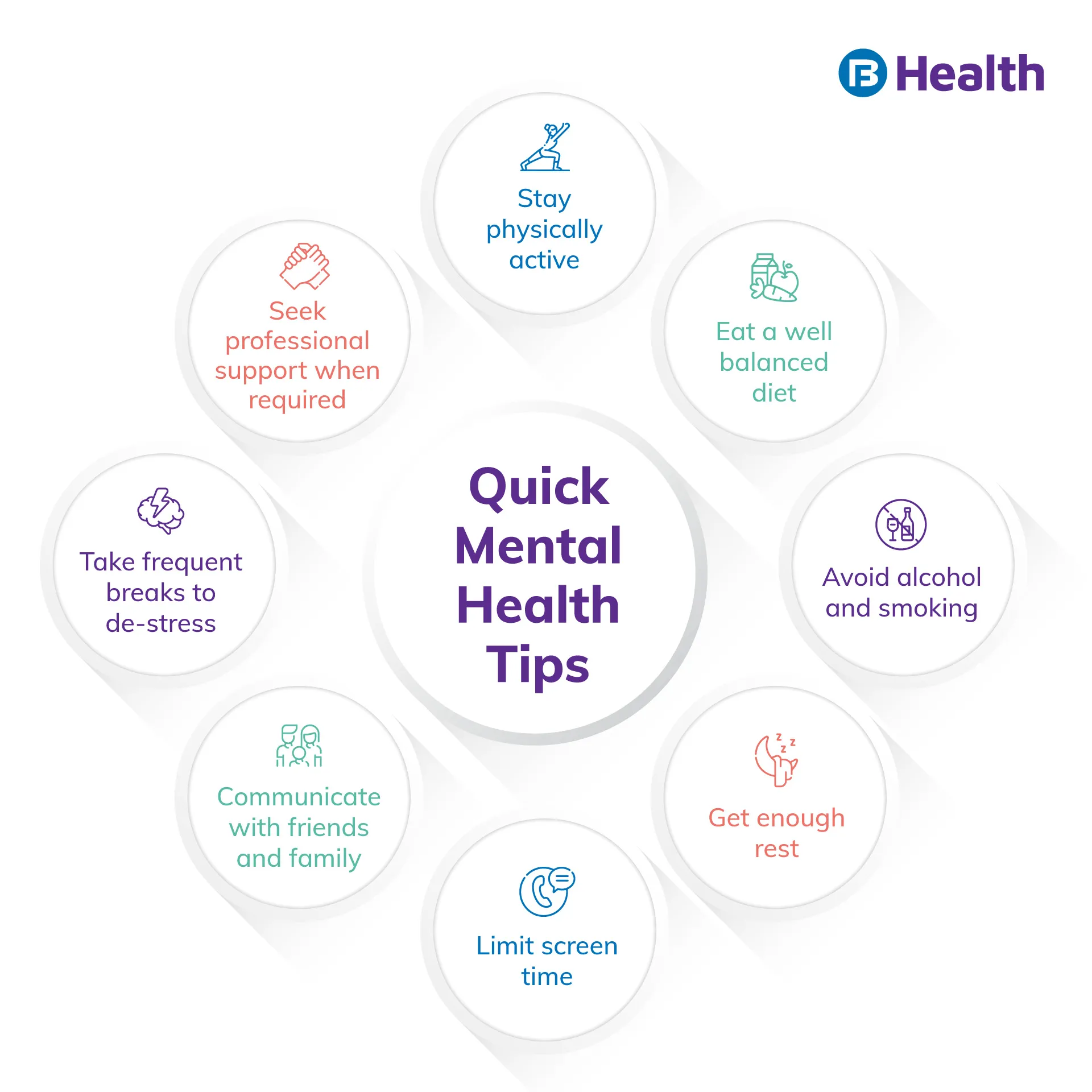
World Mental Health Day is observed every year on 10 October to raise awareness about mental health issues. Spread the word about mental health and follow healthy practices to maintain your mental well-being. Eat a balanced diet, quit unhealthy habits, stay away from negativity and addictions, and remain active. As sleep and mental health go hand in hand, make sure you get enough rest. Adapt any natural way to reduce anxiety and associated bipolar disorder symptoms before you try medication. You can also take mental health insurance to tackle the rising health expenses related to mental disorders. Another way to take care of your mental health is to book an online doctor consultation on Bajaj Finserv Health. Consult with the top mental health experts and get the right medical advice today.References
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/bipolar-disorder’
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpsy/article/PIIS2215-0366(19)30475-4/fulltext
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia/raise/what-is-psychosis
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.






