Aarogya Care | 12 min read
Health Insurance FAQs: A Guide on 35+ Commonly Used Terms
Medically reviewed by
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Knowing important terms helps understand health insurance information better
- Sum insured, premium, copay, deductible are some commonly used terms
- Understanding your policy terms can help you take an informed decision
While purchasing a health policy today is easy, understanding health insurance definition and health insurance terms is extremely important. Otherwise, you may find that the jargon and wordings of your policy are difficult to decipher. Often, technical terms used in a health insurance policy can hinder your understanding of features, benefits and limits. Having limited information can cause inconveniences such as claim rejection, partial settlement, or no cover. That is why it is important to know about common health insurance terms.
Read on to learn more about commonly used health insurance terms.
Sum insured
This refers to the maximum amount payable by your insurance provider. You cannot file a claim for an amount that exceeds your sum insured. For example, say your sum insured is Rs.5 lakh and your medical expenses amount to Rs.5.5 lakh. Your insurer is liable to pay only up to Rs.5 lakh. You will need to bear the expense of the excess Rs.50,000. You will need to choose your sum insured at the time of purchasing your policy. This also affects your premium amount.
Additional Read: Sum Insured and Sum AssuredCoverage
The coverage of your health insurance policy refers to the different medical services towards which you can claim expenses from your insurer. It includes medical procedures and treatments as mentioned by the insurer. If your insurance provider does not cover a specific treatment or a condition, they are not liable to pay for its expenses.
Premium
Premium is the amount you pay at the time of purchasing and renewing a health insurance policy. This is the cost of getting a cover for medical expenses from an insurance company. There are different factors that affect the premium amount. Some of them include:
- Age
- Family medical history
- Sum insured
- Type of policy
Insured
Insured refers to the policyholder. It can either be an individual or a group of people who are included in a health policy. As the insured, you can file a claim for your hospitalization expenses or other medical needs as per the health insurance terms and conditions of your policy.
Insurer
Insurer refers to the company that provides cover to the insured. The insurer is liable to give financial assistance for medical expenses of the insured as per policy terms.
Agent
Agents are an intermediary between the insured and the insurer. They are the points of contact for your queries regarding the features and benefits of your policy. They may also assist you in the process of filing claims.
Third party administrator (TPA)
TPA is an individual or organization that acts as an intermediary between the policyholder and insurance provider. You can find this department in every hospital where you need to submit your policy details for filing a claim. Submitting insurance details with the TPA is an important step of the claim filing process regardless of the type of claim you make.
Beneficiary or Nominee
This is the entity or an individual who is the recipient of the policy benefits or claim amount in case of policyholder’s demise.
IRDAI
Established in 1999, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India promotes and regulates the industry of insurance in India. All insurance companies, brokers, and agents have to work in compliance with the guidelines provided by IRDAI.Waiting period
Waiting period refers to the time period that you as a policyholder have to wait before your policy comes into effect. You cannot file a claim until your waiting period is over. In general, the waiting period for most health insurance policies is 30 days [1]. This also comes into effect in case of a pre-existing disease.
Grace period
Grace period is the extended time after the due date of a policy renewal. Your insurer provides this in case you miss your renewal date. Usually, the insurance provider offers a grace period of 15 days after the due date of your policy [1]. However, during this period you cannot avail coverage benefits and file a claim.
Deductible
Deductible is the fixed amount you decide when you buy your health policy. It is the amount that you as the insured will have to pay towards your medical expenses. You have to pay this amount every year before you can avail your policy benefits.
For example, if your policy has a deductible of Rs.10,000 and your medical expenses amount to Rs.5,000, the insurer is not liable to pay for your expenses. In case you raise a claim for Rs. 20,000, your insurance provider will only pay Rs.10,000 (Rs.20,000 - Rs.10,000). Since Rs.10,000 is the deductible in your plan, you have to pay it from your pocket. A higher deductive lowers your premium and vice versa.
Co-payment
Co-payment is the percentage of your claim amount that you will have to pay from your pocket. Your insurer will cover the rest. It completely depends on the claim amount and is not a fixed amount. For example, if you have a co-pay clause of 10% and your claim is of Rs.70,000, you will have to pay Rs.7,000 on your own. Your insurance provider will cover the remaining 90% or Rs.63,000.
