Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation | 6 min read
Cellulitis: What It is, Types, Diagnosis and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Key Takeaways
- Cellulitis is a frequent and often dangerous bacterial skin infection
- The affected skin is usually swollen, inflamed, and uncomfortable
- If not treated, it may spread to the bloodstream and lymph nodes and quickly turn fatal
Cellulitis meaning is a bacterial infection of the tissue that can be seen under and on the skin. Most people use antibiotics for 7 to 10 days before fully recovering from cellulitis. It can cause gangrene or septic shock if untreated, and in more difficult situations, surgery can be necessary. In addition, it's possible to develop cellulitis more than once. If you receive a cut or any open wound, keeping your skin clean will help to prevent this infection. If you're unsure of how to take care of your skin after an injury, get a doctor's consultation. It's crucial to maintain good hygiene and wound care practices to avoid cellulitis.
Cellulitis: Basics
So, what’s cellulitis? A bacterial infection of the tissues under and on your skin is called cellulitis. Legs, feet, and toes are among the parts of your body that are most frequently impacted. But it can happen anywhere in your body. Additionally, the face, arms, hands, and fingers are frequently affected. Anyone can develop cellulitis, but those with compromised immune systems or skin wounds that make it easy for bacteria to enter the body are at an increased risk.
What Triggers Cellulitis?
Cellulitis, an infection of the skin's deeper layers, can be brought on by various types of bacteria. Cellulitis can be brought on by several germs. Sometimes the skin break is too little to be noticed. However, the most common causes of cellulitis are Streptococcus (strep) and Staphylococcus (staph). [1]
The cellulitis causes are the following:
- Cuts
- Insect bites
- Surgical wounds

Early Signs of Cellulitis
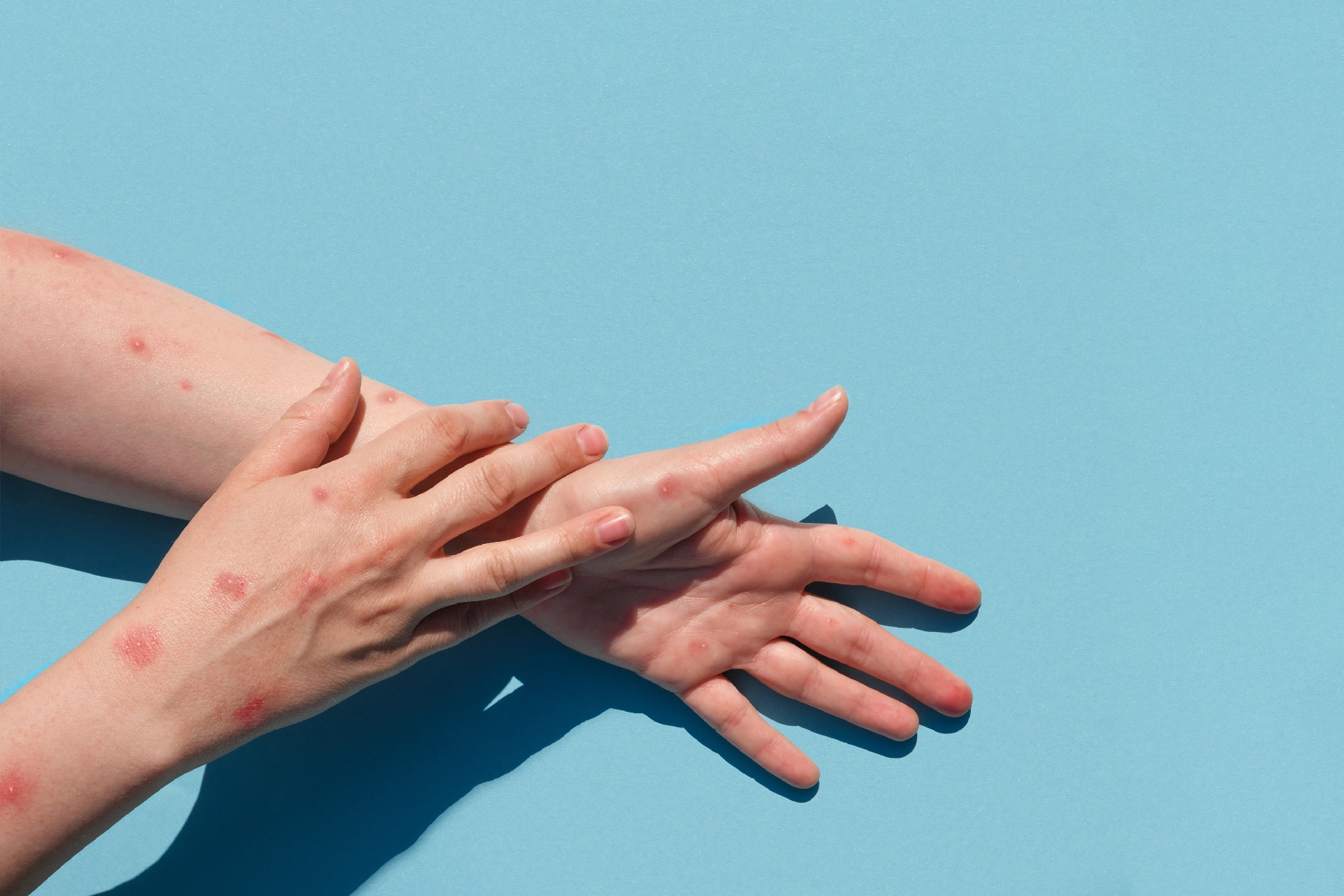
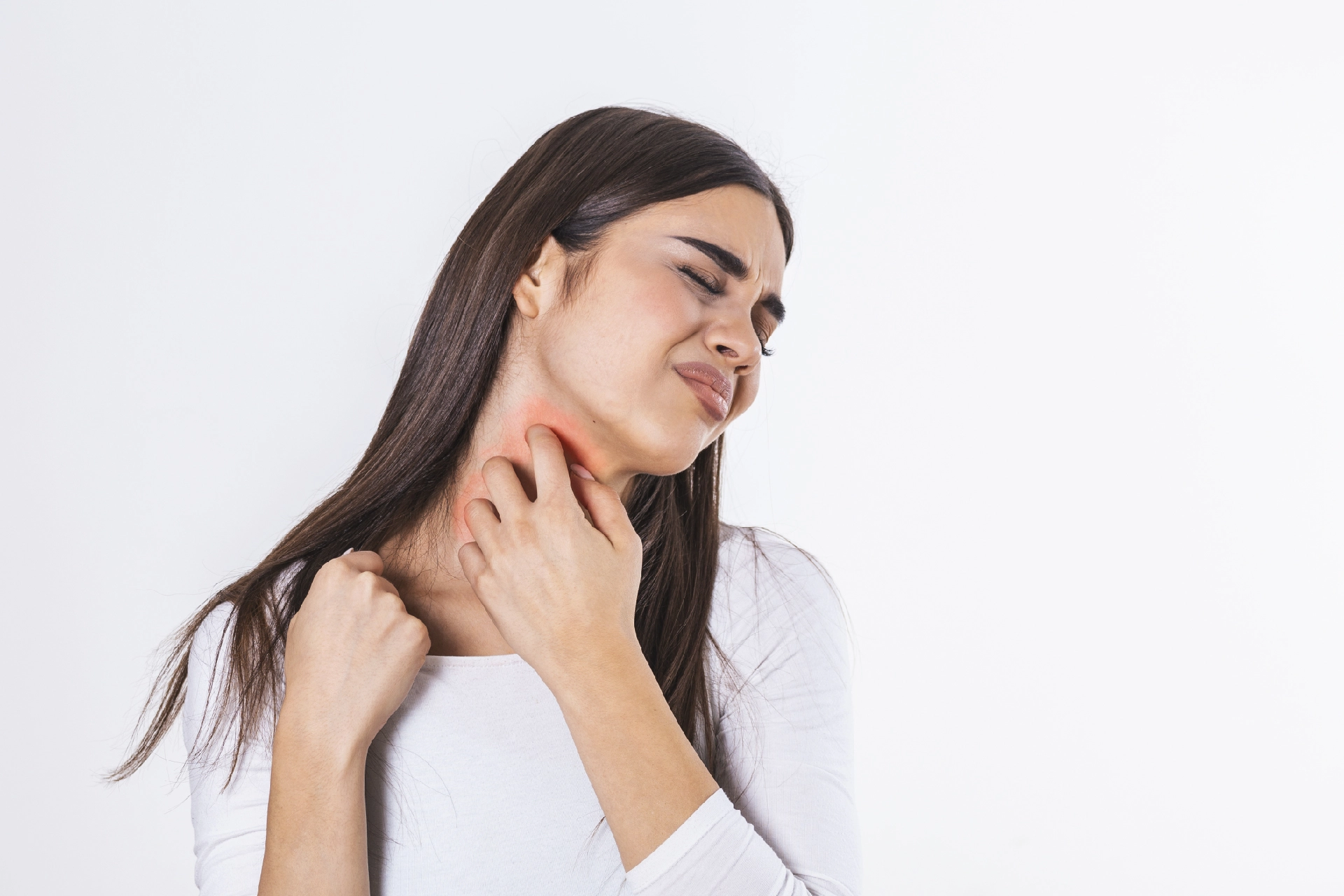
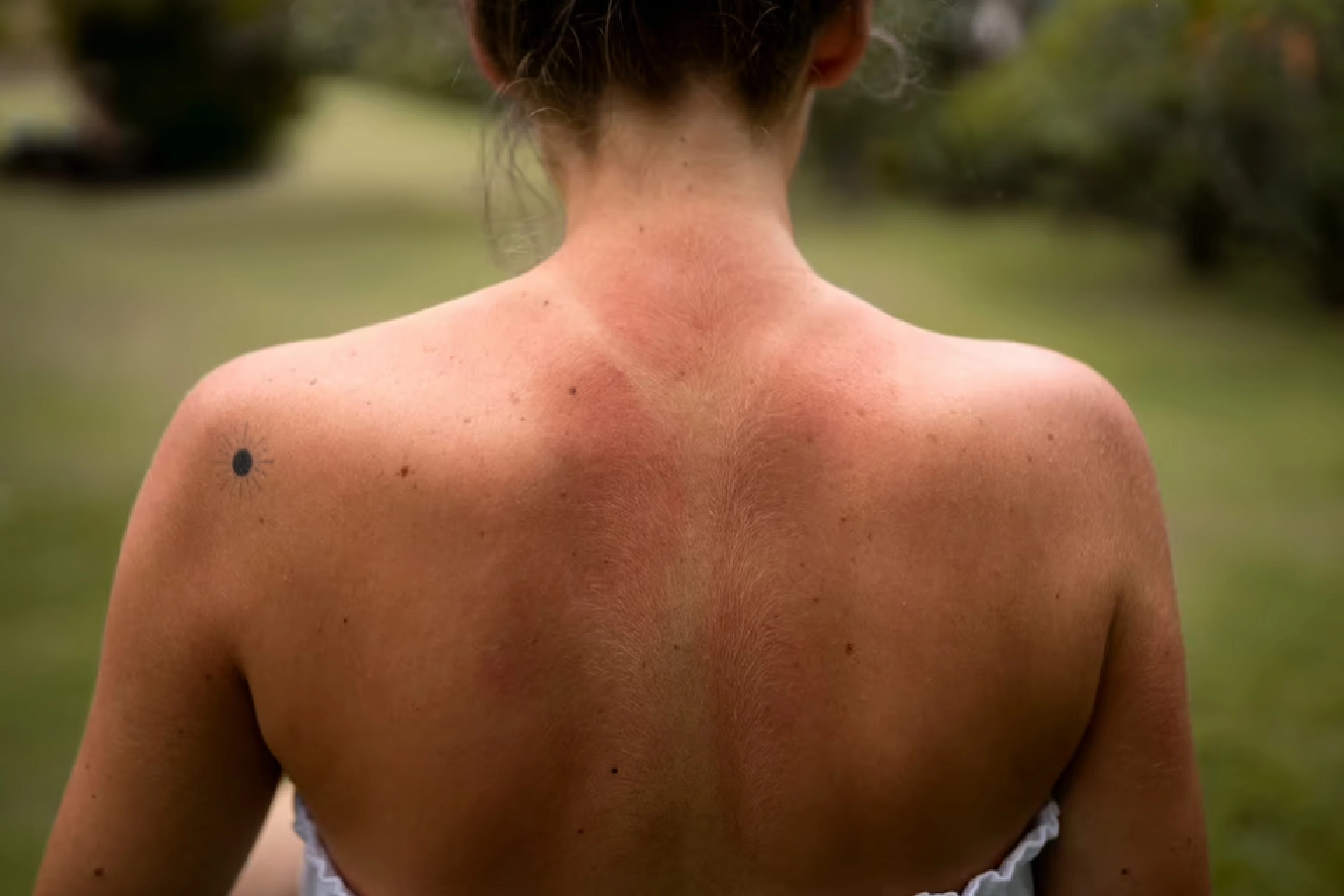
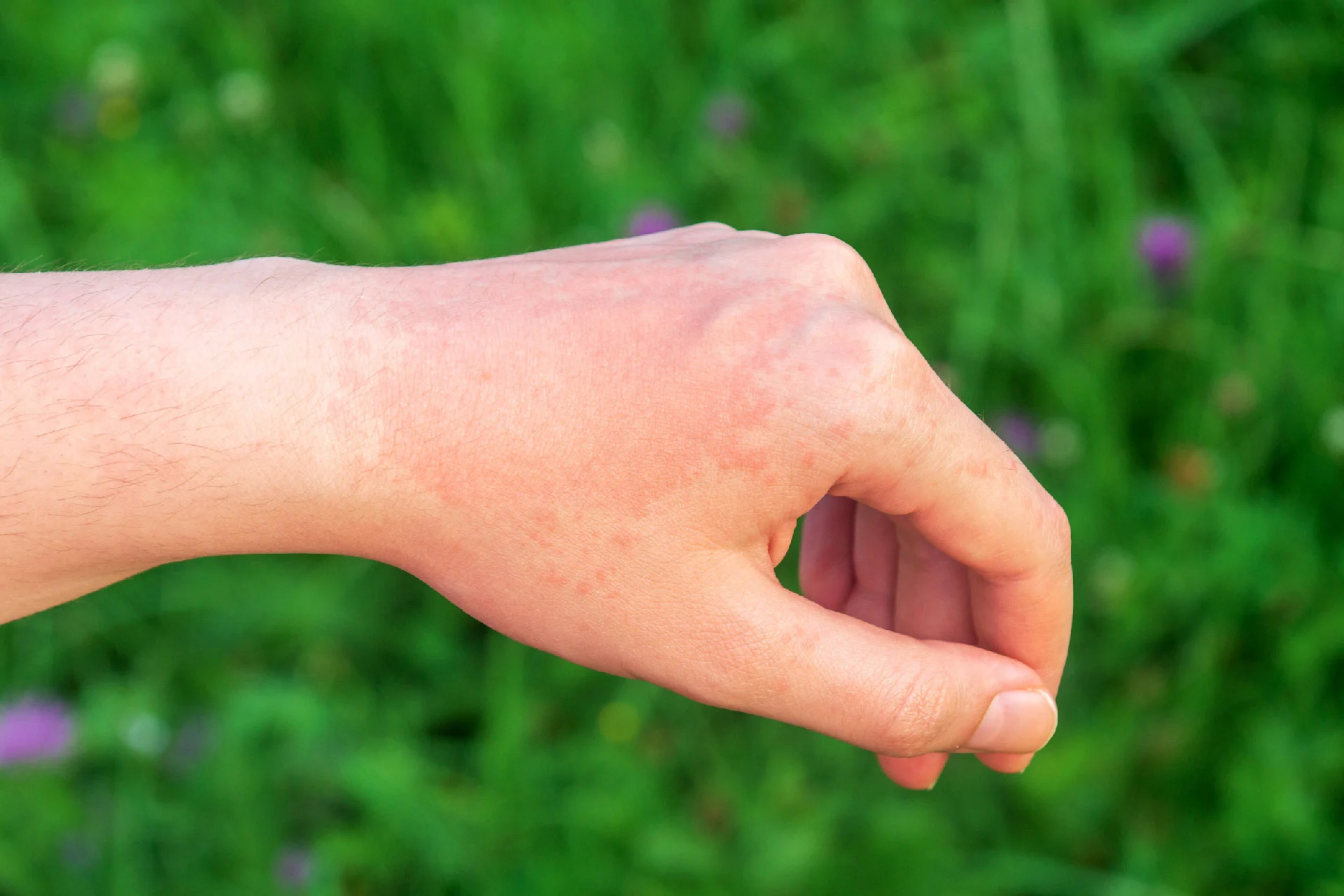
In general, cellulitis shows as a red, swollen, and painful region of skin that is warm and tender to the touch. The skin may seem pitted, similar to the peel of an orange, or blisters may form on the affected area. Some folks may also experience fever and chills. Cellulitis can arise anywhere on the body, although it is most frequent on the feet and legs.
Typically, cellulitis affects one side of the body. The warning signs of cellulitis can be:
- A sensitive region of the skin that becomes irritated
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Pain
- Warmth
- Fever
- Chills
- Spots
- Blisters
- Skin crevasses
If you have a skin problem similar to the eczema flare-Up or athlete's foot, you're more prone to get cellulitis. This is because these circumstances can develop cracks in your skin, which can allow bacteria to enter.
