Paediatrician | 6 min read
Turner Syndrome: Meaning, Symptoms, Causes, Complications
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Synopsis
Turner syndrome is a disorder that affects females and is brought on by a missing or partially absent X chromosome. Short stature, the inability of the ovaries to mature, and heart anomalies are just a few of the medical and developmental issues that Turner syndrome may bring.
Key Takeaways
- Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects females and their quality of life
- Medical conditions and complications, like heart abnormalities and Infertility, are associated with Turner Syndrome
- Counselling with a mental health expert to cope with feelings of low self-esteem is helpful for Turner syndrome
Girls with Turner syndrome may experience particular medical issues and unique physical traits; thus, supporting them in acquiring life skills and learning how to handle unusual or difficult circumstances can be done in the following ways:
- Determine how much responsibility to assign and the kinds of social activities they like. Also, treat them as per their age, not their size
- Ask the teachers for assistance in making the necessary modifications so that the girls can access the school resources and other items
- Consider counselling with a mental health expert if a girl suffers from self-esteem issues or depression. Trust your gut feeling if you think they are depressed or withdrawing
Causes of Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome causes which are due to genetic alterations might be any of the following:
Monosomy
In most cases, a fault in the mother's egg or father's sperm causes a child to be born without an X chromosome. Thus, there is only one X chromosome in each cell
X chromosome alterations
The X chromosome can have altered or missing sections. Cells contain one original copy and one modified copy. With each cell having one full and one revised copy, this defect can happen in either the sperm or the egg. Or the fault might happen during early embryonic cell division, leaving only some cells with the altered or missing pieces of an X chromosome
Y chromosomal components
Some cells in Turner syndrome contain one copy of the X chromosome, whereas other cells have one copy of the X chromosome plus some Y chromosomal material. Although these people grow physiologically as females, the Y chromosomal material raises the chance of gonadoblastoma, a kind of cancer
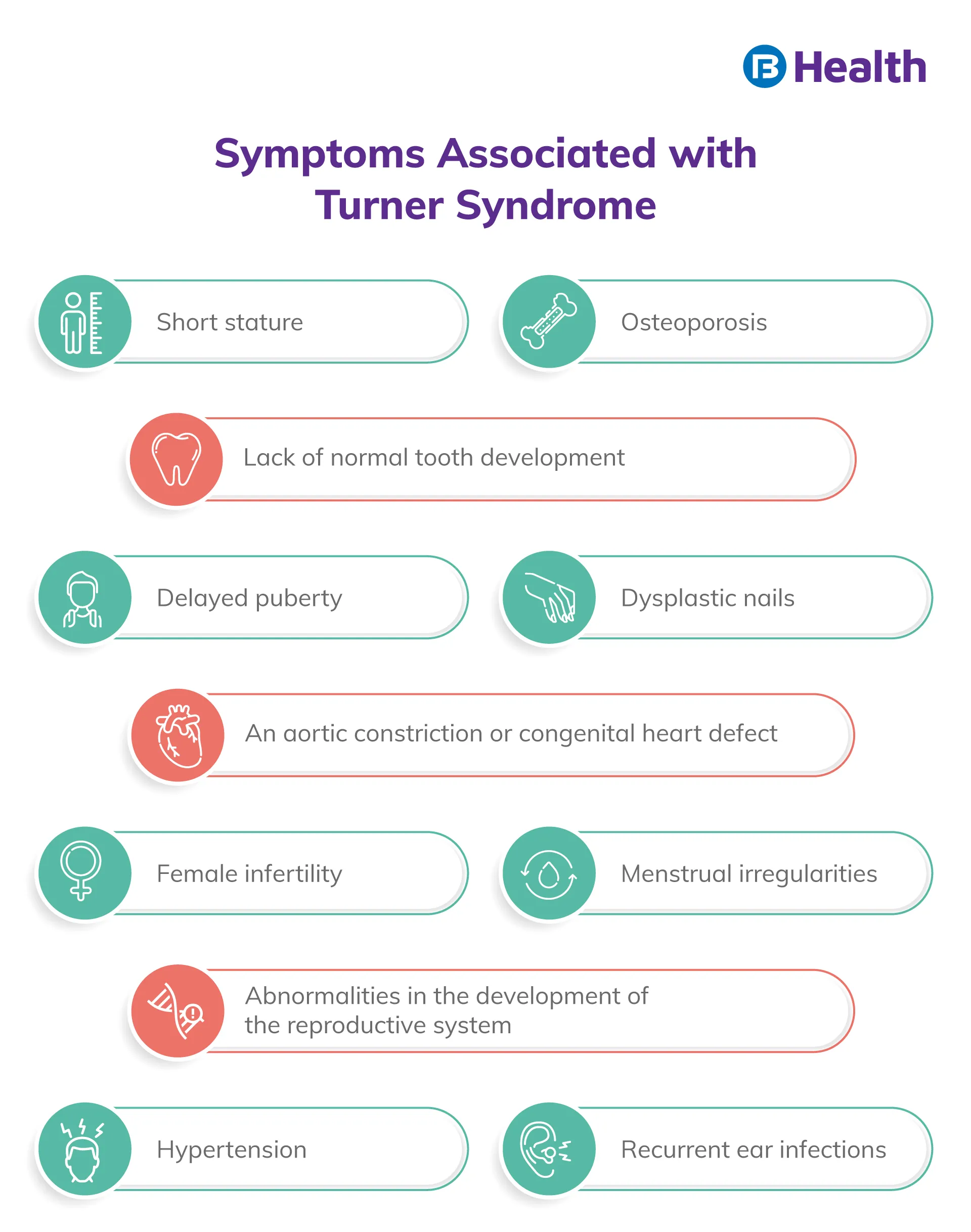
Symptoms of Turner Syndrome
Girls and women with Turner syndrome may exhibit various signs and symptoms. Turner syndrome symptoms may not always be evident in girls, but in some instances, it manifests physically in several ways that are noticeable from an early age. The most prominent sign is short stature, the opposite of which can be seen in gigantism. Signs and symptoms might be minor, slowly arising over time, or severe, like heart abnormalities.
