Gynaecologist and Obstetrician | 6 min read
Menstrual Cycle: Stages, Causes, and Symptoms
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
A menstrual cycle is a hormone-driven event that occurs in a woman’s body during the years between puberty and menopause. It is an important part of the woman’s reproductive system and prepares the body for a possible pregnancy.
Key Takeaways
- The menstrual cycle is the changes a woman’s body undergoes to prepare for pregnancy
- Normally, a menstrual cycle occurs once every 21 to 35 days
- Menstrual cycle irregularities may have various causes, and many can be treated
A menstrual cycle is a natural phenomenon that prepares a woman's body for a likely pregnancy. If not pregnant, the hormones signal the uterus to shed its lining, called the monthly period. The beginning of a period is the onset of the menstrual cycle, which repeats each month.
A menstrual phase calculation begins from the current period's first day to the next period's first day. Although every woman's cycle is different, the average length of the normal menstrual cycle is 28- 29 days. For instance, women in their teens may have 45 menstrual cycle days, while women in their 20's or 30's may have menstrual cycles ranging from 21-38 days.
The first period is called menarche, and the average age is 12-13 years, but it can begin as early as nine. When your period cycle completely stops, it is called menopause; the average age for it is 51-52, but some may attain menopause even at 60. [1]
Long menstrual cycles may occur during the early years but tend to shorten and become regular as you grow older. When you get closer to menopause, your menstrual cycle may become irregular. However, there is an increased chance of women developing endometrial cancer as they age, and you must do online doctor consultations immediately if you notice any irregular bleeding.
Certain contraceptives, birth control pills, and IUDs (intrauterine devices) can cause your menstrual cycle to vary. You can consult your physician to understand what to expect.
Menstrual Cycle Symptoms
Some common menstrual cycle symptoms are:
- Mood swings
- Food cravings
- Trouble sleeping
- Abdominal cramps
- Breast tenderness
- Acne
- Bloating

How can I Track My Menstrual Cycle?
To track the menstrual cycle with maximum accuracy, you must count the days between your last few periods. Start counting from the first day of your period to the day up to the next period. Do this for a few cycles, add the total number of days, and divide by the number of cycles to figure out the average days in your menstrual cycle.
Apart from basic tracking, you can monitor certain data points to gauge delays, misses, and other irregularities in your menstrual cycle. Some of these points may be heavy flow, mood swings, and changes in appetite and energy levels. To alleviate concerns about your cycle, try tracking the following parameters:
- The duration of your period
- The heaviness of the flow
- Any abnormal bleeding patterns
- The level of pain associated with the menstrual cycle
- Changes in mood or behavior
Cause of Irregular Menstrual Cycle?
The most common irregularities associated with menstrual cycles are:
- Periods that occur earlier than usual or polymenorrhea
- Missed period
- Periods that last longer than usual
- Painful periods
- Spotting or bleeding in between periods
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding
A missed period is usually the main indicator of pregnancy. Breastfeeding after pregnancy and delivery also delays the onset of menstruation.
Eating Disorders/Extreme Exercise or Weight Loss
Eating disorders, extreme weight loss, and sudden increased physical activity can disrupt the menstrual cycle to a large extent.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (or PCOS) is a common endocrine system disorder that may cause irregular periods and enlarged ovaries with small fluid collections called follicles.
Premature Ovarian Failure
Some women may lose normal ovarian function before age 40, referred to as premature ovarian failure or primary ovarian insufficiency. They may cause irregular and missed menstrual cycles for years.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, or PID, is an infection of the reproductive organs that can lead to irregular menstrual bleeding.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign, non-cancerous growths in the uterus. This condition can cause heavy bleeding and prolonged menstrual cycles.
