Health Tests | 7 min read
RDW Blood Test: High Causes, How to Lower RDW , Normal Range
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
The doctor prescribes an RDW blood test (Red cell distribution width) mostly if they suspect anemia. The test measures the variations in size and volume of red blood cells. This test helps to understand the cause and type of anemia. However, the RDW test is not used alone to understand the health condition. The value above or below the RDW blood test normal range indicates an underlying health problem.
Key Takeaways
- Anaemia is a state with a low number of red blood cells
- The haemoglobin, the main protein in the red blood cells, carries oxygen throughout the body
- The variation in the RDW blood test normal range interrupts the flow of oxygen, resulting in other health conditions
What is the RDW Blood Test?
The RDW blood test checks the possibility of anemia by measuring the difference in size and shape of red blood cells. The human body requires oxygen to run normally. The RDW blood test normal range enables red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body. Whereas anything outside this range signals a possible health problem that may affect body function.
The standard size of red blood cells is 6 to 8 micrometers [2]. The red blood cells are similar in normal conditions, although the high RDW blood test indicates the need for medical treatment.
The RDW test is often part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test; however, it is not the only parameter. In spite of this, it provides a higher meaning in the context of hemoglobin.
Uses of RDW Tests
The RDW blood test normal range is utilised to determine the possibility of anemia. The other uses of the RDW test include:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Liver disease
- Cancer
- Thalassemia
The RDW blood test is usually part of CBC, a complete blood count. It is a test that measures the number and characteristics of a blood component, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Low values of the RDW blood test normal range denote anemia. The health care providers orders CBC, which includes an RDW blood test if the person experiences the following cases:
- Vitamin or iron deficiency
- Chronic cases of diabetes, HIV, or Crohn's disease
- Excessive blood loss following surgery or injury
- Symptoms of anemia such as pale skin, dizziness, weakness, cold hands and feet
- Diagnosed with a disease that affects red blood cells
- Experiencing long-term infectious disease
- A family history of blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia, thalassemia
Preparing for RDW Test
A regular test will help you maintain the RDW blood test's normal range. The RDW blood test may require fasting before the test. The doctor will inform you of all the instructions in advance.
The procedure for the blood test is simple and takes less than 5 minutes. The health care provider inserts a small needle into the vein, and the blood flows into a tube. After collecting the required blood in the tube, the needle is removed, and the patient is asked to hold a piece of gauze to stop bleeding. The individual may feel uneasiness for a short time and if the discomfort or the bleeding continues, visit the doctor without delay.
Then the blood sample is sent to the laboratory for further testing.
What is a Normal RDW Range?
The RDW blood test normal range is 12-15%. In the adult female, it is 12.2 to 16.1 %, whereas in adult males, it ranges between 11.8-14.5 %. The percentage outside this range represents how much red blood cells in the given sample vary from the average size of blood cells.
To be more accurate about the condition, doctors may look at other tests, such as the MCV test, which is also a part of CBC.
The RDW blood test's low level indicates that red blood cells do not vary much from the actual measurement. In contrast, the RDW blood test's high level signifies that the size differs significantly, and the body faces difficulty making red blood cells.
The doctor also goes through the other blood test to be more specific about the treatment.
