Gynaecologist and Obstetrician | 5 min read
Uterine Fibroids: 3 Important Things for You to Know
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Risk factors for uterine fibroids include family history, hormones, and obesity
- One of the common uterine fibroids symptoms is heavy menstrual bleeding
- Popular uterine fibroids treatment options are medication and surgery
Uterine fibroids refer to noncancerous growth in the wall of a woman’s uterus. They often develop during the childbearing age. Uterine fibroids are also known as leiomyomas, fibromas, or myomas. They mainly occur in women in their early 40s and early 50s [1]. About 20-40% of women in this age group have this growth.
Uterine fibroids are the most common types of benign tumors. They largely vary from undetectable size to bulky masses that enlarge the uterus and cause severe abdominal pain.
Not every woman who has them will experience uterine fibroids symptoms. However, those who do experience them may find it agonizing.
The exact uterine fibroids causes are not known. But it is important for you to go for regular check-ups as your doctor may discover them during a prenatal ultrasound or pelvic examination. Owing to their benign nature, uterine fibroids usually do not develop into uterine cancer.Read on to learn about meaning in-depth as well as the uterine fibroids treatment and symptoms.
Additional Read: Urinary Incontinence in Females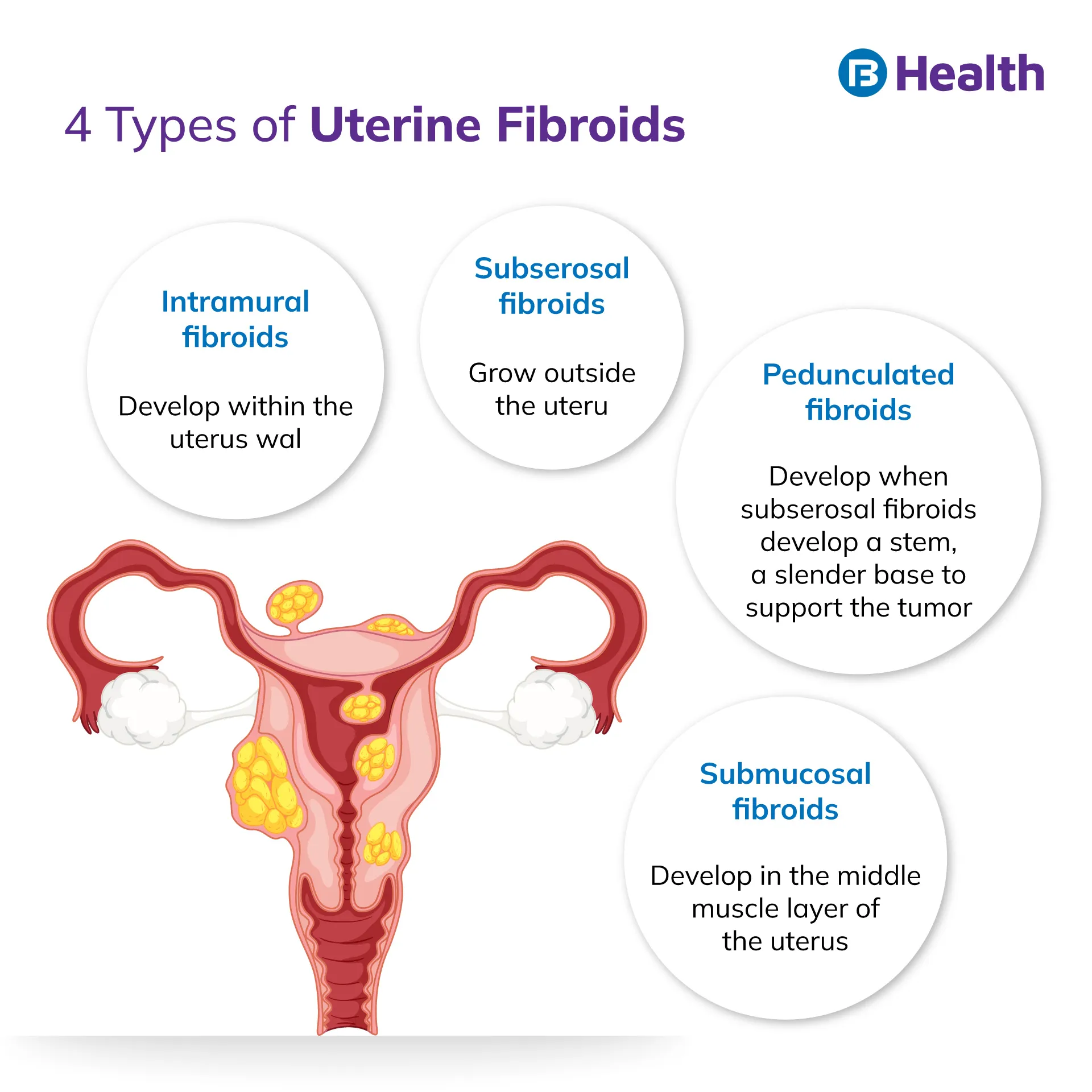
Uterine fibroids Symptoms
Uterine fibroids often cause no symptoms. For those who do experience uterine fibroids symptoms, the signs depend on various things. This includes the number, size, and location of uterine fibroids.