Additional Read: Uterine Fibroids: Symptoms, Causes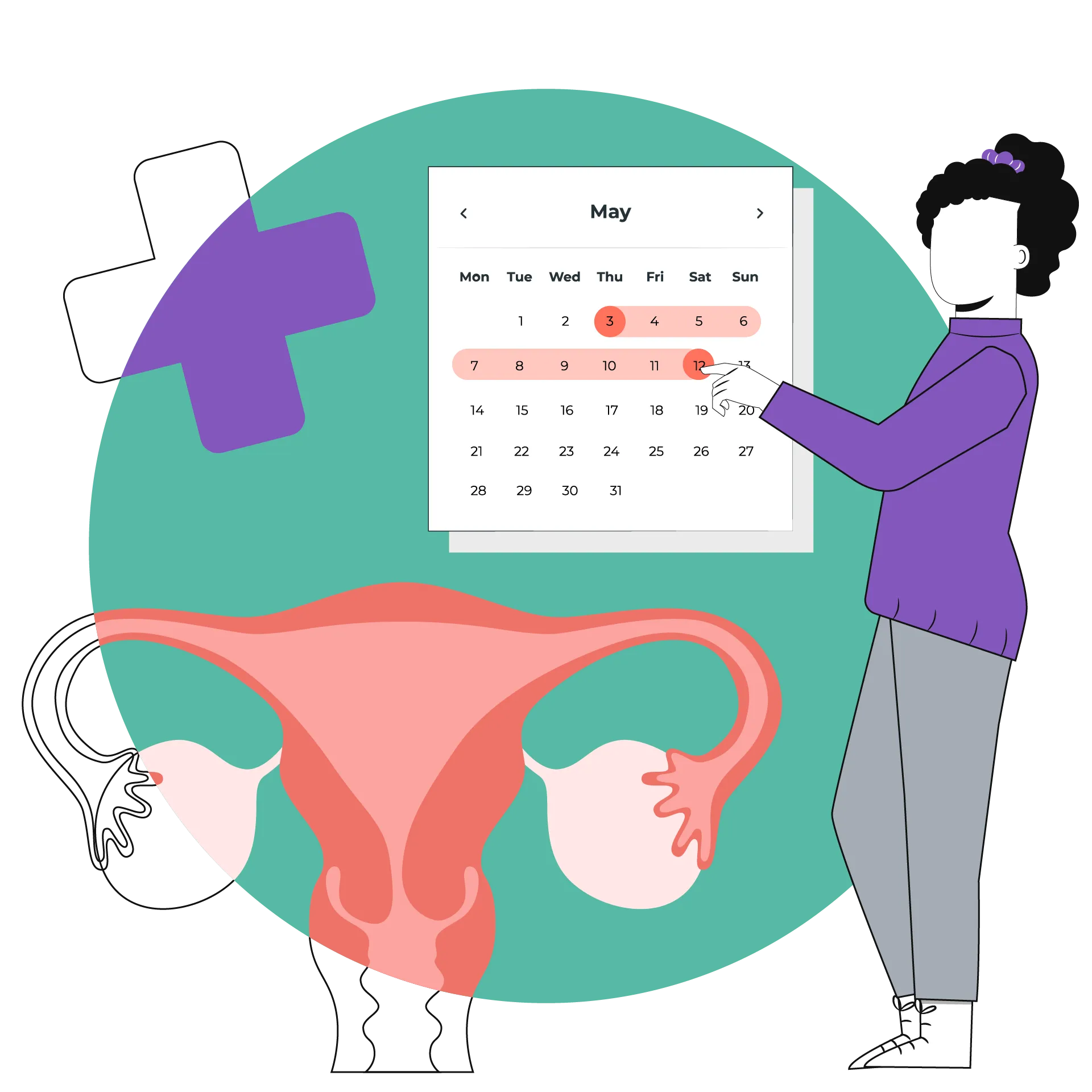
Stages of Menstrual Cycle
The count of the menstrual cycle begins on the first day of menstruation. Under the assumption that the length of the menstrual cycle is 28 days, the complete timeline of the menstrual cycle can be split into four stages:
1. Menstrual Phase
The menstrual phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts till the 5th day of the menstrual cycle. The events below occur during this phase:
- The uterus discards the innermost lining of soft tissue and blood vessels that go out of the body through the vagina
- Blood loss of around 10ml to 80ml is considered normal
- Abdominal menstrual cramps are common and caused by the contraction of abdominal and uterine muscles
2. Follicular Phase
This phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts till the 13th day of the cycle. The following events occur during this phase:
- The pituitary gland secretes hormones that help the egg cells in the ovaries grow
- One of the egg cells matures (in about 13 days) in a follicle which is a sac-like structure
While the egg cell becomes matured, the follicle releases a hormone that makes the uterus form a lining of soft tissue and blood vessels called the endometrium.
3. Ovulation Phase
This phase occurs on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle when the pituitary gland releases a hormone that makes the ovary release a developed egg cell. The released egg cell goes into the fallopian tube by the cilia - finger-like projections called fimbriae. Fimbriae are located at the end of the fallopian tube near the ovaries. Cilia are hair-like projections that occur on each fimbria.
4. Luteal Phase
This phase begins on the 15th day of the menstrual cycle and goes on till the end. The events below can be noticed in this phase:
- The egg cell released during ovulation remains in the fallopian tube for up to 24 hours
- If a sperm cell does not penetrate the egg cell during that time, the egg cell breaks apart
- The hormone that makes the uterus maintain its endometrium is used up by the end of the menstrual cycle. It leads to the onset of the menstrual phase of the next cycle
Identifying Common Issues
It is vital to identify the common issues that may occur in menstrual cycles in women and know how to treat them:
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Hormonal changes in women before their menstrual cycle can trigger several difficulties, including headaches, bloating, irritability and fatigue. This can be treated through diet and exercise.
Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea means painful periods when the uterus puts more pressure than required to expel the lining. Pain-relieving medication can be a treatment option.Heavy menstrual bleeding
If this condition is left untreated, it may result in anemia. One can take oral contraceptive pills or an intrauterine hormonal.
How to Regulate the Flow
- Amenorrhea – Amenorrhea means non-occurrence of periods. This condition is not normal except for certain situations such as pregnancy, lactation, or menopause. The likely causes of this issue are too much or too little body weight and heavy exercise.
You must contact your gynecologist if:
- Your menstrual cycles haven't begun until you are 18
- You stop menstruating suddenly
- You are bleeding more than usual
- You have very painful periods
- Your periods have not returned after stopping birth control pills for three months
- If you doubt a possible pregnancy
Menstruation is a normal physiological process for every woman. If you think any part of your menstrual cycle has altered, you must track it and keep a record. Once you identify any unusual symptoms, you can consult a doctor. Choose a comprehensive and customised healthcare plan to secure your healthcare needs with the help of Bajaj Health Finserv.
References
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-menopause
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.