Dependents
Dependents are additional members who are eligible for getting coverage in your health insurance policy. These members may include your parents, children, and spouse.
Exclusions
These are some specific health conditions or treatments that are not covered by your policy. Some common exclusions as per the IRDAI are:
- Cost of spectacles
- Dental treatment
- AIDS
- Congenital defects
- Self-injury
- Cost of hearing aids [1].
Claim
Claim is the financial assistance you receive from your insurance provider for your medical expenses. Your claim amount cannot exceed your sum insured. For instance, if your sum insured is Rs.7 lakh, you cannot file for a claim that exceeds Rs.7 lakh.
The approval of your claim amount is at the discretion of your insurance provider on the basis of the terms of the policy. Depending on the case, you may get a full or partial approval on your claim.
Additional Read: Making a Health Insurance ClaimClaim settlement
Claim settlement refers to the process where you receive the funds you are trying to claim from the insurer. Generally, there are two modes of settling a claim – reimbursement and cashless. The process for each of these modes is different and dependent on your insurance provider.
Reimbursement of claims
Reimbursement refers to the mode of claim settlement where you are repaid for your medical expenses by the insurer. This means that you will have to pay the expenses at the time of treatment and your insurer will reimburse that amount after you file a claim. You can choose a reimbursement claim at both network and non-network hospitals.
Cashless settlement
Cashless settlements are those where your insurer will directly pay your medical bills to the hospital, and you do not have to pay from your pocket. You can avail this facility only at a network hospital of your insurance provider.
Network and non-network hospitals
Network hospitals are the institutions with whom your insurer has a tie-up. At a network hospital, you can avail both a reimbursement as well as a cashless mode of settlement.
Non-network hospitals are those that do not have a tie-up with the insurer. You can avail only reimbursement mode of settlement here. You may also get discounts on other medical services not covered by your policy at network hospitals.
Porting
Porting or portability refers to the option of changing your insurance provider without losing your policy benefits. A few policy benefits include:
- Waiting period
- No claim bonus
- Total coverage
- Waiting period for pre-existing disease
You can port your policy only at the time of renewal. To port success, raise a request at least 45 days before the renewal date [2].
Group insurance
Among the different types of health insurance terms, group insurance offers cover to the employees of an organization. They generally have a low premium amount compared to an individual policy. These policies cover the employee and also their spouse, dependent parents and children. You can convert your group insurance policy to an individual or family floater policy [3].