Here are the usual uterine fibroids symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation
- Prolonged menstrual periods
- Polymenorrhea, frequent periods and shorter cycles
- Swelling of abdominal muscles
- Chronic vaginal discharge
- Bleeding in between menstrual cycles
- Difficulty during urination or inability to empty the bladder completely
- Bloating and constipation
- Leg pain or lower backache
- Anemia, low red blood cell count
- Complications during pregnancy
- Increased menstrual cramps<span data-ccp-props="{"201341983":0,"335559739":160,"335559740":240}">
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Fullness or pressure in the lower abdomen
Uterine fibroids Causes
Although doctors are not sure about the exact uterine fibroids causes, some of these factors may contribute.
Genetics
Uterine fibroids can be hereditary. That is why your chances of developing uterine fibroids may increase if women from earlier generations in your family had this condition.
Hormones
Your ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone hormones that cause the uterine lining to regenerate during the menstrual cycle. This may lead to the growth of uterine fibroids. The fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than uterine muscles.
Pregnancy
Uterine fibroids may develop during pregnancy as this increases estrogen and progesterone hormones in your body.
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
ECM makes cells stick together. It stores growth factors and is responsible for biological changes in the cells. Excessive ECM production is linked with uterine fibroids.
- Some of the other factors leading to uterine fibroids include:
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Periods at an early age
- High intake of red meat
- Consumption of alcohol
- Consumption of soybean milk
- Age - older women are more at risk
- A diet lacking green vegetables, fruits, and dairy

Uterine fibroids Treatment
The options for uterine fibroids treatment depend on various factors like your age, fibroid size and number, their location, and the symptoms you are experiencing. Based on these factors, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that may be a combination of the following.
Natural treatment
Home remedies and natural treatments such as yoga, acupuncture, massage, and applying heat for cramps can help ease uterine fibroids symptoms. You can also make dietary changes such as avoiding meat and including more green vegetables, fish, and foods high in flavonoids in your meals. Reducing weight if you are overweight and controlling your stress levels can also help you with uterine fibroids.
Medication
Your doctor may prescribe hormone-regulating pills that help shrink uterine fibroids. GnRH agonists like leuprolide lower your estrogen and progesterone hormone levels, which gradually shrinks fibroids. Other medication includes intrauterine devices, anti-inflammatory pain relievers, and birth control pills. All these help control symptoms like pain and bleeding.
Surgery
Your doctor may suggest a surgery known as myomectomy for a large uterine fibroid or multiple growths. When performing a myomectomy, surgeons make a large incision in the abdomen to access the uterus and remove the fibroids. Uterine fibroids may occur again after surgery. In case of serious conditions, doctors may also suggest a hysterectomy.
There are also non-invasive or minimally invasive surgical procedures for this condition. Forced ultrasound surgery is one of them. It requires you to lie down inside a special MRI machine that allows doctors to analyze your uterus. Uterine fibroids are then destroyed by directing high-energy and high-frequency sound waves towards them.
Other non-surgical procedures for uterine fibroids include:
- Myolysis procedures to shrink fibroids
- Endometrial ablation to destroy uterine lining
- Uterine artery embolization to cut the blood supply to the uterine fibroids
By paying heed to their menstrual and uterine health, women can live a healthy and happy life. Now that you know the basic uterine fibroids definition and the signs of this condition, do not neglect any uterine fibroids symptoms. When you notice any signs, book an online doctor consultation with gynecologists and women's health experts in seconds on Bajaj Finserv Health. This way, you can manage your health better and get the treatment you need.
References
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/uterine-fibroids
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.



