Psychiatrist | 9 min read
Dementia: 5 Common Types, Symptoms and Risk Factors
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most common forms of dementia
- Vascular, mixed and Lewy body are different dementia types
- Mood swings and forgetfulness are a few dementia symptoms
Dementia is a broad term for different symptoms affecting your thinking, social capabilities, and memory [1]. Dementia symptoms can interfere with your normal life. But we cannot think of dementia as a specific condition. Instead, a group of diseases affecting your thinking abilities results in this condition. One of the main symptoms of dementia is memory loss.
Memory loss does not always indicate dementia, but it is one of the earliest signs you should not ignore. Since it affects your cognitive skills, it can hinder your ability to comprehend, calculate and grasp new concepts. WHO reports that approximately 55 million people are suffering from dementia [2]. One of the most common forms of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease. It contributes to approximately 60-70% of total dementia cases. Read on to know more about this condition and its symptoms.
Additional Read: Types of Mental IllnessesThe difference between dementia and Alzheimer’s disease
These words get frequently used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Dementia is not a particular illness. It's an all-encompassing term that covers a variety of symptoms. The ability of people to carry out daily tasks on their own gets impacted by these symptoms:
- Decreased memory
- Altered thinking
- Impaired judgment and reasoning
- Diminished focus and attention
- Altered language
- Altered behavior
The most dominant kind of dementia is Alzheimer's disease, but it's not the only one. Dementia can have many different types and origins, including:
- Parkinson's disease dementia
- Lewy body dementia
- Frontotemporal dementia
- Vascular dementia
- Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy
- Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
- Huntington's disease
- Mixed dementia
Alzheimer's is a particular type of brain disease, whereas dementia is a general term. It gets characterized by dementia symptoms that progressively worsen over time. Early signs of Alzheimer's disease frequently involve changes in memory, thinking, and reasoning abilities because the disease first affects the area of the brain connected to learning. As the illness worsens, symptoms like confusion, behavioral changes, and other difficulties increase.
Who is more likely to get dementia?
Anyone can develop dementia, but the risk rises with age. While it's true that older people are more likely to develop dementia, it's also critical to know that most older people do not. It occurs mainly due to brain disease rather than being a typical aspect of ageing. Younger onset dementia is the term used to describe the rare occurrence of dementia in individuals under 65.
There are a few uncommon types of inherited dementia, which are known to be brought on by a particular gene mutation. Most dementia cases, however, do not involve these genes, but those who have a family history of dementia do have a higher risk.
The risk of dementia may also get influenced by lifestyle and general health. For example, untreated vascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure, and less physically and mentally active people are more at risk.
What are the types of dementia?
Dementia has three groups:
• Primary (conditions and illnesses where dementia is the primary ailment)
• Secondary (dementia due to another condition or disease)
• Reversible signs and symptoms of dementia caused by additional ailments or factors
There are different types of this disease which include:
There are different types of this disease which include:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Vascular dementia
- Lewy body dementia
- Mixed dementia
- Frontotemporal dementia
While there are many causes that result in dementia symptoms, one of the possible causes is a mutation in your genes. This may pass on from one generation to the other. One of the most important genes linked to this condition is apolipoprotein E4 or APOE.
If you are struggling with Alzheimer’s disease, there may be plaques and tangles in your brain. These protein clumps can damage your healthy neurons and the fibers that connect these neurons.
What are the early signs of dementia?
- Inability to do daily tasks
- Memory issues, particularly recalling recent events
- Growing confusion
- Diminished concentration
- Personality or behavioral changes
- Apathy and withdrawal or depression
People occasionally fail to recognize that these symptoms point to a problem. They might erroneously believe that such behavior is typical of ageing. Additionally, symptoms might appear gradually and go unnoticed for a long time. Furthermore, even if they know of a problem, some people may choose not to visit the doctor.
Symptoms of dementia
In vascular dementia symptoms, blood vessels supplying blood to the brain are severely damaged. This leads to stroke or damage of nerve fibers in the brain. A few common symptoms of this type include:
- minimal focus
- slow thinking
- problem solving difficulties
- memory loss
Lewy body dementia is a condition where certain balloon-like protein clumps forms in your brain. Neurologist Friedrich Lewy discovered this condition, which gives it its name. Protein clumps formed by this dementia are called Lewy bodies. Some common signs of this type include:
- visual hallucinations
- attention loss
- focus issues
Impaired nerve cells in the temporal and frontal lobes of your brain result in frontotemporal dementia. This condition can affect your:
- personality
- judgement
- thinking abilities
- behavior
Mixed dementia usually affects people who are above 80 years of age. As the name suggests, this condition occurs as a result of different dementia types.
What are the causes of dementia?
