Cancer | 6 min read
Uterine Cancer: Early Signs, Causes, Stages, and Treatment
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Uterine cancer is the most common type of cancer in women
- Obesity and obesity-associated diseases like diabetes and hypertension increase the risk
- Read to know more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options
Uterine cancer is the malignant growth of cells in the uterus. The uterus is the hollow, pear-shaped organ located in the pelvis. It is responsible for the complete development of the baby from conception to birth. Uterine cancer is the most common type of cancer attacking a woman’s reproductive organs.
Like other cancers, early detection and treatment are the most effective way to eliminate the problem and increase the survival rate. Studies have shown that early detection of uterine cancer has a 5-year survival rate of 96%, which drastically decreases to 16% if diagnosed after the cancer has spread. While there are multiple risk factors such as age and family history, obesity and obesity-associated diseases like diabetes and hypertension have been seen to elevate the risk of uterine cancer in women.
Continue reading to know more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options related to uterine cancer.
Uterine Cancer Causes
The common uterine cancer causes and risk factors are include the following.
Age
The average age of uterine cancer diagnosis is 60. Women over 50 years of age are at a high risk of developing this disease. While uterine cancer is barely diagnosed below 40, this is the right time to go for regular check-ups and screenings.
Genetics
A family history of colon cancer can make you highly susceptible to uterine cancer. Furthermore, a family history of Lynch syndrome or hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) can also elevate the risk of developing uterine cancer. Therefore, it is recommended that women under 70 years of age with endometrial cancer, irrespective of a family history of any cancer, should have their tumour tested for Lynch syndrome.
Obesity
Obesity highly elevates the risk of developing uterine cancer because a high density of fatty tissues increases the production of oestrogen in the body. This, along with increased BMI, increases the risk of uterine cancer.
Diabetes
Diabetes increases the risk of developing uterine cancer as it is commonly linked to obesity. All obesity-related diseases, such as hypertension, blood pressure, and heart problems, increase uterine cancer risk.
History of cancers
Women with a history of ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and colon cancer are at a higher risk of being diagnosed with uterine cancer.
Additional Read: Symptoms of Breast CancerRadiation therapy
Women that have previously undergone radiation therapy around the pelvis area are at a high risk of being diagnosed with uterine cancer.
Hormonal imbalance
Excess production of oestrogen in the body, especially after taking hormone replacement therapy after menopause, can cause uterine cancer. In general, hormonal imbalance can cause a lot of risk factors like early periods before the age of 12 or late menopause. Furthermore, never being pregnant can also be one of the uterine cancer causes.
Tamoxifen
Women that consume tamoxifen while undergoing treatment for breast cancer are at a high risk of being diagnosed with uterine cancer.
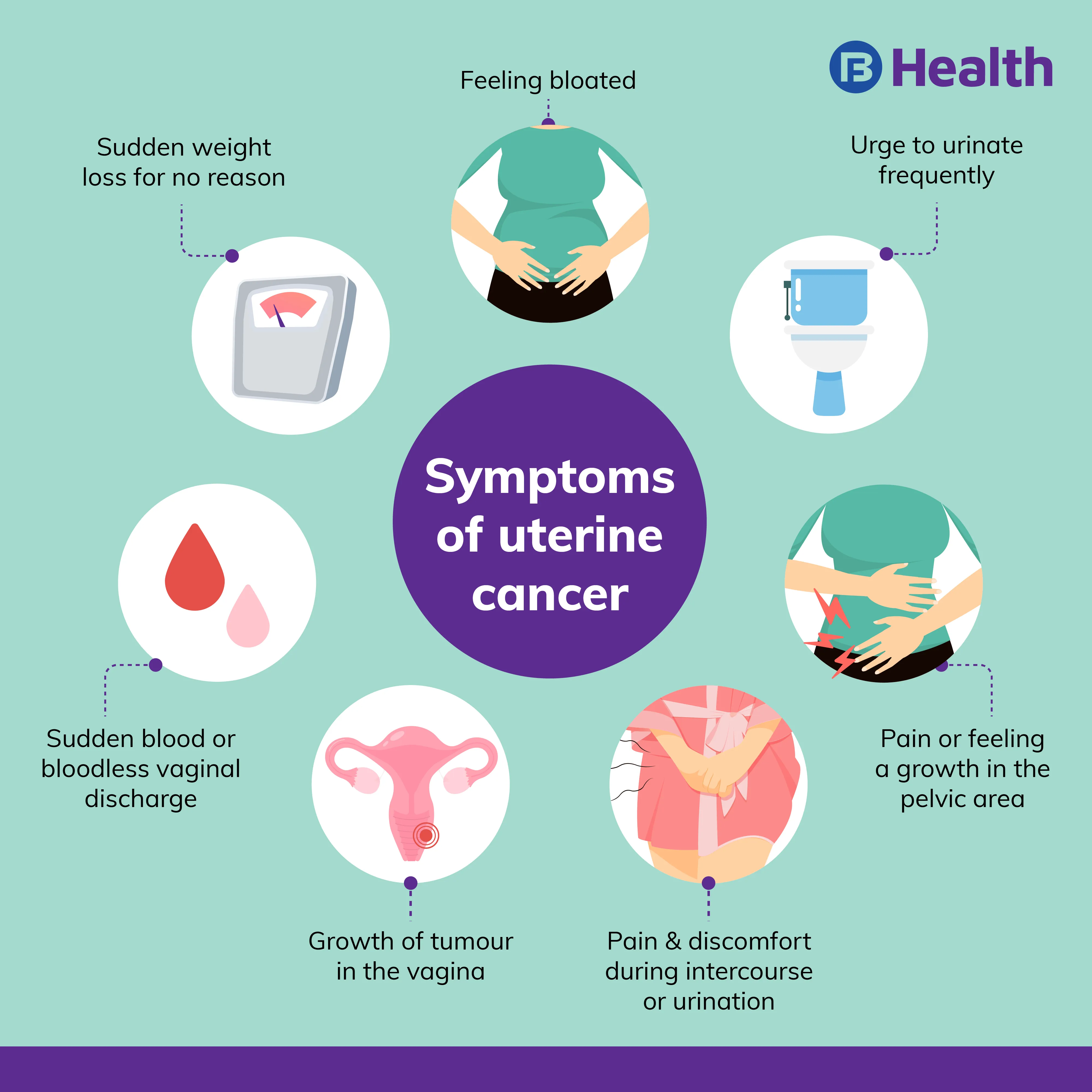
Uterine Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms differ as per the type of uterine cancer. Abnormal and sudden bleeding is commonly observed as an early sign in women with endometrial cancer.