Symptoms of Cellulitis
Cellulitis causes your skin to become uncomfortable, heated, and swollen. The area is normally red, but this is less noticeable on brown or black skin. Symptoms of cellulitis include:
- The affected area feels uncomfortable and painful
- Skin shows redness or irritation
- A rapidly expanding skin rash or sore with tight, shiny, or puffy skin
- The presence of a warming sensation
- A feverish abscess with pus
- Like the surface of an orange, the skin seems bumpy or pitted
- A rapid heartbeat or rapid breathing
- Disorientation or confusion
- Cold, pale skin and clammy skin
- Loss of consciousness
Cellulitis symptoms that are more severe include:
- Shaking
- Chills
- Being sickly tired
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Aching muscles
- Heated skin
- Sweating
If cellulitis is not treated, it might spread to other body parts. You can experience a few of the symptoms listed below if it spreads:
- Dark brown or red streaks on the skin
- Lethargy
- Blisters
- Exhaustion
How to Treat Cellulitis Fast
Antibiotics are normally taken orally for at least five days as part of the cellulitis treatment. Additionally, your doctor might advise painkillers. But occasionally, medical professionals will start giving intravenous (IV) antibiotics as soon as they recognize symptoms.
Rest is advised till your symptoms become better. Oral antibiotics may not work for severe cellulitis instances. Your healthcare practitioner will use a tiny needle and tubing to administer the IV antibiotics directly into a vein if you need to be hospitalized.
7 to 10 days after taking antibiotics, cellulitis should clear up. [2] If your infection is more serious, your treatment may take longer.
Keeping the affected limb elevated can help reduce swelling and hasten the healing process if the infection is in the arm or leg.
It is crucial to take all the medications your doctor prescribes, even if your symptoms disappear within a few days.
Additional Read: Hives On Skin
Cellulitis Diagnosis Criteria
The doctor will ask you about symptoms and examine the affected area physically in order to determine whether you have cellulitis. Hence, cellulitis is most likely diagnosed by examining your skin. To rule out other conditions, you may need to have a blood test or other tests performed.
A physical examination may reveal the following:
- Skin edemas
- Redness and warmth in the afflicted area
- Glandular swelling
How to Prevent Cellulitis Infection?
Cellulitis can reoccur in certain people. Having cellulitis once does not make a person immune to getting it again. There are steps you can follow to protect yourself and others even though there is no vaccine to prevent group A strep infections.
You should do the following to help prevent group A strep infections:
Frequently wash your hands
- Frequently washing your hands is the most effective technique to avoid contracting or transmitting group A strep infection. This is especially crucial after coughing or sneezing, as well as before preparing or consuming meals
Cleanse and treat injuries
- Wash your hands often: If it is not possible to clean your hands with water, then you can use an alcohol-based hand rub
- Clean Wounds: With soap and water, clean any minor cuts or wounds that break the skin (such as blisters and scratches)
- Bandaged injuries: Clean and dry bandages should be used to cover draining or exposed wounds until they heal
- Go to a doctor: For a puncture and other serious wounds, visit a doctor.
Protect Infections and Wounds
- Avoid being in the following places if you have an open wound or skin infection:
- A hot tub
- Watering holes
- Natural water bodies (e.g., Oceans, Lakes, Rivers)
- Avoid being in the following places if you have an open wound or skin infection:
What Complications Can Arise From Cellulitis?
If the infection is not treated immediately, other parts of the body, including bones, muscles, and blood, can also get affected. Cellulitis complications can be serious if left untreated duly. Complications may include:
- Severe tissue damage (gangrene)
- Amputation
- Damage to diseased internal organs
- Septic shock
- Death
The other complications of cellulitis include the following:
- Bacteremia (blood infection)
- Arthritis with pustules (bacterial infection in a joint)
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
- Endocarditis (swelling of the heart's inner chambers and heart valves' inner linings)
In addition, thrombophlebitis can result from cellulitis (swelling by a blood clot in a vein).
Types of Cellulitis
According to the location of the infection, there are many forms of cellulitis.A few examples are:
- Cellulitis that appears around the eyes is periorbital cellulitis
- Face cellulitis manifests around the cheeks, nose, and eyes
- Cancer of the breast
- Perianal cellulitis manifests itself around the anal orifice
The hands and feet are two places on the body where cellulitis can develop. Cellulitis typically affects the lower leg in adults but the face or neck in youngsters.
Cellulitis, an infection in the deeper skin layers and the tissue below, can be extremely uncomfortable and potentially fatal. However, when treatment is sought as soon as symptoms arise, it is likely that it will be cured without any complications.
If you need a consultation with a dermatologist, you can talk to the experts at Bajaj Finserv health. In addition, you can choose the best physicians in your area, make appointments, set up reminders for taking your medications, save all of your medical information in one location, and more.
References
- https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-hcp/cellulitis.html#:~:text=Cellulitis%20is%20an%20infection%20that,Streptococcus%20(group%20A%20strep).
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/cellulitis/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.