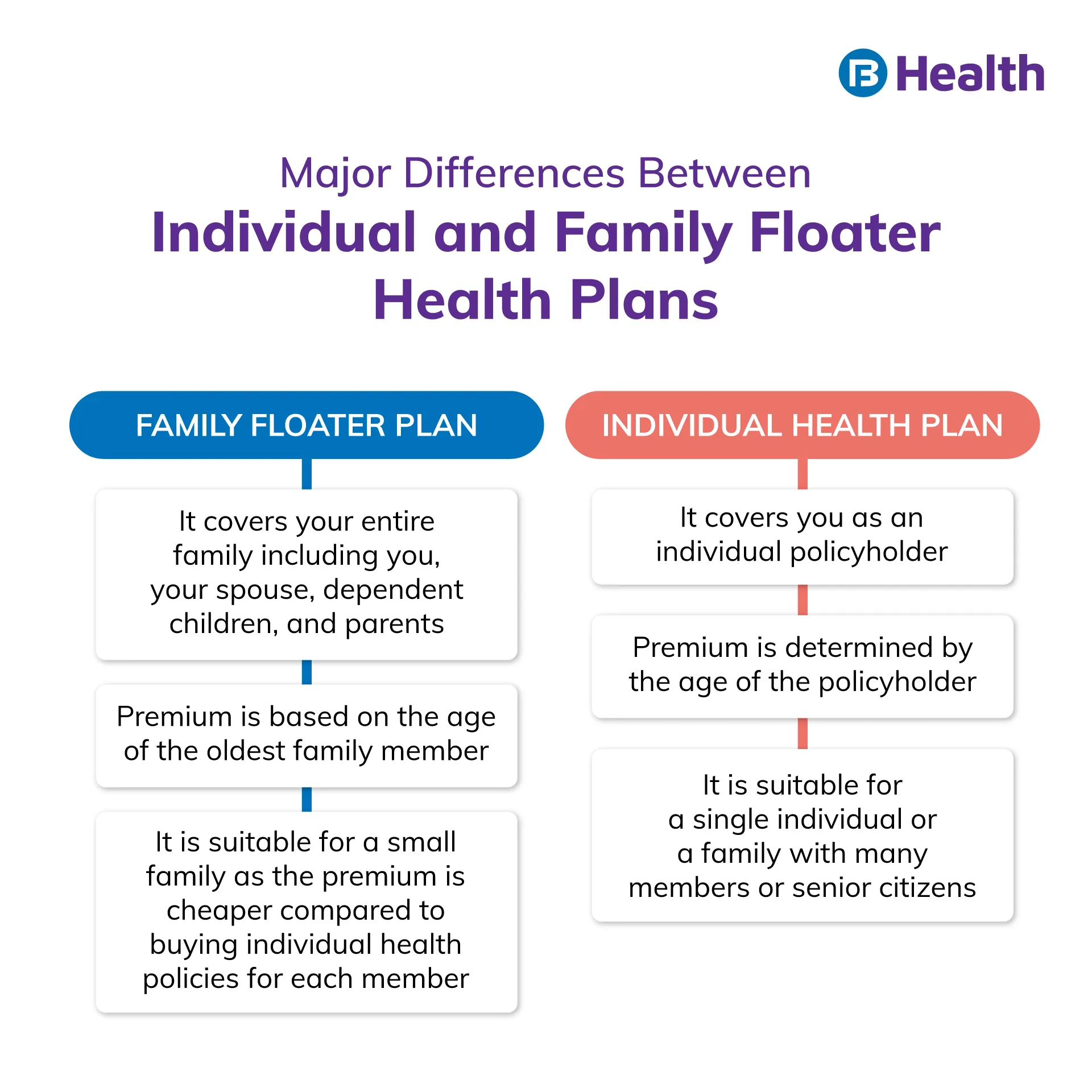
Family floater policy
This insurance policy offers coverage for a family under a single sum insured amount. Apart from the policyholder, this plan covers children, spouse, or dependent parents. Under a family floater policy, a single sum insured is shared among all the members included in the policy. This means that if you have a family floater policy for 4 people with sum insured of Rs.10 lakh, all 4 members of the policy will be collectively covered under the sum insured.
Individual health insurance
As the name suggests, this refers to a health insurance policy purchased for an individual. For instance, if you have taken a total sum insured for Rs.10 lakh vi an individual health policy, only you can avail its benefits. To cover other family members, you need to buy other policies.
Senior citizen health insurance
Among the different types of health insurance plans, these policies are tailor-made to suit the needs of senior citizens. They offer cover to people above 60 and under 70 years. These may cover domiciliary, AYUSH, or psychiatric treatment too. The eligibility criteria and terms and conditions of Senior citizen health insurance & other policies vary among insurance providers. The premiums for these may be higher.
Additional Read: Senior Citizen Health Plan
Top-up
You usually buy top-up plans with your standard health insurance plan. However, you can also purchase a top-up without a base health plan. These plans help you get additional financial cover in case you exhaust your existing insurance cover. You receive the cover of a top-up plan over and above your base insurance plan.
For example, if your health insurance policy has a sum insured of Rs.7 lakh, and your top up is of Rs.3 lakh, your total sum insured will be Rs.10 lakh. However, you can claim this top-up of Rs.3 lakh only after you exceed the existing health insurance coverage of Rs.7 lakh.
Area covered
While most insurance companies offer cover within India, some may also offer cover for medical emergencies outside India. The area covered under a health insurance policy is dependent on your insurer.
Free look period
Free look period refers to the period after purchasing your policy, where you can look for another insurer without bearing any charges or penalties. In health insurance policies free look period is applicable only if the duration of the policy is for at least 3 years. Free look period is for a minimum of 15 days after the policy purchase date, and it varies among insurers [4].
Renewal date
This refers to the date before which you need to extend or renew the validity of your health insurance policy. This allows you to avail the existing benefits of your policy.
Add-ons or riders
Add-ons or riders refer to the extra protection that you can get from your insurance provider. These include cover for treatments or conditions not covered under your existing health insurance policy. AYUSH, maternity, and personal accident are some add-ons which insurance providers generally offer.