Common Uterine Cancer Symptoms
Other common uterine cancer symptoms are as follows.
- Sudden bloodless vaginal discharge
- Experiencing pain and discomfort during intercourse or urination
- Experiencing pain or feeling a growth of mass or tumour in the pelvic area
- Undergoing sudden weight loss for no reason
Early Uterine Cancer symptoms
Sudden vaginal bleeding and spotting is an early, common sign of uterine sarcoma. Other symptoms of uterine cancer include the following.
- Urge to urinate frequently
- Growth of tumour in the vagina
- Feeling bloated
- Experiencing pain in the abdomen
The occurrence of these symptoms warrants immediate medical attention for further diagnosis.
Uterine Cancer Diagnosis
On visiting a gynecologist, you will be first asked about your family and personal medical history. This is followed by a physical pelvic examination to check for any abnormalities. Then, a doctor may conduct a transvaginal ultrasound exam, a non-invasive screening test, to look for lumps and tumours.
If the gynecologist notices any abnormalities or mass growth, he/she may order other tests to confirm and stage cancer. These tests include the following.
Hysteroscopy
Here, a flexible tube with a fibre optic camera is inserted in the uterus via the vagina to examine the endometrium for any abnormalities visually.
Endometrial biopsy
In this test, a small flexible tube is passed through the cervix into the uterus. Then, suction is applied to remove a small piece of infected tissue from the endometrium via the tube.
Dilation and curettage
If the biopsy fails to give a precise diagnosis, the doctors dilate the patient’s cervix and, using a special tool, collect tissues from the endometrium.
Uterine Cancer Staging
If you are diagnosed with uterine cancer, then the doctor will order more tests to determine the spread and uterine cancer stage.
Uterine cancer stages are as follows:
- Stage 1: Cancer is limited to the uterus
- Stage 2: Cancer has spread from the uterus to the cervix
- Stage 3: Cancer has spread to the fallopian tubes, vagina, surrounding lymph nodes and ovaries
- Stage 4: Cancer has invaded distant organs such as the rectum and bladder
Uterine Cancer Treatment Options
Treatment of uterine cancer depends on the uterine cancer stage and type. Here are some common uterine cancer treatment options.
Surgery
A type of surgery called hysterectomy is performed to remove the uterus. If cancer has spread, then bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy or BSO is performed to remove the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Usually, both these procedures are done at the same time. To know the extent of the spread, the doctors may even perform lymphadenectomy to remove surrounding lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy
This is prescribed when cancer has spread to other parts of the body. It involves using a single combination of cancer-killing drugs administered orally as a pill or through IV.
Radiation therapy
Here, high-energy radiation beams are used to kill cancer cells. This can be done externally, where beams are targeted on the pelvic region close to the uterus, or internally by placing radioactive materials in the uterus or vagina.
Hormone therapy
Here, hormone-blocking drugs are used to slow the growth of cancer cells.
While there is no way to prevent cancer entirely, you can reduce your risk of uterine cancer by taking a few measures. These include making healthy lifestyle choices to maintain ideal weight and BMI, taking contraceptive pills that help maintain hormonal balance and reduce the overgrowth of the uterine lining and regularly going for full body health checkup and screening tests.
Do all of this with ease on Bajaj Finserv Health. Book in-clinic appointments or video consultations with specialists near you in seconds. You can also opt for health plans that offer you medical packages and discounts from top partners including labs, clinics and hospitals.
References
- https://journals.lww.com/obgynsurvey/Abstract/2014/03000/Impact_of_Wait_Times_on_Survival_for_Women_With.13.aspx
- https://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/27/9/985?utm_source=nov18&utm_medium=carousel4&utm_campaign=180264#sec-4
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.