Impairment to brain cells leads to dementia. This is because it prevents brain cells from communicating with one another. Thinking, behaviour, and feelings can get impacted when brain cells do not communicate normally.
The brain has various regions, each of which performs a different function. (For example, memory, judgment, and movement). Damaged cells prevent them from normal functioning.
For instance, high levels of specific proteins inside and outside of brain cells contribute to Alzheimer's disease by making it difficult for brain cells to maintain their health and communicate with one another.
In addition, memory and learning get controlled by the hippocampus, a region of the brain, and this part of the brain frequently experiences damage first. For this reason, memory loss is usually the first sign of Alzheimer's.
When this condition is treated or addressed, thinking and memory issues brought on by the following conditions may improve:
- Depression
- Side effects of medications
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Thyroid issues
- Lack of vitamins
The changes taking place inside your brain are what cause this condition. Though the exact reason is unknown, experts link many genetic mutations to dementia. Nerve cell damage and impaired connections can lead to dementia. Based on the affected part of your brain, your symptoms may also differ.
Dementia risk factors
There are many risk factors you can attribute to this condition. One of the most important ones is age. Though dementia can occur in young people too, it is more likely to affect those above the age of 65 years. If you have a family history of dementia, you are at a higher risk of this condition. If you have Down’s syndrome, it is also possible for you to develop early dementia symptoms.
There are a few risk factors that you may be able to modify by making slight changes in your lifestyle.
- Lack of nutrition and exercise
- Cardiovascular risk factors
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- Depression
- Smoking
- Air pollution
- Vitamin and nutritional deficiencies
Dementia symptoms
Here are a few common symptoms you may notice in the early stage of this condition.
- Confusion
- Poor vocabulary
- Mood swings
- Anxiety and anger issues
- Inability to adapt to new changes
- Apathy
- Forgetfulness
- Difficulty in completing your daily routine
Dementia treatment
While there is no permanent cure for this condition, certain medications may help you manage dementia symptoms. Cholinesterase inhibitors may help in reversing the symptoms of this condition [3]. Doctors prescribe memantine to improve the functioning of your brain. To reduce symptoms like depression and sleep issues, doctors may give you other medication. You can manage this condition by following occupational therapy and practicing mindfulness techniques. All these remedies can boost the functioning of your brain.
Additional Read: Boost Your Mental Health ResolutionHow is Dementia diagnosed?
A dementia diagnosis can be challenging to confirm. Dementia can be brought on by or progress to other illnesses and conditions. Many of its symptoms are also present in numerous other diseases.
Your doctor will:
• Enquire about the progression of your symptoms
• Enquire about your medical background
• Examine your current medication regimen
• Find out if Dementia or other diseases run in your family
They may also request tests, such as lab, imaging, and neurocognitive tests (Thinking tests)
Complications in Dementia
All of your bodily functions get coordinated by your brain. Eventually, as your brain functions deteriorate, your general health deteriorates too. Dementia can lead to a variety of diseases and conditions, such as:
- Dehydration and malnutrition
- Bedsores (pressure ulcers)
- Fall-related injuries and bone fractures
- Strokes
- Cardiac arrests
- Kidney disease
- Aspiration pneumonia and pneumonia (food particles get inhaled into your lung and cause infection)
- Sepsis (Infection)
Can you prevent Dementia?
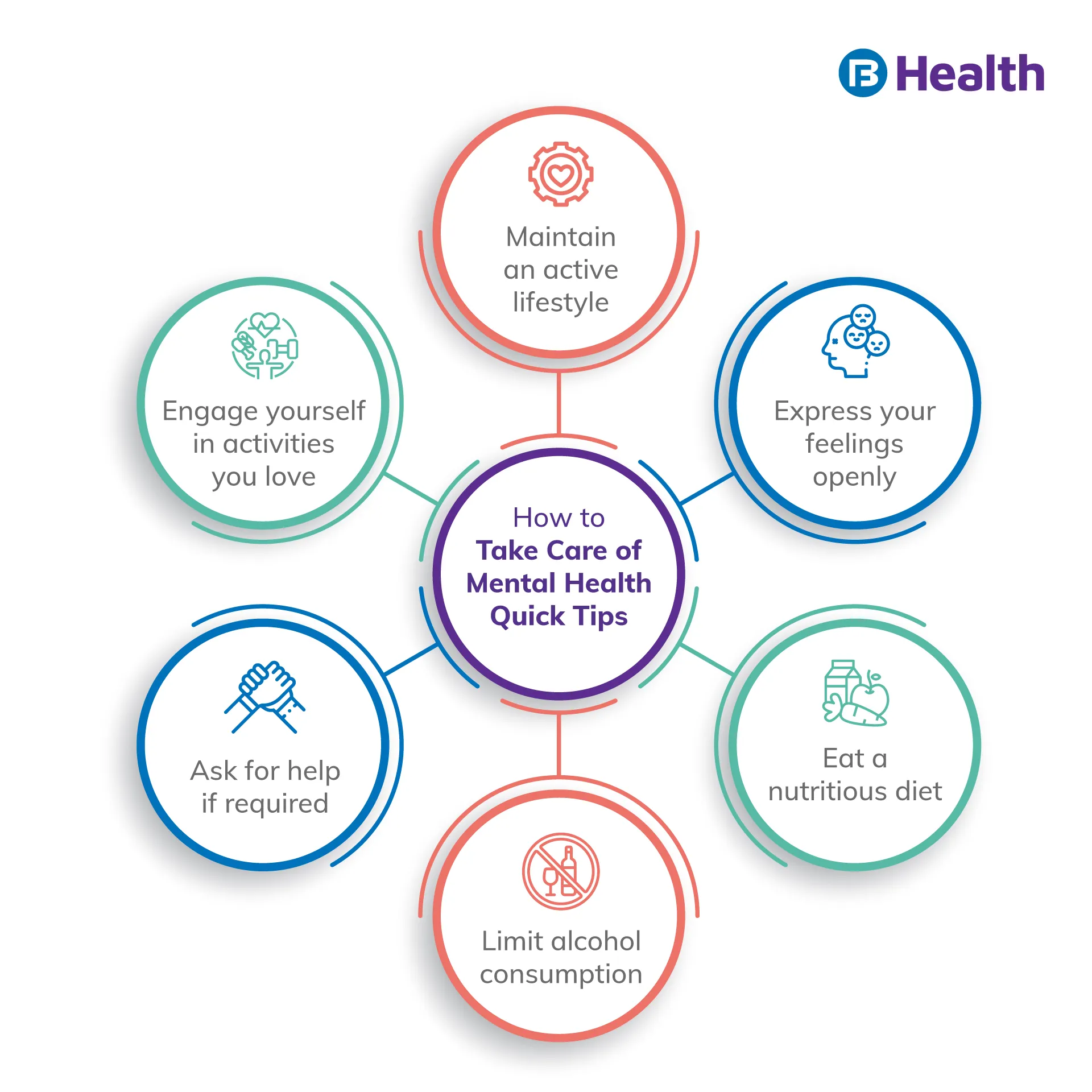
Even though Dementia cannot be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may lessen the risk factors for some forms of Dementia.
Your brain requires oxygen and nutrients to function at its highest level by maintaining blood vessels free of cholesterol build-up, normal blood pressure, healthy blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, etc., and staying as healthy as possible.
Actions you can take are as follows:
- Give up smoking
- Eat a diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, fish, shellfish, nuts, beans, olive oil, and little to no red meat, such as the Mediterranean diet
- Exercise. Walk for at least 30 minutes most days a week
- Keep your mind active. Play word games, solve puzzles, and engage in other mentally challenging activities
- Maintain your social life. Engage your mind, heart, and soul by interacting with others and chatting about current events
What are the early stages of dementia?
Dementia typically progresses through these stages. However, it might differ based on the part of the brain that is affected.
1. No disability
A person in this stage does not exhibit symptoms, but tests could find a problem.
2. Very slight decline
Your loved one will remain independent, though you might observe some behavioral changes.
3. A slight decline
- More shifts in their reasoning and way of thinking will become apparent
- They might struggle with making plans and frequently speak in the same way
- They might also struggle to recall recent events
4. Moderate deterioration
- Dementia patients, in this stage, struggle more to remember recent events and make plans
- They might find it challenging to handle money and travel
5. A decline that is not too severe
- Dementia patients might not recall the phone numbers or names of their grandchildren
- They might be uncertain of the time or the day of the week
- They will now require assistance with a few basic daily tasks, like choosing what to wear
6. A drastic decline
- Start to lose track and may even forget the name of their spouse
- Eating and using the restroom will require assistance
- Their emotions and personality may change
7. Extremely rapid decline
- Unable to express ideas verbally
- Walking becomes challenging
- They will be in bed for the most part of the day
Dementia management
You can manage this condition by doing exercise on a daily basis. This helps improve your cardiovascular health and increases your strength. Another way to manage it is to try and communicate in simple sentences. Doing different activities like dancing, singing or painting also helps. They help you focus and increase your concentration.
It is important to look after your mental health and that of your loved ones. If you notice any warnings signs of neurological conditions, do not ignore them. Talk to a mental health specialist at the earliest. Now, you can connect with top psychologists on Bajaj Finserv Health. Book an online doctor consultation and address all warning signs without any delay.
References
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-is-dementia#:~:text=Dementia%20is%20the%20loss%20of,and%20their%20personalities%20may%20change.
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9170-dementia
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.