Causes of a High RDW Blood Test
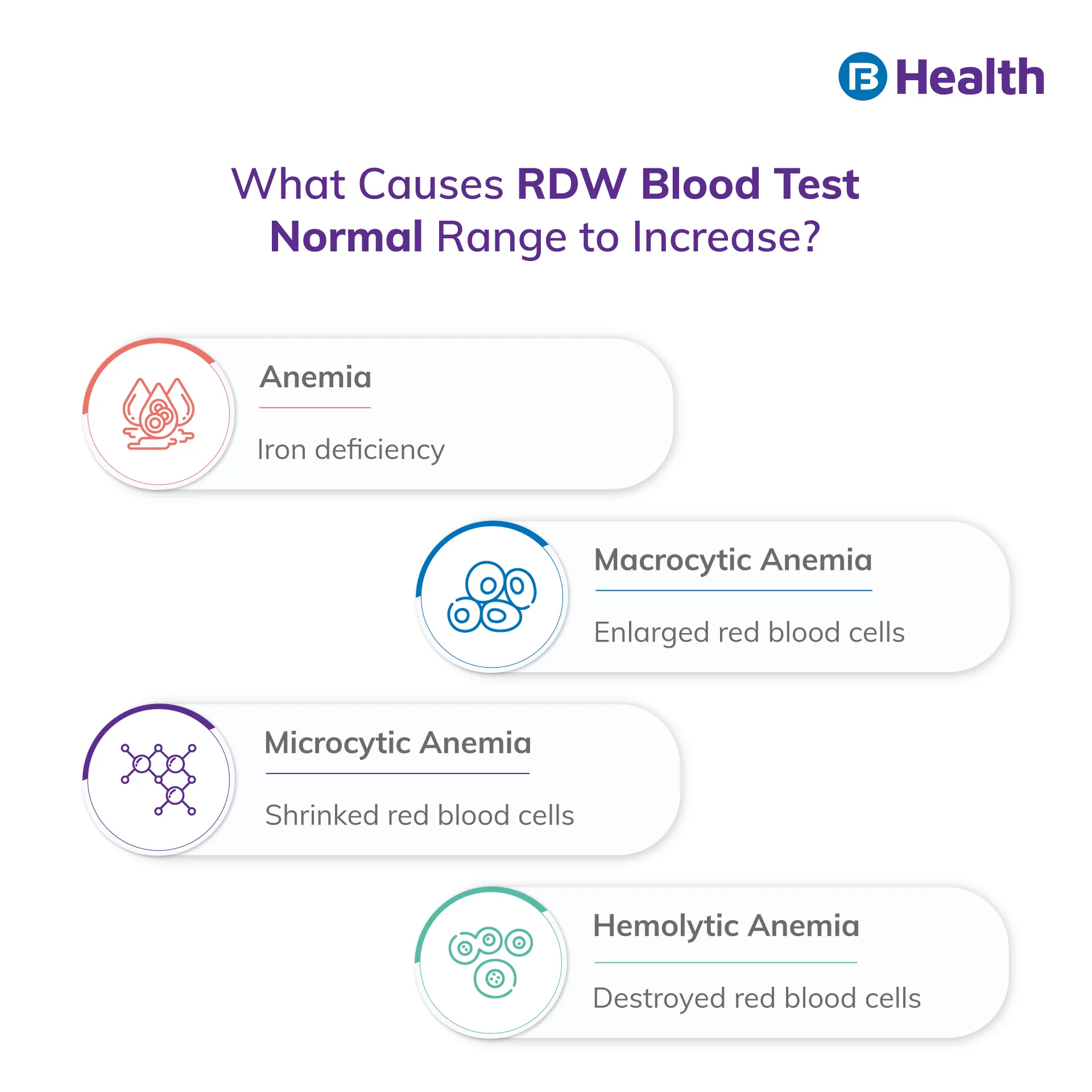
A high RDW blood test value indicates a deficiency of vitamin B-12. Folate and iron. The elevated level outside the RDW blood test normal range helps to identify the type of anemia. Here are the types of anemia associated with a high RDW blood test.
Macrocytic anemia:
Due to a deficiency of folate or vitamin B-12, the body doesn't produce enough blood cells, which are larger than usual. This will also be a reason for the RDW blood test normal range to go higher
Microcytic anemia:
The red blood cells are smaller than normal in this condition
Hemolytic anemia:
This type of anemia occurs when the body destroys the red blood cells faster than they are produced
Iron-deficiency anemia:
This occurs due to a deficiency of iron. In pregnant women, this can put the baby's development at risk. This reason also causes high levels of the RDW blood test normal range
RDW blood test high results can be due to:
- Liver disease: The RDW blood test elevates due to various liver diseases, including liver cancer, alcoholic liver cirrhosis, and hepatitis
- Blood transfusions – This factor reduces the accuracy of the RDW test. The blood cell difference between donor and recipient leads to the hike. However, in most cases, it is a temporary change
- Cancer: Various factors like chronic inflammation and poor nutritional status may interfere with red blood cell production. Hence this leads to high RDW blood tests in cancer patients
- Kidney Disease- Patients with decreased kidney function have a higher RDW blood test. A hormone called erythropoietin is essential for red blood cell production and development. During reduced kidney function, an abnormal flow of this hormone is seen, which results in an RDW blood test high
- Alcohol: Excess drinking may lead to the production of enlarged dysfunctional red blood cells. These larger blood cells perish faster than normal
- Inherited red blood cell disorder: Other factors include hereditary diseases like thalassemia and sickle cell anemia.