Before Birth
An infant with Turner syndrome may exhibit the following during pregnancy:
- Significant fluid buildup at the back of the neck or other unusual fluid collections (oedema)
- Heart conditions
- Abnormal kidneys
At the Time of Birth or Infancy
Turner syndrome symptoms that may be present at birth or in a baby include:
- Web-like or wide neck
- Drooping ears
- Nipples that are widely spread on a broad chest
- The roof of the mouth (palate) is tall and thin
- Elbows that extend outward in the arms
- Light, upward-curving toenails and fingernails
- Swelling of the hands and feet, particularly during pregnancy
- Somewhat shorter at birth than usual in height
- Sluggish growth
- Cardiac issues
- Receding or tiny lower jaw
- Short toes and fingers
Additional read: How to Accurately Measure Your Height at Home
In Adolescence, Childhood, and Adulthood
The most prevalent Turner Syndrome symptoms in nearly all adolescent girls, teens and women are shorter stature and ovarian insufficiency due to ovarian failure. Ovarian failure can start at birth or evolve gradually during infancy, adolescence, or young adulthood. These include the following signs and symptoms:
- Sluggish growth
- No growth spurts at the typical ages of infancy
- Adult height is far less than what may be anticipated
- Expected sexual changes at puberty do not occur
- Teenage years see a 'halt' in sexual development
- The inability to conceive without fertility treatment affects most females with Turner syndrome
Diagnosis of Turner Syndrome
Parents typically see the signs of Turner syndrome. They occasionally notice signs immediately; other times, it happens in early childhood. For instance, they could notice:
- Skin webbing on the neck and swollen hands or feet
- The growth that stops or short growth patterns
Stunted and slow growth is the main symptom. In contrast, other genetic disorders like progeria cause children to age rapidly.
It can be determined genetically via a procedure called karyotype analysis. It can tell if an X chromosome is wholly or partially absent.
The diagnosing process includes a thorough evaluation of the heart because many patients have cardiac issues.
Additional read: Height Weight Chart For Men and WomenTreatment of Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome treatment usually emphasises hormone treatment and care for associated medical conditions. Treatments might consist of:
Human growth hormone
Human growth hormone injections can make you taller. These injections can add several inches to a patient's ultimate height if therapy is initiated early [1]
Estrogen Therapy
People with Turner Syndrome frequently require estrogen treatment, a female hormone. Girls who get this hormone replacement treatment may grow breasts and start menstruating. Additionally, it can aid in the uterus's average-size growth. Estrogen replacement also enhances bone health, heart health, liver health, and brain growth.
Cyclic progestins
If blood tests reveal a shortfall, these hormones are frequently administered from age 11 or 12. Progestins will bring on cyclic menstruation. Therefore, the doses are often initiated at extremely low levels and then progressively raised to replicate natural puberty.
Additional read: Low Estrogen SymptomsComplications of Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome complications can interfere with the healthy growth of several bodily systems. However, this differs widely amongst individuals with the disease. Among the potential complications are the following:
1. Heart issues
Many newborns with Turner syndrome are born with cardiac defects or even minor structural variations in the heart, which raises their chance of developing life-threatening issues. The aorta is a significant blood conduit that branches from the heart and carries oxygen-rich blood to the body. As a result, heart abnormalities frequently include problems with the bloodstream.
2. Elevated blood pressure
It can raise the risk of high blood pressure, which increases the possibility of heart and blood vessel problems.
3. Loss of hearing
A frequent symptom of Turner syndrome is hearing loss. It can occasionally be attributed to the progressive loss of nerve function. Hearing loss can also be brought on by a higher incidence of middle ear infections.
4. Vision issues
Turner syndrome can cause nearsightedness, other vision issues, and inadequate muscular control of eye movements (strabismus)
5. Kidney issues
Kidney abnormalities may be related to Turner syndrome, which can result in urinary tract infections
6. Infertility
Most Turner syndrome-affected females are sterile. A very tiny percentage, nevertheless, might conceive on their own, and other women might use fertility medication.
Additional read: Is IVF Treatment Covered by Health Insurance?
Turner Syndrome brings several complications that may stand in the way of one's daily life. However, learning more about this condition can help affected people receive the support they need. If you or someone you know are suffering from the following symptoms, visit a doctor as soon as possible. For more information and help, contact Bajaj Finserv Health to speak to a doctor. To receive the right advice and know more details on Turner Syndrome, you can schedule a virtual teleconsultation right from the comfort of your home.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7472824/
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.