No-claim bonus
This is the bonus you get when do not file a claim during the policy period. You can accumulate it over time and enjoy a higher sum insured at the same premium as a benefit.
Pre- and post-hospitalization expenses
Your insurance provider will offer financial assistance not only during your hospital stay but also for the pre- and post-hospitalization expenses. If you have diagnostic bills or other medical expenses prior to your hospitalization, your insurer may cover those as per the health insurance terms. Similarly, your insurance provider covers medical expenses that occur after your discharge too. Generally, pre- and post-hospitalization refer to the expenses incurred up to 30 days before and 60 days after hospitalization [5].
Critical illness
Critical illnesses are those that are severe, chronic or life-threatening. Usually, the cover for these is not sufficient in a standard insurance policy. This is why insurers offer cover for these as a rider or as a standalone policy.
Additional Read: Health Insurance PlansPre-existing disease (PED)
This refers to a health condition of the insured that has been diagnosed at the time of policy purchase or before. A condition is classified as a PED if it is diagnosed, treated or suspected 48 months prior to the issue of first policy by the insurer [6]. The cover for this is usually offered after a waiting period of 4 years. However, some insurance companies do offer cover for these diseases from the date of purchase for an additional payment.
Maternity cover
This is an add-on that is specially designed for women who are planning to have children, are already pregnant, or have a newborn. It covers delivery, prenatal and postnatal expenses and infant care expenses. This also comes with a waiting period after which you can avail its benefits.
Cover for day-care procedures
Day-care procedures refer to treatments at a hospital or health clinic that do not extend beyond 24 hours. Cataract, dialysis, chemotherapy, and angiography are some day-care procedures. The cover for these depends on your policy.
Domiciliary treatment cover
When you receive treatment under professional care at your home, it is called domiciliary treatment. The cover for this is not included in all health insurance plans. Some insurance providers may offer cover for domiciliary treatment as an add-on or as a rider.
Daily hospital cash
This is the monetary benefit you get during every day of your hospitalization based on your policy and insurer. The purpose of this is to cover expenses that are not generally covered under a policy. The other purpose is to compensate you for loss of income. You can decide the fixed amount at the time you purchase the policy.
Outpatient department treatment (OPD) cover
When you receive treatment or diagnosis without hospitalization, it is known as OPD treatment. Here, you are called the outpatient and the department that offers this service is known as the outpatient department. There are many health policies by top insurers that come with OPD cover.
AYUSH treatment
This refers to alternative treatment as compared to conventional or allopathic treatment. AYUSH stands for Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy. The expenses of this treatment or hospitalization for these services may be covered either as a part of your policy or as a rider.
Additional Read: Benefits of Comparing Health Insurance PlansNow you know about the basic health insurance terms and types of health insurance in India. Make sure you carefully read and understand your policy before you buy it. It is also essential that you compare and analyze different policies to make an informed decision.
You can also check out the Aarogya Care plans with a cover of up to Rs.25 lakh available on Bajaj Finserv Health. With comprehensive cover, the variants under this plan can be tailor-made to meet your health needs. The benefits of these plans go from preventive health check-ups to cover for the treatment of COVID-19. Choose a plan that offers the best cover at affordable premiums and prioritize your health!
References
- https://www.policyholder.gov.in/Faqlist.aspx?CategoryId=73
- https://www.policyholder.gov.in/portability_of_health_insurance.aspx
- https://www.irdai.gov.in/ADMINCMS/cms/whatsNew_Layout.aspx?page=PageNo3987&flag=1
- https://www.policyholder.gov.in/free-look__period.aspx#
- https://www.irdai.gov.in/admincms/cms/uploadedfiles/Guidelines%20on%20Standard%20Individual%20Health%20Insurance%20Product.pdf
- https://www.irdai.gov.in/ADMINCMS/cms/Uploadedfiles/RTI_FAQ/FAQ_RTI_HEALTH_DEPT.pdf
Disclaimer
Please note that this article is solely meant for informational purposes and Bajaj Finserv Health Limited (“BFHL”) does not shoulder any responsibility of the views/advice/information expressed/given by the writer/reviewer/originator. This article should not be considered as a substitute for any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult with your trusted physician/qualified healthcare professional to evaluate your medical condition. The above article has been reviewed by a qualified doctor and BFHL is not responsible for any damages for any information or services provided by any third party.