- Lifestyle: Not maintaining a proper lifestyle may also result in this condition. It is recommended to keep a sleep pattern of 7-8 hours. Anything below or above this range may affect red blood cells. People opting for rotational shifts also have a risk of RDW blood test high
- Inflammation: The elevated RDW blood test is found in people suffering from inflammation-associated diseases such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and PCOS. The anti-mullerian hormone is significantly higher in women suffering from PCOS. The higher RDW blood test is linked to impairment of erythropoiesis resulting in chronic inflammation and increased oxidative stress, both of which signal the presence of type 2 diabetes. Hence c peptide test helps to confirm diabetes. The c peptide test normal range is between 0.5 to 2.0 (ng/ml) or 0.17 to 0.83 (nmol/L)
- Autoimmune disorders: like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus also result in RDW blood test normal range hikes
- Hemorrhage: Internal bleeding may also result in high RDW blood tests
Additional Read: Iron Deficiency Anaemia

How to Lower RDW
As already discussed, lifestyle may also result in a high RDW blood test by making small changes to the daily routine. You can attain an RDW blood test normal range. Here are a few easy steps to control the elevated RDW test:
1. Improve Iron Deficiency
To manage iron deficiency, include iron-rich foods mentioned below.
- Egg yolks
- Beans
- Green vegetables like spinach, kale
- Red meat
- Dried fruits
2. Improve Folic acid Deficiency
To improve folic acids, include certain vitamin B-9 food in your diet.
- Nuts
- Cereals
- Lentils
- Peas
- Green vegetables
3. Improve Vitamin Deficiency
Include vitamin-A foods to increase red blood cell production.
- Carrots
- Red peppers
- Green vegetables, sweet potatoes
- Fruits such as watermelon, grapes
A B12 injection is recommended by doctors in case of difficulty in nutrient absorption:
- Regular Exercise: Daily exercise promotes well-being. Vigorous exercises develop a need for more oxygen for your body. Hence the brain signals to create more red blood cells. According to a study conducted by Medical News Today, increased weekly workout sessions reduced the risk of RDW blood test high. Exercise can be anything from jogging, running, and swimming.
- Sleep: Maintaining a good sleep pattern benefits a healthy life. Getting a proper 7-8 hours of sleep lowers the RDW level.
- Alcohol: Vitamins such as vitamin B12 and folate are required for red blood cell production. Excessive alcohol damages red blood cells and decreases the absorption of these essential nutrients.
- Smoking: RDW blood test high values can also be aggravated because of smoking for long durations. Therefore, quitting smoking is highly beneficial for overall well-being.
Other Tests
The doctor may recommend other tests, such as the PCV blood test (packed cell volume test), also called the hematocrit test, used to diagnose anemia, dehydration, and polycythemia. The test measures the number of red blood cells in the blood. With increased red blood cells, PCV blood test values also rise. The PCV test normal range for females is 36.1 to 44.3%, and for males, 40.7-50.3%.
Additional Read: Iron Test: Important to Check Your Iron LevelsMedical treatment at early stages ensures speedy recovery from anemia and maintains RDW blood test normal range. However, with delay, the complication level elevates and may become a life-threatening disease. Hence if you are witnessing any irregular symptoms like weakness or shortness of breath, consult the doctor immediately.
To consult the doctor at your convenience, you can visit Bajaj Finserv Health and get an online doctor consultation. It's quick and easy, and you don't even have to leave the comfort of your home. So why delay when a single click is enough to find the best health solution?
References
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/anaemia
- https://www.labce.com/spg579126_red_blood_cell_rbc_size_variation.aspx
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.